Mania: Diagnosis | CAMH
16 hours ago Mixed features is defined as a minimum of three pre-specified depressive symptoms while experiencing hypomania or mania, or three hypomanic symptoms while experiencing a major depressive episode. If a patient manifests mixed or manic features while taking an antidepressant for depression or immediately upon discontinuing it, a diagnosis of ... >> Go To The Portal
Explore
The health care providers have the access to the patient medical report. They keep the medical report as a history of medical records. Also, patients’ access to the patient medical report is a must.
Who has the access to the patient medical report?
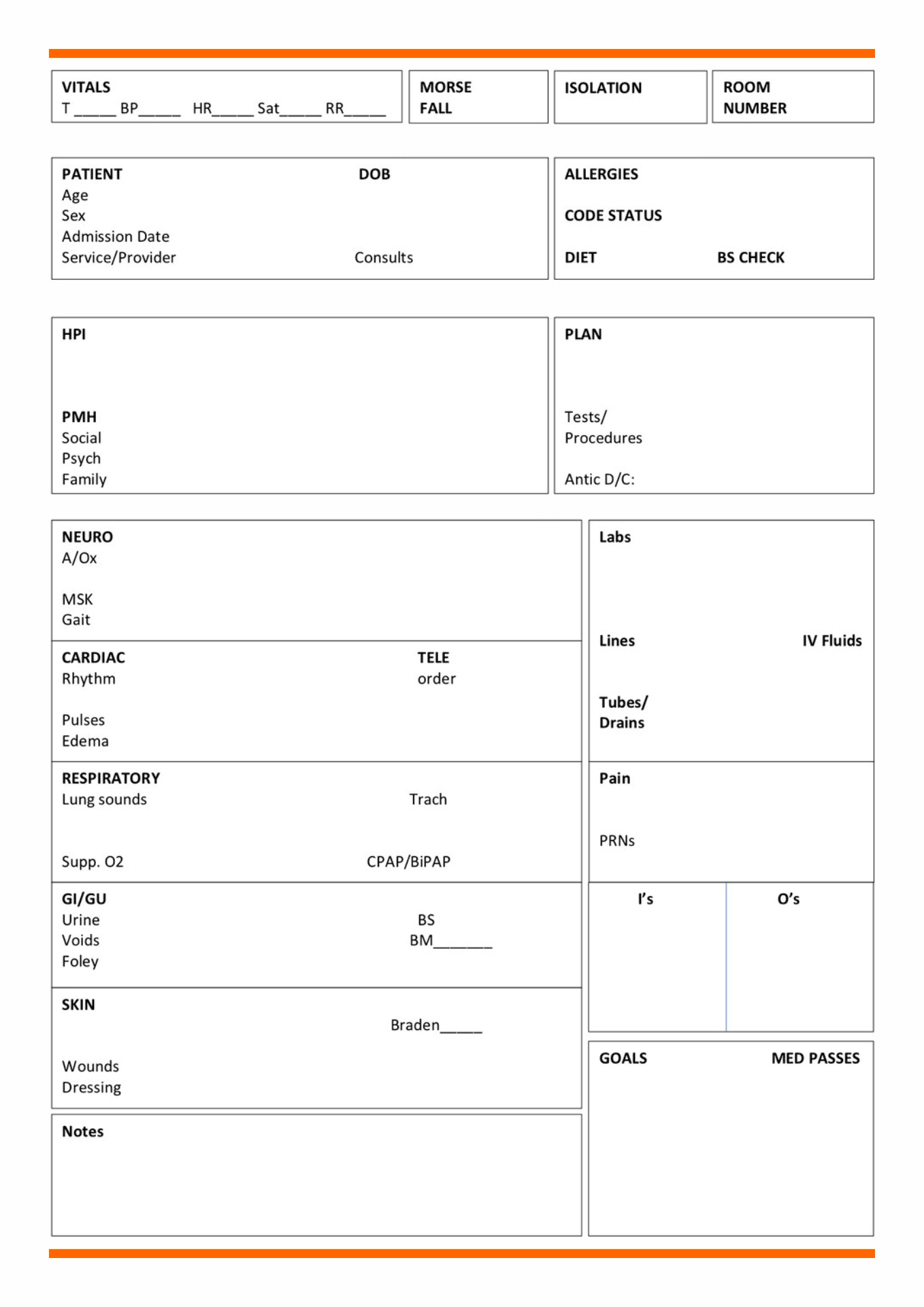
A patient medical report is a comprehensive document that contains the medical history and the details of a patient when they are in the hospital. It can also be given as a person consults a doctor or a health care provider. It is a proof of the treatment that a patient gets and of the condition that the patient has.
