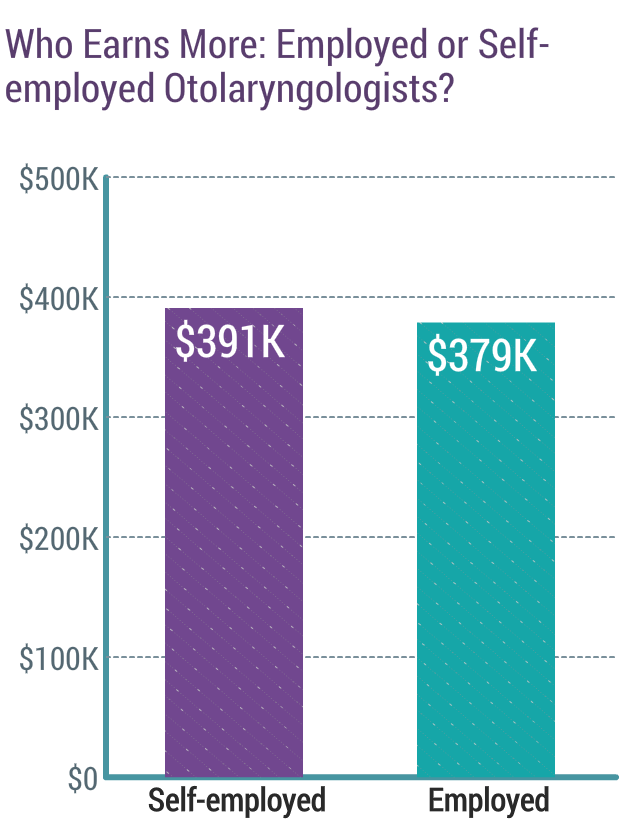
Master Patient Index (MPI) | Health Information Exchange …
22 hours ago · The abbreviation MPI stands for Master Patient Index, also known as client or patient registry. It is one of the crucial and significantly contributing resources in the healthcare sector. Traditional MPI used to be in paper format, but electronic MPI has made the process even easier thanks to the prevalence of technology. >> Go To The Portal
What is a Master Master Patient Index (MPI)?
Master Patient Index (MPI) technically refers to a single source system and all its patients. MPI is also used as shorthand for Enterprise Master Patient Index (eMPI), which is a database that brings together, or “links”, patient records from multiple source systems. What Does a Modern eMPI Do?
How does the MPI generate a patient ID?
The MPI generates a unique patient ID, called an EUID, for each enterprise record. The MPI Enterprise Record consists of one or more facility records. The best demographic information for the patient will be used to create the Single Best Record.
What MPI data can be pulled up in a person search?
DQM can pull up certain MPI data for searching, viewing, editing, and matching. On the Person Search screen, a user can search by various methods, including the EUID, Local ID, SSN, and Demographic Data, which includes Date of Birth, Address, and Phone Number.
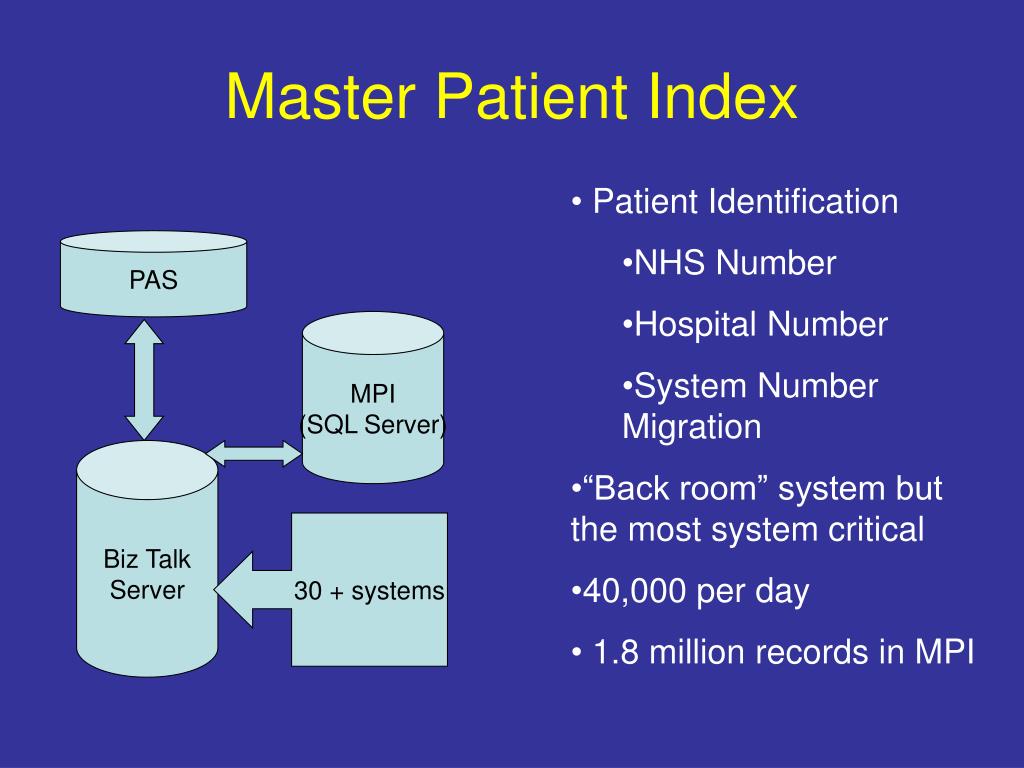
What is included in a master patient index?
The MPI lists the medical record or identification number associated with the name and must contain enough demographic data to readily identify a patient and his or her record. If the MPI serves more than one healthcare facility, the index should also indicate the facility in which the admission or encounter occurred.
How long should the master patient index be retained?
10 yearsUnless otherwise specified by state law, the recommended retention period for a disease index is 10 years.
What is the MPI and why is it important?
The MPI, also known as an Enterprise Master Patient Index (EMPI), contains critical information necessary for the prompt location of every patient's complete and accurate medical record. It is the link to track patient activity across care settings in an enterprise or health information exchange.
What data elements are included in an MPI?
The data elements suggested for use in an MPI to index and search records that have been recommended by AHIMA (American Health Information Management Association) are:Internal patient Identification.Patient Name.DOB.DOB qualifier.Gender.Race.Ethnicity.Address.More items...•
