Individuals’ Access and Use of Patient Portals and …
18 hours ago Sep 21, 2021 · FINDINGS. ★ About one in five patient portal users (22%) accessed their health information using both a smartphone health app and a computer in 2020. ★ Patient portal users most commonly accessed their health information through a computer (83%) – six in 10 portal users accessed their health information using only this method. >> Go To The Portal
Overwhelmingly, patients use the portal to view their lab results (85 percent). Sixty-two percent of patients are also using the tool for more clinical tasks, such as scheduling appointments, completing paperwork, and refilling prescriptions.
What percentage of patients actually use patient portals?
Sep 21, 2021 · FINDINGS. ★ About one in five patient portal users (22%) accessed their health information using both a smartphone health app and a computer in 2020. ★ Patient portal users most commonly accessed their health information through a computer (83%) – six in 10 portal users accessed their health information using only this method.
What is the patient portal adoption rate?
Apr 16, 2018 · Overwhelmingly, patients use the portal to view their lab results (85 percent). Sixty-two percent of patients are also using the tool for more clinical tasks, such as scheduling appointments, completing paperwork, and refilling prescriptions. Only 14 percent of patients are using the portal to transmit medical records to another provider, despite federal calls for …
What is a patient portal in healthcare?
Two recent systematic reviews in adults have demonstrated that patient portals are positively associated with improvements in medication adherence, increases in preventative medicine, improved disease management in chronic conditions, enhanced patient-provider communication, better use of office visit time, and greater satisfaction with care. 2,3 Portal sign-up rates have …
Do patients use online patient portals to access electronic health records?
Oct 04, 2018 · Patient Portal Activation Rates: Influence of Age, Gender, Race, and Geographic Location Overall, female patients were found to have a higher rate of patient portal account activation than their male counterparts ( Figure 1A ). Activation rate across all female patients was 39.9%, while males had an overall activation rate of 31.9%.
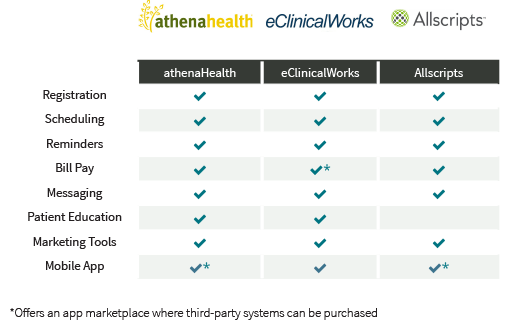
Can patient portals increase engagement?
Patient portals may enhance patient engagement by enabling patients to access their electronic medical records (EMRs) and facilitating secure patient-provider communication.
What is the most popular patient portal?
Top 10 Patient Portal Software By EMRSystemsEpic EHR Software's MyChart.athenahealth EMR Software's athenaCommunicator.PrognoCIS EMR Software.Cerner Specialty Practice Management Software.eClinicalWorks EMR Software's Patient Portal and Healow App.Greenway PrimeSUITE EHR Software.NextGen Healthcare EHR Software.More items...•
Why do patients not use patient portals?
Disadvantages of patient portals result in these lower rates of use. For some people, they avoid using the portals altogether for reasons like security issues, low health literacy, or lack of internet. Even for those who do access their accounts, there are still other disadvantages of patient portals.
How effective are patient portals?
Patient portal interventions were overall effective in improving a few psychological outcomes, medication adherence, and preventive service use. There was insufficient evidence to support the use of patient portals to improve clinical outcomes.
How do you improve patient portals?
5 steps to maximize your patient portal and boost practice...Meet patient priorities. ... Integrate the portal into practice workflow. ... Identify patients who will most benefit from portal use. ... Promote the portal. ... Evaluate portal use and modify practice operations.
What are the different types of patient portals?
There are two main types of patient portals: a standalone system and an integrated service. Integrated patient portal software functionality usually comes as a part of an EMR system, an EHR system or practice management software. But at their most basic, they're simply web-based tools.