What is a patient medical report?
One thing that a doctor should have documented in the patient medical report is the medical diagnosis that he has found in the patient. Whatever disease that a patient has should be clearly stated in the medical report. The name of the disease should be clearly written and some explanations about the current condition of the patient.
What should a doctor document in a medical report?
In a primary care setting, rapid assessment of a possibly manic or hypomanic patient primarily needs to address the safety of the patient and family or caregivers, as well as health care practitioners. The complexity and severity of symptoms in mania often necessitate hospitalization and require rapid and effective symptom control.
What is a rapid assessment of a possibly manic or hypomanic patient?
How is mania diagnosis?
There is no laboratory test that can diagnose mania. Some medical illnesses can affect your mood, and so your doctor may run laboratory tests to rule out such concerns. Your doctor may then conduct a physical exam, ask you about your personal medical and family history, and then evaluate your signs and symptoms.
How do you assess a manic patient?
Using a screening tool such as the Mood Disorder Questionnaire is an efficient way to probe for bipolar symptoms. This self-administered questionnaire involves 13 items about manic and hypomanic symptoms. Answering “yes” to at least seven questions constitutes a positive screen.
What are the differential diagnosis of mania?
The main mental illnesses which mimic bipolar mania are schizophrenia, severe anxiety, severe obsessive-compulsive disorder, or major depressive disorder with psychotic features. Any mixed mood disorder should be in the differential for bipolar disorder, especially when psychosis is present.
What is observed in mania?
The change to include increased energy or activity as a core symptom of the BD diagnosis is consistent with the self-report of manic patients who often describe that they have more energy than usual and are observed to be physically restless, fidgeting and changing posture and position frequently.
What assessment findings would you expect to see in a client in the manic phase of bipolar disorder?
Increased energy and activity. Excessive talk; racing thoughts. Inflated self-esteem. Unusual energy; less need for sleep.
Which is the best assessment tool for mania symptoms?
The most common approach to measuring the severity of manic symptoms has been clinician-rated interviews. The Young Mania Rating Scale (YMRS) and Bech-Rafaelsen Mania Rating Scale (MAS) are two of the most widely used clinician-rated scales for assessing symptom severity.
What are symptoms of mania?
Maniafeeling very happy, elated or overjoyed.talking very quickly.feeling full of energy.feeling self-important.feeling full of great new ideas and having important plans.being easily distracted.being easily irritated or agitated.being delusional, having hallucinations and disturbed or illogical thinking.More items...
What are the three stages of mania?
Thus, when the term “manic episode” is used it may refer to any one of the three stages of mania: hypomania, acute mania, or delirious mania. Manic episodes are often preceded by a prodrome, lasting from a few days to a few months, of mild and often transitory and indistinct manic symptoms.
Which of the following is a clinical feature of mania?
Both a manic and a hypomanic episode include three or more of these symptoms: Abnormally upbeat, jumpy or wired. Increased activity, energy or agitation. Exaggerated sense of well-being and self-confidence (euphoria)
What nursing intervention should be implemented when a client is in the manic phase?
Clients with bipolar disorders are at a high risk for suicide. Although clients in the manic phase are briefly agitated, energized and elated, their underlying depression makes them likely to inflict self-injury....Desired Outcomes.Nursing InterventionsRationaleProvide frequent rest periods.Prevents exhaustion.7 more rows•Mar 18, 2022
What does manic behavior look like?
In the manic phase of bipolar disorder, it's common to experience feelings of heightened energy, creativity, and euphoria. If you're experiencing a manic episode, you may talk a mile a minute, sleep very little, and be hyperactive. You may also feel like you're all-powerful, invincible, or destined for greatness.
What causes mania episodes?
high levels of stress. changes in sleep patterns or lack of sleep. using recreational drugs or alcohol. seasonal changes – for example, some people are more likely to experience hypomania and mania in spring.
What is the primary care setting for a manic patient?
In a primary care setting, rapid assessment of a possibly manic or hypomanic patient primarily needs to address the safety of the patient and family or caregivers, as well as health care practitioners. The complexity and severity of symptoms in mania often necessitate hospitalization and require rapid and effective symptom control. Agitation, irritability and severe aggression are common elements of mania and are associated with self-harm ( Suppes et al., 2017 ).
How many questions are asked in the mood disorder questionnaire?
