Patient Portals and the HIPAA Security Rule - Compliancy …
6 hours ago Sep 09, 2019 · Patient Portals and the HIPAA Security Rule. Healthcare providers frequently allow patients to access their electronic health records (EHRs) through a patient portal. Online patient portals allow patients to view their medical records, schedule appointments, and even request refills of prescriptions, anywhere the patient has access to the Internet. Patient portals contain … >> Go To The Portal
Extensive password protection and MFA (multi-factor authentication). Your HIPAA
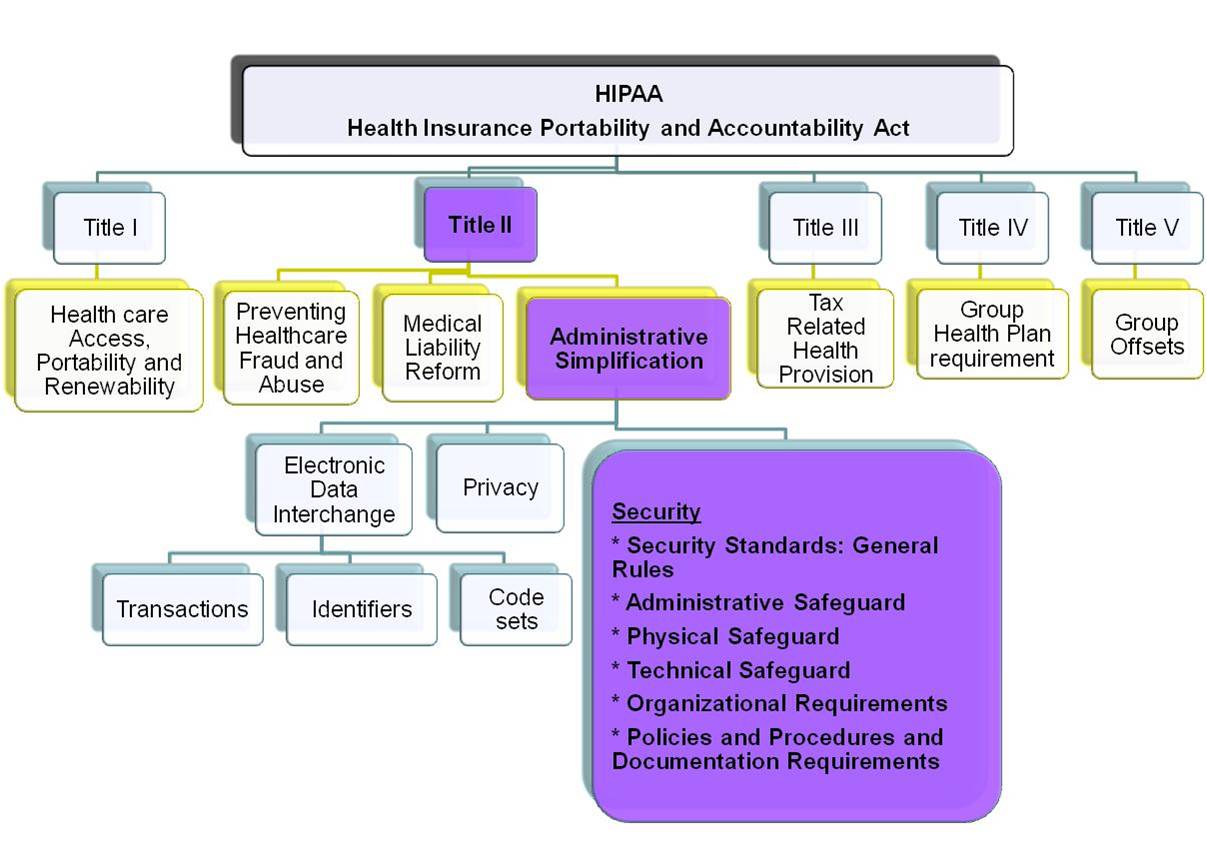
Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act
The Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 was enacted by the 104th United States Congress and signed by President Bill Clinton in 1996. It was created primarily to modernize the flow of healthcare information, stipulate how Personally Identifiable Information maintained by the healthcare and healthcare insurance industries should be protected from fraud and theft, and address lim…
What are the security requirements for a HIPAA compliant portal?
