FREE 14+ Disability Report Forms in PDF - sampleforms
26 hours ago File Format. PDF. Size: 45 KB. Download. This sample form for disability report is utilized to assess one’s current health conditions, despite the disabled person’s involvement to other organizations. The form technically shows a report of the health and medical assessment of … >> Go To The Portal
How do you write a nursing plan for depression?
Nursing Care Plans for Major Depression. Nursing care plan goals for patients with major depression includes determining a degree of impairment, assessing the client’s coping abilities, assisting the client to deal with the current situation, providing for meeting psychological needs, and promote health and wellness.
What is the best citation for a case study of depression?
Part of the Psychology Commons Recommended Citation Allison, Barbara Ann Marie, "Case study of a client diagnosed with major depressive disorder" (2005). Theses and Dissertations. 958.
What are the care plan goals for patients with major depression?
Nursing care plan goals for patients with major depression includes determining a degree of impairment, assessing the client’s coping abilities, assisting the client to deal with the current situation, providing for meeting psychological needs, and promote health and wellness.
What are the DSM-IV-TR diagnostic criteria for major depression?
According to the DSM-IV-TR, the client is exhibiting characteristics matching that of a Major Depressive Disorder. Loss of interest or pleasure in most activities is evident. Changes in sleep habits. Weight, appetite, and energy level are seen, as well as levels of psychomotor activity.
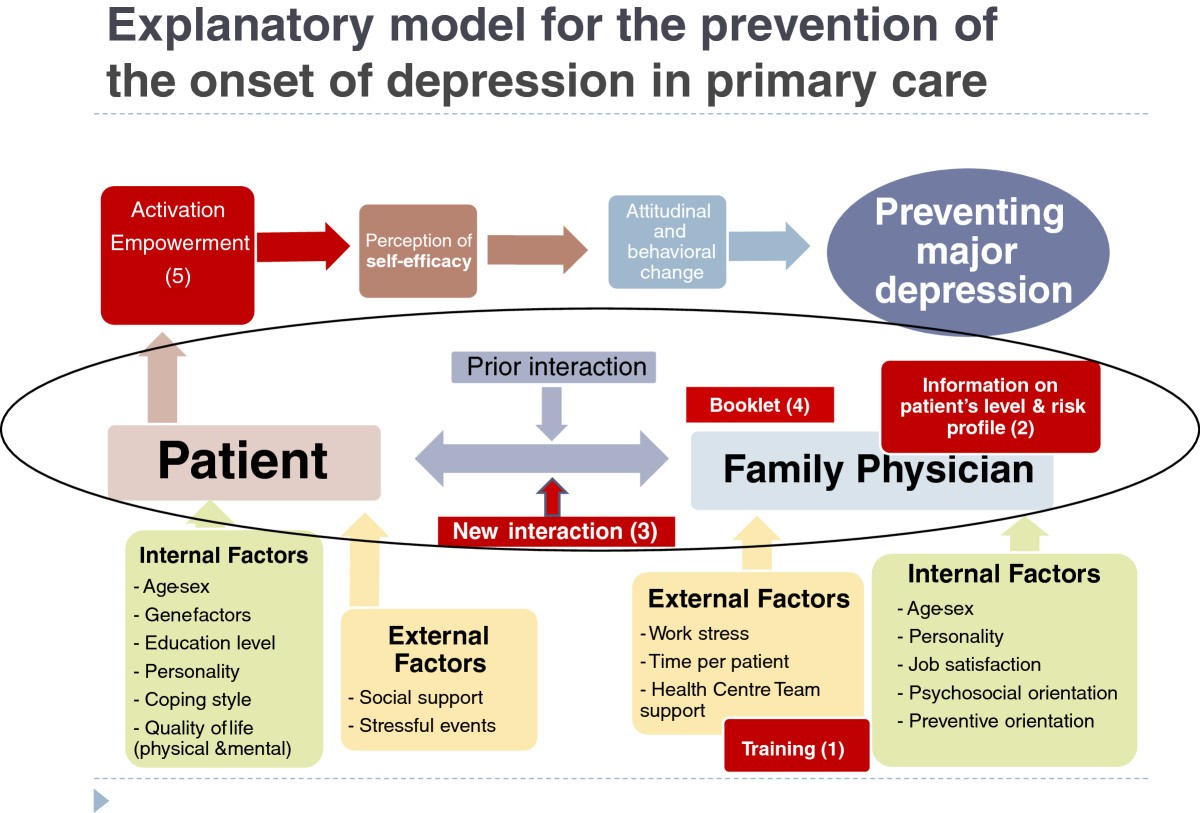
How do you write a patient summary report?