This self-administered questionnaire involves 13 items about manic and hypomanic symptoms. Answering “yes” to at least seven questions constitutes a positive screen. It also indicates that at least some of the symptoms are occurring concurrently and are causing moderate functional impairment. Explore a positive screen further to confirm or rule out a bipolar diagnosis ( Hirschfeld et al., 2000 ).
Should bipolar patients be screened?
Consider routine screening for bipolar disorder in all patients who present with affective symptoms ( Das et al., 2005 ). Patients with co-occurring anx- iety disorders, substance use disorder or impulse dyscontrol (e.g., gambling disorders) should be closely scrutinized for clinical presentations that suggest bipolar disorder.
What was Mr. A's diagnosis?
Mr A’s sensorium fluctuated (eg, he was confused and disoriented to place and time), and a presumptive diagnosis of delirious mania was made. He was transferred to the medical floor (with psychiatric consultation-liaison service involvement) for further workup of altered mental status. Possible causes for delirium including polypharmacy, urinary tract infection, active cellulitis, uncontrolled diabetes mellitus type 2, constipation, acute kidney injury, hypertension, nephrogenic diabetes insipidus, and benign prostatic hypertrophy were addressed without significant improvement. Neuroimaging (magnetic resonance imaging [MRI] of the brain) was unremarkable with no evidence of hemorrhage or space-occupying lesion. A trial of intravenous lorazepam failed to improve his mental status. Concerns about corrected QT value (QTc) prolongation and Torsades de pointes (TdP) precluded the use of haloperidol for Mr A given his electrocardiogram (ECG) showed a QTc interval reading >c500 msec.
What tests are needed for delirious mania?
Table 1 includes a list of conditions associated with altered mental status and is organized systematically by organ system to display the wide differential diagnosis of delirious mania. Laboratory tests should be performed, including complete metabolic panel, complete blood count with differential, urinalysis, and vitamin (eg, B 12 /folate) and nutritional studies (eg, albumin/prealbumin), and pregnancy screening for female patients of reproductive age should be ordered to assist with the workup of delirious mania to rule out these potential etiologies. 2 Creatinine phosphokinase, iron studies, and blood and urine cultures should be ordered if there is fever, rigidity, or autonomic instability. If clinically indicated, an electroencephalogram (EEG), arterial blood gas, serum drug levels (eg, lithium), chest x-ray, ECG, thyroid and liver function tests, lumbar puncture, neuroimaging (eg, computed tomography or MRI of the brain), and other blood serum tests (eg, human immunodeficiency virus, hepatitis A/B/C, syphilis, Lyme disease, antinuclear antibodies) can be ordered. 2
How to treat delirious mania?
Treatment of delirious mania typically targets underlying neuro-medical causes; however, there is a first-line role for benzodiazepines, especially if catatonic features are present, despite their usual contraindication in delirium. 2 A lorazepam challenge usually starts with 2 mg of lorazepam (intravenous is easiest to administer; however, oral and intramuscular formulations are potential options) with observation for effect. 8 If there is no effect, the same dose may be repeated in 3 hours and again after another 3 hours if necessary, with a target dose of at least 6 mg over a 24-hour period. If clinical response is favorable, ongoing treatment of 6 mg (and up to 20 mg) of lorazepam per day in divided doses is indicated. Close monitoring for respiratory suppression, or alternatively for paradoxical worsening of confusion, is recommended during lorazepam challenge. If no improvement occurs, electroconvulsive therapy (ECT) should be considered. 2 ECT is the most effective treatment to resolve symptoms and signs of delirious mania within 2 to 4 sessions, although 12 or more ECT sessions may be required on occasion. 2 Benzodiazepines should be held during the morning hours prior to ECT sessions, as they increase seizure threshold and interfere with effective convulsive activity. Moreover, antiepileptic agents used for psychiatric conditions (eg, valproic acid, carbamazepine, lamotrigine) should be held for ECT unless they are part of a specific treatment plan for epilepsy. 2 Bitemporal (compared to unilateral) ECT is most effective for treatment of catatonic features, although it is associated with potentially more prominent cognitive side effects. 8 If catatonic or malignant features (eg, rigidity, fever, autonomic instability) are present, antipsychotics should be discontinued, as they may precipitate neuroleptic malignant syndrome and lead to significant morbidity and mortality. Antipsychotics may be used if catatonic malignant features are not present. There is a potential role for mood stabilizers in delirious mania; however, response is much slower than with ECT or benzodiazepines (eg, days/wk vs minutes/h). 2
What is the gold standard treatment for delirious mania?
Electroconvulsive therapy is the gold standard treatment for cases of delirious mania, and psychiatric advance directives about the use of this treatment should be prioritized.