Sep 09, 2019 · Patient Portals and the HIPAA Security Rule. Healthcare providers frequently allow patients to access their electronic health records (EHRs) through a patient portal. Online patient portals allow patients to view their medical records, schedule appointments, and even request refills of prescriptions, anywhere the patient has access to the Internet. Patient portals contain …
What are the HIPAA rules?
HIPAA eCommerce compliance requires patient portals to have strong security and privacy protections to prevent unauthorized access of these confidential PHI records. HIPAA Compliance is Key Failing to adhere to HIPAA standards can result in serious fines. Investing in a HIPAA compliant website can keep your medical business out of trouble.
What are the benefits of a HIPAA portal?
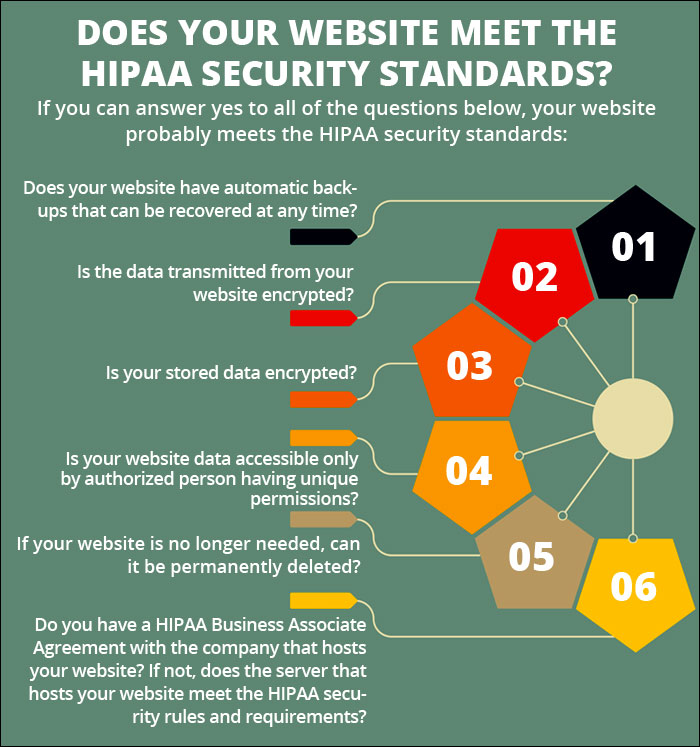
The HIPAA Security Rule includes security requirements to protect patients’ ePHI confidentiality, integrity, and availability. The Security Rule requires you to develop reasonable and appropriate security policies. In addition, you must analyze security risks in your environment and create appropriate solutions.
What are the HIPAA basics for providers in 2021?
Oct 12, 2018 · A HIPAA compliant client portal must secure patient information – which is why a custom HIPAA compliant web hosting portal can be an especially delicate prospect. Below, we explore a recent request our sales team received for such a portal, and how to go about meeting the requirements for a HIPAA compliant client portal.
Are patient portals HIPAA compliant?
Patient healthcare portals help medical practices adhere to HIPAA regulations both by providing patients with easy access to their medical records and by using security measures to protect those records.
How do you secure a patient portal?
These four tips can help organizations bring their patient portal security up-to-date and keep their networks safe from unauthorized access:Automate the portal sign-up process. ... Leverage multilayer verification. ... Keep anti-virus and malware software up-to-date. ... Promote interoperability standards.Oct 16, 2018
What are the 3 types of safeguards required by HIPAA's security Rule?
The HIPAA Security Rule requires three kinds of safeguards: administrative, physical, and technical. Please visit the OCR for a full overview of security standards and required protections for e-PHI under the HIPAA Security Rule.