A good medical summary will include two components: 1) log of all medications and 2) record of past and present medical conditions. Information covered in these components will include: Contact information for doctors, pharmacy, therapists, dentist – anyone involved in their medical care. Current diagnosis.
How does depression cause disability?
Depression is considered a psychiatric disability under the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA). It's a significant mood disorder that's known to interfere with daily activities, which may include your ability to work. Depression sometimes becomes so severe that you can no longer go to work.
What mental illness is considered a disability?
Mental illnesses that can be covered by Social Security disability include depression, anxiety and anxiety-related disorders, autism, ADHD, learning disabilities, and intellectual disability.
Is depression a disability in Australia?
Of the 1.1 million people with psychosocial disability: over one-third (35.1%) had depression/mood affective disorders, similar to 2015 (37.6%)...Long-term health conditions.Selected long-term health conditionsPsychosocial disability (%)Other disability(d) (%)Depression mood affective disorders(a)35.17.18 more rows•Sep 25, 2020
Is Major Depression leading cause of disability?
Depression is a common mental disorder. Globally, it is estimated that 5.0% of adults suffer from depression (1). Depression is a leading cause of disability worldwide and is a major contributor to the overall global burden of disease. More women are affected by depression than men.
How do you prove mental disability?
To prove your mental disability, you will need to have medical documentations, records and notes from any physicians you are seeing to show that your mental disability makes it impossible for you to work full time. The more medical evidence you have, the easier it is to prove your mental disability.
Can you collect disability for depression and anxiety?
The good news is that those with either depression and anxiety can qualify for SSDI benefits. The Social Security Administration has a process for evaluating your right to collect Social Security disability benefits based on claims of a mental health problem.
What is the most approved disability?
1. Arthritis. Arthritis and other musculoskeletal disabilities are the most commonly approved conditions for disability benefits. If you are unable to walk due to arthritis, or unable to perform dexterous movements like typing or writing, you will qualify.
Can't work because of anxiety and depression?
If you've been diagnosed with depression and you expect that you won't be able to work for at least a year because of depression, you can file a claim for Social Security disability benefits.
Is depression a permanent disability?
Mental illnesses, among which depression and anxiety are most common, are the leading cause for permanent disability.
Is severe mental health a disability?
A Mental illness can is considered a disability by the Social Security Administration (SSA), and if you have a mental illness you may be able to qualify for Social Security disability benefits.
Is depression classed as a disability?
Currently, the law considers the effects of an impairment on the individual. For example, someone with a mild form of depression with minor effects may not be covered. However, someone with severe depression with significant effects on their daily life is likely to be considered as having a disability.
How many sessions were conducted to deal with the patient’s problems?
13 sessions were conducted to deal with the patient’s problems. Patient reported the improvement in her inactivity and anger outburst. She reported that her interpersonal relations with her in laws were got better by using assertiveness training. At the end of therapy she got improvement about 50%.
What is Beck Depression Inventory?
Beck, is a 21-question multiple-choice self-report inventory, for measuring the severity of depression (Beck, 1996).
How long does it take for a therapist to write down a conflict?
Therapist then asked the patient to take 20 minutes and write down all her thoughts and feelings about the conflict with her husband and her in laws that made her tensed and worried.
What is Freud's view on depression?
It is relevant to case in such as way that her father was died before few days of her marriage.
What is a clinical interview?
Clinical Interview was conducted to patient in order to gather information regarding her history of present illness and her current complaints, as well as the nature, severity and duration of her symptoms. It was also carried out to get detailed information about her personal history, family history, social life, financial situation and other factors such as predisposing, precipitating, maintaining and protective factors that contributed to increase her present condition.
How to help a patient with depression?
Avoid feigned cheerfulness, but don’t hesitate to laugh with him and point out the value of humor. Educate patient about depression. Explain that depression can be eased by expressing feelings and engaging in pleasurable activities. Emphasize that there are effective methods available for relief of symptoms.
What is the pathophysiology of major depressive disorder?
The underlying pathophysiology of major depressive disorder has not been clearly defined. Current evidence points to a complex interaction between neurotransmitter availability and receptor regulation and sensitivity underlying the affective symptoms.
What is the best treatment for depressive disorder?
There are a number of evidence-based psychotherapeutic treatments for adults with major depressive disorder such as behavioral therapy, cognitive therapy, cognitive behavioral analysis system of psychotherapy, interpersonal psychotherapy, problem-solving therapy, and self-management or self-control therapy.