What is Mr A's lithium level?
Mr A, a 61-year-old man, was transferred to our psychiatric unit for the management of acute mania and lithium toxicity (lithium level: 1.6 mmol/L; reference range, 0.8–1.2 mmol/L) in the setting of acute kidney injury. His psychiatric history was notable for bipolar affective disorder type I and an episode of probable delirious mania 17 years earlier (which resolved following treatment with lithium and olanzapine). His medical history included poorly controlled essential hypertension, diabetes mellitus type 2, hypothyroidism, and gastroesophageal reflux disease.
What is the psychiatric consultation service?
The Psychiatric Consultation Service at Massachusetts General Hospital sees medical and surgical inpatients with comorbid psychiatric symptoms and conditions. During their twice-weekly rounds, Dr Stern and other members of the Consultation Service discuss diagnosis and management of hospitalized patients with complex medical or surgical problems who also demonstrate psychiatric symptoms or conditions. These discussions have given rise to rounds reports that will prove useful for clinicians practicing at the interface of medicine and psychiatry.
Why did Mr. A require intermittent restraints?
Mr A required intermittent restraints due to significant physical aggression toward staff members (including a traumatic brain injury suffered by a nurse). For the safety of the patient and staff, he was sedated in the intensive care unit (ICU) using dexmedetomidine for 2½ days with only mild resolution of his manic symptoms upon emergence from sedation.
What is included in a comprehensive physical exam?
Comprehensive physical exam including a BMI calculation, blood pressure and an EKG.
Is divalproex good for a manic episode?
Divalproex is an anticonvulsant with good efficacy data for treatment of manic episodes. It is generally well tolerated in the geriatric population. It can be started at 500 mg/day with target serum concentrations of 70-99 µg/ml. (Young 2017). Common side effects include nausea, sedation, weight gain, and benign tremor. Divalproex has rarely been associated with liver failure and pancreatitis. Monitoring of weight, complete blood count, and liver function tests should be done every 3 months for the first year, then annually.
Who makes the patient medical report?
Health care providers do the patient medical report. The health care professionals make the documentation for a patient. It includes all the physicians, nurses, and doctors of medicine. It also includes the psychiatrists, pharmacists, midwives and other employees in the allied health. It is part of their job to make a patient medical report because the health condition of all the patients should be documented. Hospitals keep history of medical records. The functions of medical records are more than important, so they continually keep track on the patient’s health conditions.
Why should a patient's medical report include lab results?
It is also needed because sometimes the laboratory and the test results are the proof of the sickness of the patient. For example, if the patient has a blood cancer, it can be seen with the blood tests. If the patient has a brain tumor, it can be seen through a brain CT scan. A CT scan for the body can also tell whether we have a fracture or not.
Why should you ask a patient about his medical history?
Ask the patient about his medical history. You should put it to have a better analyzation of the medical condition of the patient. It can also make the doctors to be careful with the medication that they can give to the patient. Whatever is the sickness that a patient has before he is admitted to the hospital should be written in the patient medical report.
Why should medication be documented in a medical report?
The treatments or medications should also be documented because it can provide a good information about the medical history of a patient. Put the names of the medicines and tell how often did the patient takes it. You can also document its effect and tell whether it is effective for them.
Is a medical report a legal document?
If it is signed by a health care professional, then it is a legal document. It is permissible in any court of law. It is an evidence that the patient is under your care. Thus, it can be used in court as an essential proof. So, keep a patient medical report because you may need it in the future.
Do health care providers have access to patient medical records?
The health care providers have the access to the patient medical report. They keep the medical report as a history of medical records. Also, patients’ access to the patient medical report is a must. It is their right to see their medical report. It is against the law not to show them their medical report. It can be a proof if there is any doctor withholding treatments. So, to avoid conflict, the patient medical report should be shown to the patients. HIPAA (Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act) has been passed in the Congress of United States. Passed in 1996, it specifies who can have an access to all the health information. You can research for that law, so you can have the exact details to who can have an access to a patient medical report. It is better because you can have a legal source. It can tell you all the things that you need to know about it.
Popular Posts:
- 1. ptr sports patient portal
- 2. rivers edge family medicine patient "portal"
- 3. dr. robert stokes patient portal how do i get on
- 4. patient portal sierra care physicians
- 5. piedmont cardiology hickory nc patient portal
- 6. ivy falls family medicine patient portal
- 7. ucla doctors report patient
- 8. idaho gastroenterology associates patient portal
- 9. cerner community works patient portal
- 10. sierra view medical center patient portal