Connect Patient Portal | ColumbiaDoctors - New York
7 hours ago What can I do with the online patient portal? Please call 646-426-3876 (646-42-NEURO), Monday-Friday, during the hours of 9 a.m.-5 p.m. What is Columbia connect? To schedule an appointment with Columbia Neurology in New York City, call 646-426-3876. Are there programs that connect neurologic patients and caregivers with the Arts? >> Go To The Portal
How do I contact Columbia nephrology?
Call Columbia Nephrology at 803-252-9907 and ask for the Portal Secretary. They will work with your doctor to clarify the information. Can I un-enroll from FollowMyHealth@ColumbiaNephrology?
What can I do with the online patient portal?
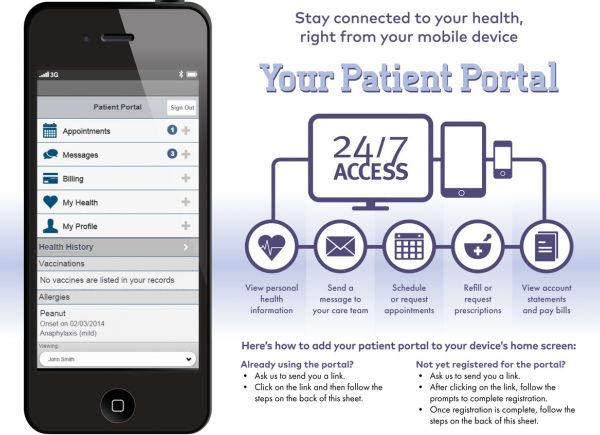
Our online patient portal provides a secure, convenient way to manage your personal health care and receive communication directly from your doctor. Use it at any time of day or night to: Review and update your personal health history and demographic information
What is Columbia connect?
Connect is a joint effort of Columbia, NewYork-Presbyterian, and Weill Cornell Medicine, so a single Connect account links you to all three institutions. With the Columbia Connect app, you can access convenient services to help manage your health.
Why choose Columbia nephrology?
Columbia Nephrology. Columbia Nephrology Associates offers the latest diagnostic technology and treatment plans for a wide variety of kidney conditions. As the Midlands' largest nephrology practice, we specialize in treating chronic kidney disease, hypertension, anemia, diabetes and gout.
ColumbiaDoctors Neurology
Welcome to ColumbiaDoctors Neurology! Whether you are visiting for the first time or have an established health care relationship with one of our physicians, we want your patient care experience to be the best it can be. After your visit, please let us know how we are doing by emailing us at columbianeurology@columbia.edu (link sends e-mail) .
Online
Please fill out our online appointment request form and a member of our scheduling team will contact you during business hours to confirm your appointment.
Columbia Connect
Telehealth appointments are currently available across all of our neurological specialties. A Connect Patient Portal account is suggested for all patients and is REQUIRED for access to Telehealth appointments.
Art Programs Engage Patients and Educate About Neurologic Disorders
Various programs around the country connect neurologic patients and caregivers with the arts. One such example is Arts & Minds, an organization founded by Dr. James M. Noble
PANDA Symposium
William Black Medical Research Building, 650 W. 168 St., New York, NY 10032 Alumni Auditorium
Message from the Chair
A welcome message to the Department of Neurology from the Chair, Richard P. Mayeux, MD, MSc.
What is neuro-icu?
A Neuro-ICU employs a variety of innovative drug therapies which have proven useful in treating serious neurological illness. Pentobarbital and Propofol are two medications which are specialized for the management of patients in a neurological critical care unit:
What is neurocritical care?
Neurological diseases and emergencies tend to be complex and relatively uncommon, and are best treated by Neurocritical Care specialists who have been highly-trained to meet the specific, often dire needs of critically ill neurological patients. In addition to our expert neurologists, the Neurocritical Care Unit at NewYork-Presbyterian/Columbia University Medical Center provides constant surveillance by neurocritical care nurses and on-call neurologists with the expertise to act immediately to administer specialized interventions. This highly-specialized team approach to patient care makes it possible to correct or reverse worsening medical conditions that might otherwise lead to permanent brain damage or death.
What are the most common neuromuscular diseases?
If this weakness affects the muscles of respiration then a patient's breathing can be dangerously compromised. Myasthenia Gravis and Guillain-Barré syndrome are the two most common neuromuscular diseases. Both disorders are caused by the presence of antibodies in the bloodstream which are directed against part of the neuromuscular system. In the case of myasthenia gravis the antibodies are directed against the nerve-muscle junction, and in Guillain-Barré syndrome antibodies become directed against the lipid (myelin) sheath which insulates nerves.
What is invasive hemodynamic monitoring?
Invasive hemodynamic monitoring refers to the assessment of blood flow and blood pressure via devices placed within blood vessels. In many medical settings these devices are used to measure circulatory function in the presence of heart or lung disease. A Neuro-ICU uses these techniques to ensure that the brain is being properly perfused with blood. The instruments used to measure circulatory function are known as catheters. Blood pressure is recorded by a fluid-filled catheter and this pressure is transmitted to a transducer which converts the information into an electrical signal visible on a monitor. There are two general techniques to monitor blood pressure:
What is the maximum intracranial pressure?
A common complication of many serious neurologic conditions is an elevation of the pressure within the skull, the intracranial pressure or ICP. In adults, the average ICP ranges from 0-10 mm Hg. 20 mm Hg is considered to be the maximal upper limit of desirable ICP and pressures exceeding 40 mm Hg are considered extremely elevated. Intracranial pressure may be high for several reasons. ICP can be elevated if there is a rise in the pressure of the fluid circulating around the brain (the cerebrospinal fluid). This condition is known as hydrocephalus. Alternatively, the blood vessels supplying the brain can leak fluid into the brain causing the brain to swell, a situation referred to as cerebral edema. Whatever the underlying cause an increase in intracranial pressure is extremely dangerous.
What is a stroke in ICU?
A form of stroke commonly managed in a Neuro-ICU is subarachnoid hemorrhage, a bleeding into the subarachnoid space between the brain and the skull. This bleeding usually occurs as the result of the rupture of a brain aneurysm. A brain aneurysm is a swelling or ballooning of a small segment of an artery in the brain. Unfortunately such aneurysms commonly rupture a second time, resulting in a dangerous rebleeding of the brain aneurysm. Endovascular GDC Coils are small, stainless steel platinum coils which are placed inside the lumen of a brain aneurysm. The coils are packed inside the swollen portion of the artery until the aneurysm sac is completely filled with coils. Essentially, these coils act as a blood clot (or thrombus) which prevents blood from flowing into the aneurysm. Also, the metallic coils are coated with thrombogenic fibers to aid in clot formation. The aneurysm is thus prevented from bursting a second time and causing a rebleed.