How long are closed files usually kept?
Usually, closed files are retained in Records Offices for a period of three or five years. The retention period is specified in the disposal schedule (See below).
What is the difference between EHR and MPI?
An EMR provides the clinical information about a patient, while the MPI is the index for that data. An MPI typically lists data points about a patient, such as a patient's last name, first name, date of birth, gender, address, phone number, and dates and types of visits to the healthcare organization.”
Who is responsible for the master patient index?
the Health Information Management departmentThe other type of error, known as an overlay is a bit more serious and is where two different patients share a single MRN, intermingling their medical information. Typically, it is the job of the Health Information Management department to maintain the MPI.
What is a MPI?
Myocardial perfusion imaging (MPI) is a non-invasive imaging test that shows how well blood flows through (perfuses) your heart muscle. It can show areas of the heart muscle that aren't getting enough blood flow. This test is often called a nuclear stress test.
What MPI means?
Marginal Propensity to Invest (MPI) Definition.
How do I create a master index?
Follow these steps to create the database.Step 1: Analyze the Master Index Database Requirements.Step 2: Create a Master Index Database and User.Step 3: Define Master Index Database Indexes.Step 4: Define Master Index External Systems.Step 5: Define Master Index Code Lists.Step 6: Define Master Index User Code Lists.More items...
What three indexes are used in healthcare?
list the kinds of indexes used in healthcare:Master patient index.Disease index.Procedure index.Physician index.
What are the basic information required on a patient name index card?
It should include the name of the organization e.g., hospital, clinic, etc., address, and telephone number of the hospital or clinic.
What is a master patient index?
A Master Patient Index (MPI) aims to identify individual patients by storing and analyzing demographic information and assigning a unique identifier to that person. This electronic database holds information in a centrally accessible location for all healthcare providers thus allowing personal healthcare records to be shared more easily and cost-effectively. By following a successful implementation plan used by many in the industry an effective MPI can be established.
What is robust matching algorithm?