Do doctors like patient portals?
The findings, published in the journal Health Affairs, indicate a lack of physician, health system and insurer engagement in promoting portal use—nearly 40% of patients in the study reported not being offered it.
Do patients like patient portals?
Eight studies reported that patients or their caregivers want more portal education, training, or support. Two studies found that their participants want human connection as they learn about the portal and how to use it, as well as when they encounter issues.
What is the most common barrier to the use of the patient portal?
Among nonadopters (n=2828), the most prevalent barrier to patient portal adoption was patient preference for in-person communication (1810/2828, 64.00%) (Table 2). The second most common barrier was no perceived need for the patient portal (1385/2828, 48.97%).
Are patient portals easy to use?
Portals provide physicians with a fast and easy way to communicate with chronically ill patients. They are a place to get complete and more accurate patient information. Portals empower patients to take ownership of their own healthcare, so they remain aware of the entire care process.
Why is the patient portal a good tool for patient engagement?
Many healthcare providers design and implement patient portals to increase patient engagement because these tools give patients convenient, 24-hour access to personal health information from anywhere with an Internet connection.
Why is patient portal important?
The patient portal does have a lot to offer patients, and because of certain regulatory requirements, may be the tool best positioned to fulfill certain benchmarks. But to gain a meaningful return on investment with the tool, organizations must aim higher than offering the tool.
What is PGHD in medical terms?
PGHD is health data that has been contributed by the patient, either from medical histories, patient observations, wearable sensors, or other biometric measuring devices.
What is a patient portal?
As per the scope of the report, the patient portal is a web-based access point that is connected with the electronic health records (EHR) systems and is focused on patient’s access to health records. The patients can share their health information and communicate remotely. These allow patients to look into various data points. Some portals allow patients to check medical history data and view demographics.
Which country has the largest patient portal market?
North America has been the largest patient portal market due to wide technological advancements in the region. Countries, such as the United States and Canada, have been successful in implementing IT technologies in their healthcare systems, which as a result, may boost the market growth.
What are the technologies that are used in healthcare?
Healthcare technology, genomics, connected devices, big data analytics, and artificial intelligence are generating vast amounts of health data and insights, which are enabling healthcare providers to make better and faster diagnoses and more informed treatment decisions.
Abstract and Figures
Using a unique longitudinal dataset, we exploit within-patient variations in the timing of activation and subsequent use of the patient portal. Active portal use is motived by a significant uptick in office visits and phone encounters.
References (15)
Technological advancements have proven to be indispensable for improving patient care, yet they continue to present a host of problems. One of the most pressing concerns is how to improve quality of care while controlling costs. Beyond clinical care, one plausible solution is to share patient information freely and efficiently.
What are the benefits of patient portals?
One clear benefit many patients gain from patient portals is a more structured approach toward both managing and resolving their health concerns. Empowered with the right information, many patients are able to take better ownership of their health, which is yielding encouraging outcomes in several areas:
Is patient portal good?
There are patients who think using a patient portal is not a good idea or a waste of time. Typically, patients who are relatively healthy do not see sense in using a patient portal . A report from the GAO corroborates the fact that many patients who are either old or healthy do not see the need to access their EHRs using patient portals. Health care providers must ensure these particular groups understand the benefits of a patient portal. The most obvious benefit is that a patient information portal reduces friction between the health care process and the patient.

Popular Posts:
- 1. how to read radiology report on ms patient
- 2. tjsampson patient portal
- 3. covenant hospital patient portal lubbock
- 4. patient portal for dr. wells warner robins
- 5. orthodontist patient portal doctor albertson
- 6. umc patient portal login
- 7. yourhealthfile patient portal
- 8. dr. espinosa westchester il patient portal
- 9. lighthouse patient messaging portal
- 10. heart city patient portal