What security features need to be added to health care databases?
Here we look at what features are required for patient portal security, and the protection and confidentiality of collected health information.Encrypted database features. ... Provide Role-Based Access Control (RBAC). ... Extensive password protection and MFA (multi-factor authentication). ... Audit Trails. ... Consent.More items...•Jun 3, 2020
What are the security issues associated with engaging patients through an online patient portal?
Some of these risks include: reliance on the patient portal as a sole method of patient communication; patient transmission of urgent/emergent messages via the portal; the posting of critical diagnostic results prior to provider discussions with patients; and possible security breaches resulting in HIPAA violations.Mar 1, 2021
What is the advantage of a patient portal for the patient?
The Benefits of a Patient Portal You can access all of your personal health information from all of your providers in one place. If you have a team of providers, or see specialists regularly, they can all post results and reminders in a portal. Providers can see what other treatments and advice you are getting.Aug 13, 2020
What are HIPAA security safeguards?
Safeguards include such actions and practices as securing locations and equipment; implementing technical solutions to mitigate risks; and workforce training. The Privacy Rule's safeguards standard is flexible and does not prescribe any specific practices or actions that must be taken by covered entities.
What are the four safeguards that should be in place for HIPAA?
Technical SafeguardsAccess Control. A covered entity must implement technical policies and procedures that allow only authorized persons to access electronic protected health information (e-PHI). ... Audit Controls. ... Integrity Controls. ... Transmission Security.
What three types of safeguards must health care facilities provide?
What are the three types of safeguards must health care facilities provide? Physical safeguards, technical safeguards, administrative safeguards.
What security considerations need to be made to ensure patient information is secure?
To truly secure patient information you must regularly review your security controls, update policies and procedures, maintain software and security solutions, and upgrade when new, better solutions are developed. There is no single security solution that can be used to secure patient information.Oct 13, 2021
How security of patient information can be enhanced?
Encrypt data Under the HIPAA security rule, patient data should be encrypted whenever possible. ... In many cases, security training can prevent those kinds of breaches, he says. Practices can buy online HIPAA security training or get free training from some hospitals and medical societies.Apr 25, 2017
What does information security entail in healthcare?
2 INFORMATION SECURITY IN HEALTH CARE Information security is the protection of information and information systems from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, disruption, modification or destruction. Information security is achieved by ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of information.
What is HIPAA protected health information?
The HIPAA Privacy Rule protects the privacy of individually identifiable health information, called protected health information (PHI), as explained in the Privacy Rule and here - PDF - PDF. The Security Rule protects a subset of information covered by the Privacy Rule, which is all individually identifiable ...
When was HIPAA released?
HHS developed a proposed rule and released it for public comment on August 12, 1998.
What is the Privacy Rule?
The Privacy Rule, or Standards for Privacy of Individually Identifiable Health Information, establishes national standards for the protection of certain health information. The Security Standards for the Protection of Electronic Protected Health Information (the Security Rule) establish a national set of security standards for protecting certain ...
How long do covered entities have to maintain security policies?
A covered entity must maintain, until six years after the later of the date of their creation or last effective date , written security policies and procedures and written records of required actions, activities or assessments. 30
What is the goal of the Security Rule?
A major goal of the Security Rule is to protect the privacy of individuals’ health information while allowing covered entities to adopt new technologies to improve the quality and efficiency of patient care.
When was the Security Rule published?
The final regulation, the Security Rule, was published February 20, 2003. 2 The Rule specifies a series of administrative, technical, and physical security procedures for covered entities to use to assure the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of e-PHI. The text of the final regulation can be found at 45 CFR Part 160 and Part 164, ...
What is administrative safeguards?
The Administrative Safeguards provisions in the Security Rule require covered entities to perform risk analysis as part of their security management processes. The risk analysis and management provisions of the Security Rule are addressed separately here because, by helping to determine which security measures are ...
What is the HIPAA Privacy Rule?