Robust Matching Algorithms within the MPI must automatically match and link identifiers for the same patient from different systems, but do so without incorrectly matching records that are not for the same patient. An MPI must employ both deterministic and probabilistic methods to match records. A deterministic method searches for an exact match between attributes, while a probabilistic method searches for an approximate match between two records.
What is a master patient index?
The Master Patient Index (MPI) (also Master Person Index) is a database that is maintained by a health care organization for the purpose of identifying a patient and their medical record.
What are the problems with MPI?
The three problems that most often occur at registration are duplicate medical record numbers, overlap and overlay.
What is MPI in medical records?
The MPI began as a paper based card file system that was arranged alphabetically by the patient’s last name. In larger institutions, the patient was assigned a medical record number and this number was linked to the patient’s chart. The medical record number became the unique identifier for patients being treated at a facility. It was used to avoid duplication at patient registration in order to provide connection to one authentic record. (1) As institutions became computerized, an increasing amount of data was housed in the MPI. This data now includes demographics and visit information.
Why do we need to audit MPI?
Regular audits of the MPI database must be done in order to identify any errors before they are compounded. The unique identification of a patient within an organization is the first step in making sure that data is consistent and comparable. (4)
What is a master patient index?
The terms “Master Patient Index” and “Enterprise Master Patient Index” are used interchangeably but they are different. Master Patient Index (MPI) technically refers to a single source system and all its patients. MPI is also used as shorthand for Enterprise Master Patient Index (eMPI), which is a database that brings together, or “links”, patient records from multiple source systems.
What is the difference between a master patient index and an enterprise patient index?
The terms “Master Patient Index” and “Enterprise Master Patient Index” are used interchangeably but they are different. Master Patient Index (MPI) technically refers to a single source system and all its patients. MPI is also used as shorthand for Enterprise Master Patient Index (eMPI), which is a database that brings together, or “links”, patient records from multiple source systems.
What Does a Modern eMPI Do?
There are four objectives that a modern eMPI should support. They are:
How Does an eMPI Work?
An eMPI constantly looks for potential matches across all data sources that are loaded into the eMPI. The matching is handled by a match algorithm that locates and assesses the quality of matches even when demographic information is missing or wrong. The algorithm follows the same sort of logic that a well-trained data integrity specialist would when comparing two records to see if they belong to the same person. The algorithm should account for:
How to use EMPI?
There are four objectives that a modern eMPI should support. They are: 1 Identifying that records from different source systems belong to the same patient and linking them together even when key information such as social security number is missing or wrong. To link the records together, an eMPI will assign the same enterprise identifier to each record belonging to the same patient in each source system. 2 Making use of outside semi-public data to reduce or eliminate the manual effort involved in patient matching. 3 Generating a golden record that contains the best-known information for a person whose information is spread across many different sources. 4 “De-duping” a transactional system by identifying cases where there’s more than one record for the same patient and providing workflow for resolving them.
What is the tricky part about measuring recall and precision?
The tricky part about measuring recall and precision is that you need something to compare your results to.
Can eMPIs use Lexis Nexis?
Many eMPIs have the ability to use semi-public information from third party data aggregators like Lexis Nexis to help identify people. You may hear this functionality referred to as Research Automation or Referential Matching. The result is that many of the maybe matches will be turned into yes matches, shrinking the amount of manual work required. Those maybe matches that are left become tasks that will need to be reviewed by a data integrity person.
Why do hospitals spend millions of dollars on patient records?
Hospitals spend millions of dollars and countless hours resolving patient record matching issues due to lack of interoperability — money and time that could be saved by using enterprise master patient index (EMPI) support tools, a new Black Book Research report finds.
How long does it take to reconcile a hospital?
The average time if takes a hospital with over 150 beds to clean up and reconcile records averages five months, the report found.
What is integrated health model?
The Integrated Health Model Initiative’s focus is on patient-centric information and finding data elements most predictive of improved outcomes.
Is there a national patient identification system?
Patient identification is a serious problem. Currently, there is no national patient identifier system in the U.S. Con gress continues to ban federal funding to develop an NPI, and technology companies are reluctant to share proprietary information at risk of losing market share.