Accuracy of Internet-Based Patient Self-Report of …
32 hours ago · To our knowledge, this is the first study of the accuracy of patient self-report using a commercial payer claims database as a reference that (1) minimizes the potential for underreporting due to leakage across specialties, care settings, and institutions, (2) enables measurement of self-report among patients attesting to either the presence or absence of … >> Go To The Portal
With an overall survey completion rate of 76.8% (285/371), patients were found to have accuracy of self-report characterized by a kappa of 0.80 and agreement of 0.99 and a kappa of 1.00 and agreement of 1.00 for 90-day hospital admissions and pulmonary embolism, respectively.
Full Answer
How accurate are computer-based patient records data?
Data in computer-based patient records (CPRs) are used in patient care, clinical research, health-system management, health-services planning, total quality improvement, billing, risk management, and government reporting. The accuracy of these data is therefore of great importance.
How accurate is data accuracy in cardiopulmonary resuscitation?
The accuracy of this data is critical to the optimal outcome of many health care activities. This review shows that our understanding of data accuracy in CPRs is not commensurate with its importance. It is imperative that we both measure and characterize the accuracy of data in CPRs and investigate ways to improve it.
How should diagnostic accuracy studies be presented in clinical practice?
For diagnostic accuracy studies to usefully inform clinical practice, their results should be related to decisions regarding management of patients. Presentation in terms of individual patients is often best, 1 and formats such as animations with smiley faces have been successful. 7
How accurate is health information data?
Certain types of data, such as immunization status, medications, and demographics, tended to be more accurate than other types, such as problem lists and complications of surgical procedures, but the lowest rates of accuracy for the “more” accurate types of data overlapped with the highest rates of accuracy for the “less” accurate types.
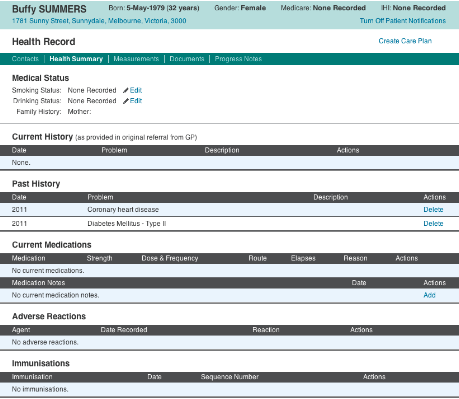
How do you ensure accuracy of medical records?
Start with your own best practices.Tips to Ensure Accuracy. ... Ensure Healthcare Records Are Legible. ... Sign the Notes in Every Healthcare Record. ... Don't Scribble in the Notes. ... Keep All Healthcare Documents in Order. ... Be Objective with Healthcare Notes. ... Properly Store Healthcare Records.
How can patient history be accurate?
Generally speaking, most patient history conversations are as follows:Greet the patient by name and introduce yourself.Ask, “What brings you in today?” and get information about the presenting complaint.Collect past medical and surgical history, including any allergies and any medications they're currently taking.More items...•
Why is accurate patient charting important?
Accurate documentation ensures the Federal health care programs pay the right amount—not too much and not too little—to the right people. Good documentation is important to protect your patients. Good documentation promotes patient safety and quality of care.
What is data accuracy in healthcare?
Data accuracy refers to error-free records that can be used as a reliable source of information. In data management, data accuracy is the first and critical component/standard of the data quality framework.
Why is patient history important?
Patient medical history is often a crucial step in evaluating patients. Information gathered by doing a thorough medical history can have life or death consequences. In less extreme cases medical history will often direct care.
What makes a good medical history?
A good history is one which reveals the patient's ideas, concerns and expectations as well as any accompanying diagnosis. The doctor's agenda, incorporating lists of detailed questions, should not dominate the history taking. Listening is at the heart of good history taking.
Why is accurate and effective documentation most important?
Why is accurate and effective documentation most important? Documentation constitutes a legal record. Which example may illustrate a breach of confidentiality and security of patient information?
Why is it important to keep accurate records in healthcare?
Their clarity and accuracy is paramount for effective communication between healthcare professionals and patients. The maintenance of good medical records ensures that a patient's assessed needs are met comprehensively.
Why proper documentation is important?
In every field, it's important to minimize as much risk as possible. Documentation is a great tool in protecting against lawsuits and complaints. Documentation help ensure consent and expectations. It helps to tell the narrative for decisions made, and how yourself or the client responded to different situations.
How do you check data accuracy?