What neurotransmitters are involved in the pathophysiology of major depressive disorder?
Other neurotransmitters implicated include norepinephrine, dopamine, glutamate, and brain-derived neurotrophic factor. The role of CNS 5-HT activity in the pathophysiology of major depressive disorder is suggested by the therapeutic efficacy of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
What are some examples of antidepressants?
Examples include citalopram (Celexa), paroxetine (Paxil), and sertraline (Zoloft).
How do medications help with depression?
Ideally, medications should be combined with various therapies. Drugs generally work by modifying the activity of relevant neurotransmitter pathways. Antidepressants are classified according to class:
What is Beck Depression Inventory?
ADVERTISEMENTS. Beck Depression Inventory is a psychological test used to determine symptom onset, severity, duration, and progression.
What is Major Depression?
Major depression (or major depressive disorder) is classified under mood disorders which are characterized by disturbances in the regulation of mood, behavior, and affect that go beyond the normal fluctuations that most people experience.
Nursing Care Plans for Major Depression
Nursing care plan goals for patients with major depression includes determining a degree of impairment, assessing the client’s coping abilities, assisting the client to deal with the current situation, providing for meeting psychological needs, and promote health and wellness.
References and Sources
References and recommended sources for this care plan guide for major depressive disorder:
See Also
Nursing Care Plan: The Ultimate Guide and Database – the ultimate database of nursing care plans for different diseases and conditions! Get the complete list!

Session Report
- History taking was done through Clinical interview
- BDI was administered
- Dysfunctional thought record was given
- Mental state examination was done
Case Summary
- The patient S.S was 33 years old female, married, educated till high school and was youngest among her 6 siblings. She came to Psychiatry Department of Hospital with the complaints of low mood, weeping spells, anger outburst, irritability, muscle tension as well as lack of interest in daily routine activities and disturbed sleep. She was referred to the trainee Clinical Psychologist for P…
Source and Reason For Referral
- The patient came to Psychiatry Department of Hospital, with the complaints of depressed mood, weeping spells, anger outburst, irritability, muscle tension as well as lack of interest in daily routine activities and disturbed sleep. The patient was referred to trainee Clinical Psychologist for the assessment and management.
History of Present Illness
- Patient reported that when her father died in 2000, she became very low and upset. It was a sudden heart attack. She was very close to her father and was unable to overcome the grief. Meanwhile she got married after few days of her father’s death, her marriage was held in simple way. It was difficult for her to cope from that loss as well as manage her marital life. At that time…
Background Information
- Patient’s father died at the age of 60 years with heart attack. She had close relation with her father as compare to her mother. He was humble and compassionate by temperament. Patient reported that her father was very caring and loving towards her which made her stubborn. She was attached with her father. Patient’s mother was 65 years old, illiterate and housewife. She was str…
Preliminary Assessment
- Assessment was done on two levels such as formal and informal way to assess the problematic behavior of patient.
Informal Assessment
- Informal assessment was carried out on following levels 1. Clinical Interview 2. Mental State Examination (MSE) 3. Visual Analogue (Subjective Rating of Symptoms) 4. Functional Analysis of Dysfunctional Thought Record (DTR)
Formal Assessment
- For formal assessment, following scale was done. 1. Beck Depression Inventory (BDI-II) Clinical Interview was conducted to patient in order to gather information regarding her history of present illness and her current complaints, as well as the nature, severity and duration of her symptoms. It was also carried out to get detailed information about her personal history, family history, social …
Visual Analogue
- The patient was asked to rate the presenting complaints during clinical interview. The subject rating was based on 0 – 10 rating scale in which “0” indicates the absence of symptoms, 5 means of moderate severity of symptoms and 10 means extreme severity of symptoms. The purpose of this rating was to assess the severity of presenting complaints of patient before and after the im…
Diagnosis
- According to DSM-V 296.32 (F33.1) Major Depressive Disorder, Moderate, Recurrent episode. Idiosyncratic Case Conceptualization (Beck et al,. 1979)
Popular Posts:
- 1. mywmc patient portal
- 2. followmyhealth patient portal macgregor
- 3. patient portal shore physicians
- 4. anhc patient portal
- 5. brookdale patient portal
- 6. info to set up patient portal
- 7. heart center patient portal huntsville al
- 8. hickman mills clinic patient portal
- 9. coalition health center patient portal
- 10. hans evers patient portal