The HIPAA Privacy Rule gives patients the right to obtain copies of their medical records, treatments and protected health information or PHI. These requirements go further if medical providers want to receive reimbursement from Medicare and Medicaid -- patients must be able to access their records online, download copies and transmit the information to third-party providers. Most medical practices are finding it necessary to develop patient portals where patients and physicians can interact, share information and perform important functions such as practices billing patients and accepting payments online. HIPAA standards rule requires that these patient portals have strong security and privacy protections to prevent unauthorized access of these confidential PHI records.
What are the challenges of implementing HIPAA compliant patient portals?
The challenges of implementing HIPAA compliant patient portals depend on a provider's IT infrastructure and its operating system's complexity and interoperability. There are also the legal and regulatory requirements that include meeting mandatory HIPAA guidelines and voluntary best practices. The challenges of HIPAA compliant portal development include:
How do portals benefit patients?
The benefits of patient portals increase exponentially with each patient who uses one, so encouraging patients and their families to use the portals can strengthen the cost-value and time-saving advantages of the technology. Surveys show that medical practices can optimize portal use by engaging Millennials and Baby Boomers to meet Stage 2 Medicare/Medicaid requirements, but these campaigns can work effectively for all patients. [3] Business concerns necessarily impact each medical practice, but decision-makers can enhance the benefits of adopting patient portals with strong campaigns to encourage patient use. Best practices for optimizing patient use include:
What are patient portals?
Patient portals generate many associated mandatory and medical compliance issues. Practices must consider their business associates and chain-of-trust issues that arise when sending information by electronic transmission. Medical companies deal with insurance companies, Internet service providers, labs, pharmacies, billing and coding services, hospitals and other practices across different medical-related specialties.
What stakeholders are involved in developing a patient portal?
These include the practice's senior leadership, patient advocates in the community, risk management stakeholders like insurers and legal counsel, physicians and clinicians and marketing staffs and health information management professionals who need to sell the benefits of using the patient portal to patients, caregivers and even some staff members who might hesitate to interact with patients electronically. Patient portals enhance communications, and sounding out these stakeholders is essential for developing an effective portal because each will be using the technology at ever-increasing rates.
What is the Privacy Rule?
The Privacy Rule protects PHI held or transmitted by a covered entity or its business associate, in any form, whether electronic, paper, or verbal. PHI includes information that relates to all of the following:
What is the HHS Office of Civil Rights?
The HHS Office for Civil Rights enforces the HIPAA Privacy, Security, and Breach Notification Rules. Violations may result in civil monetary penalties. In some cases, criminal penalties enforced by the
What is breach notification?
Generally, a breach is an impermissible use or disclosure under the Privacy Rule that compromises the security or privacy of PHI. The impermissible use or disclosure of PHI is presumed to be a breach unless you demonstrate there is a low probability the PHI has been compromised based on a risk assessment of at least the following factors:
How to protect PHI?
The Security Rule dictates that there should be protections in place physically, technically, and administratively so that electronic PHI is kept safe. Healthcare plans, providers, and clearinghouses have to do the following: 1 Make sure that all the protected health data they create, store, receive, or send is available, uncorrupted, and kept private. 2 Locate and set up defenses against any elements of the environment that could sabotage the integrity or security of data. 3 Set up protections so that uses or disclosures that are foreseeable and are not allowed under the law do not occur. 4 Make sure that everyone on staff stays compliant with HIPAA.
What is a healthcare professional?
A healthcare professional was researching a client portal solution for her organization. She was setting up a one-stop shop for each of the client facilities through which all users could access a shared docs area, a secure document portal, a navigation area for online resources, and other tools. The executive wanted to build a system that would include content/version management and that could reflect any modifications immediately across several different sites.
Is cloud computing HIPAA compliant?
The HHS considers the use of cloud solutions for the processing and storing of electronic protected health information (i.e. to build any solutions that you need to be HIPAA-compliant) with cloud components as HIPAA-compliant.