How Do You Know If Your Data is Accurate? A case study using search volume, CTR, and rankingsSeparate data from analysis, and make analysis repeatable. ... If possible, check your data against another source. ... Get down and dirty with the data. ... Unit test your code (where it makes sense) ... Document your process.More items...•
What is data accuracy?
Data Accuracy is the measure of data quality based on factors like accuracy, completeness, and reliability. Data Accuracy is the first and foremost critical part of the data quality framework.
Why is accuracy of information important?
Accuracy is to be ensuring that the information is correct and without any mistake. Information accuracy is important because may the life of people depend in it like the medical information at the hospitals, so the information must be accurate.
What happens when patient data is inaccurate?
However, when patient data is inaccurate, there are bound to be inconsistencies before, during, or after providing patient care. For instance, the patient receives proper care but someone else receives the bill due to a medical record error down the line.
Why is patient data important in healthcare?
Patient data accuracy in healthcare facilities, as a result, must be immaculate at all times. Ensuring patient data integrity helps healthcare providers improve patient outcomes, gain accurate insights into the patient’s medical history, personalize the treatment, make informed decisions, and provide the right treatment at the right time.
What is personalized care?
It means using a combination of techniques, solutions, and strategies to ensure that the patient is engaged with their care and provide them with a customized experience – usually the way they want it.
Why do hospitals use EHR?
Hospitals and health systems exist primarily to treat their patients , and as the majority of healthcare providers have gone for EHR (electronic health record) systems , ensuring patient data integrity at all times becomes a priority.
Is one size fits all in healthcare?
After all, a “one size fits all” approach is quite obsolete, even in healthcare. For instance, a patient might have several illnesses, and this requires a personalized approach to provide care for them.
Can data inaccuracies lead to wrong treatment?
This one is quite unsurprising – it’s quite natural that data inaccuracies will lead to the wrong treatment, medical errors, and worse, as physicians are armed with wrong information. Physicians make life-changing decisions, and if armed with the wrong information, it can be disastrous for the patients.
What is diagnostic test accuracy?
A diagnostic test accuracy study provides evidence on how well a test correctly identifies or rules out disease and informs subsequent decisions about treatment for clinicians, their patients, and healthcare providers.
When a test has only a single threshold or cutpoint value, what are the results?
When a test has only a single threshold or cutpoint value (for instance, positive or negative for disease, such as a biopsy), results are naturally presented in pairs, usually sensitivity and specificity, or PPV and NPV (see fig 1).
What is net benefit measure?
Net benefit measures can provide an overall impact across changes in paired measures. For example, the weighted comparison (WC) measure 13 is an index weighting the difference in sensitivity and difference in specificity of two tests, taking into account the relative clinical cost (misclassification costs) of a false positive compared with a false negative diagnosis and disease prevalence. We note that the WC measure is similar to the net reclassification index (NRI), 14 if the latter is adapted to account for disease prevalence and relative misclassification costs.
Should diagnostic tests be compared?
Ideally, diagnostic tests should be compared within the same patients or, if this is not practical, on randomised groups from the same population of patients. This ensures that differences in observed test results are because of the tests rather than differences in characteristics of patients or study methods.

Why Patient Data Accuracy in Healthcare Facilities Is So Crucial
Consequences of Patient Data Inaccuracies
- They Lead to Medical Record Errors
One of the most common consequences of patient data inaccuracies is the creation of medical record errors such as duplicates or overlays – most of which occur during the registration process. It’s quite simple but deadly – a patient comes in, and due to inaccuracies within the EH… - They Lead to Patient Safety Incidents
This one is quite unsurprising – it’s quite natural that data inaccuracies will lead to the wrong treatment, medical errors, and worse, as physicians are armed with wrong information. Physicians make life-changing decisions, and if armed with the wrong information, it can be disastrous for t…
Practices That Ensure Patient Data Accuracy in Healthcare Facilities
- Hospitals and health systems need to ensure that patient data is accurate, relevant, consistent, and complete at all times. While all of this might be overwhelming, it reduces costly mistakes and cases down the line, as explained in the previous points. Hospitals and health systems can: 1. Allocate personnel to routinely check EHR systems for inconsistencies such as new duplicate m…
Hospitals Must Prioritize Patient Data Accuracy in Healthcare Facilities
- While many healthcare providers are already ensuring data accuracy in EHRs by utilizing the above practices, others are still suffering from patient misidentification, medical record mix-ups, lower patient data quality, litigation costs, and more. While they might be facing these issues due to different factors, working on improving patient data integrity is a good starting point that will …