7 Core Patient Portal Features You Should Look For ...
7 hours ago Jul 19, 2017 · Patient Portal UI. The Patient Portal UI (patient-portal-ui) is a patient user interface component of Consent2share (C2S) used by the patient to manage his or her health information and consent. Patients can use this application to register, log in, visit their home page, review their health records, conduct consent management activities, and ... >> Go To The Portal
What are the key features of a patient portal?
Jul 19, 2017 · Patient Portal UI. The Patient Portal UI (patient-portal-ui) is a patient user interface component of Consent2share (C2S) used by the patient to manage his or her health information and consent. Patients can use this application to register, log in, visit their home page, review their health records, conduct consent management activities, and ...
Is your patient portal software stand-alone or integrated?
Sep 27, 2018 · Giardina: Our study highlights the need for user-centered design in patient portal design. Identifying patients’ information needs through needs assessments and requirement studies is a first step. However, interfaces must be designed so that the information patients need is presented in a way that is easy to use and easy to interpret.
Are patient-facing IT tools patient portals or applications more effective?
Sep 01, 2017 · To increase use, user-experience, adoption, and functionality, patient portals need to incorporate innovative design and user-friendly features, such as simplified data displays, easy log-in access, and alerts, pings, or notifications that explain results in layman's terms and tell the patient if additional care is needed.
How do I get more patients to use my Portal?
Apr 13, 2022 · Market Leader: athenahealth. Healthcare IT rating agency KLAS recently selected athenahealth’s athenaCommunicator as the #1 patient portal, with a score of 91.8 on the most recent Best in KLAS awards . athenahealth’s suite was also ranked #2 overall for practice sizes from 1-75 physicians. Even though it is part of an integrated system ...
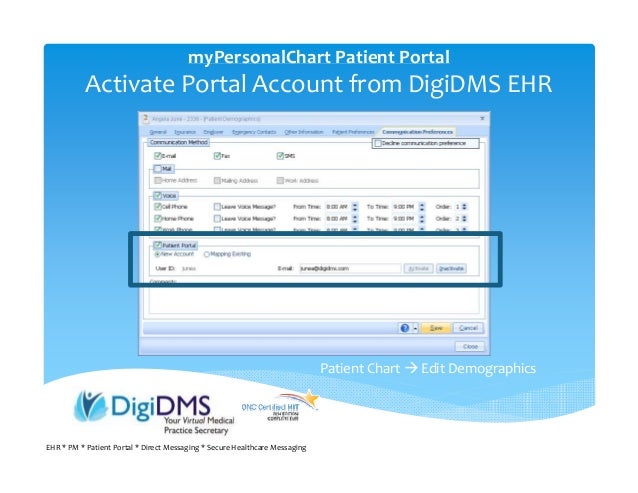
What is patient portal system?
A patient portal is a secure online website that gives patients convenient, 24-hour access to personal health information from anywhere with an Internet connection. Using a secure username and password, patients can view health information such as: Recent doctor visits. Discharge summaries. Medications.Sep 29, 2017
What should be included in a patient portal?
A robust patient portal should include the following features:Clinical summaries.Secure (HIPAA-compliant) messaging.Online bill pay.New patient registration.Ability to update demographic information.Prescription renewals and contact lens ordering.Appointment requests.Appointment reminders.More items...
How do you create a patient portal?
Let's find out how to make a patient portal step-by-step.Identify your target audience. ... Follow your patients' priorities. ... Keep patient portal requirements in mind. ... Evaluate the efficiency of the portal. ... Consider data security concerns. ... Find your software development partner.
What is the difference between EHR and patient portal?
As EMRs have matured, many have offered Patient Portals – web-based ways in which patients can view some of the information contained in their physician's EMR. When a Patient Portal is added to an EMR, it is often then called an EHR. Patient Portals are populated by EMR data, and not updatable by the patient directly.Jul 28, 2009
What are the duties of a portal in hospital?
The Portal Enrollment Specialist uses resources to anticipate, address, and overcome barriers to care and to guide patients through the health care system. Portal Enrollment Specialist may assist patients by updating demographic and pharmacy information.
What are the different types of patient portals?
There are two main types of patient portals: a standalone system and an integrated service. Integrated patient portal software functionality usually comes as a part of an EMR system, an EHR system or practice management software. But at their most basic, they're simply web-based tools.Feb 12, 2021
What is a standalone patient portal?
Standalone Patient Portals Standalone systems usually include more features and do not rely on sunk costs to keep their contracts. Additionally, third-party vendors are often more attentive to detail and offer a better user experience, but they are not without limitations.
What is a portal login?
captiveportallogin requires the user to key in their login details or accept the terms of use before accessing the intended information. The login purpose is to prevent access to the web page until the user has the required information.Jun 17, 2021
How much does it cost to implement patient portal?
Holmes estimates portal costs in the range of $30-$40 per provider per month, on average. Some vendors charge a fee per patient per month. Partly to compensate for this extra cost, some practices charge patients for viewing their own records on the portal.Apr 29, 2015
What is the difference between PHR and patient portal?
The Portal is controlled by the source system (EMR/EHR/Hospital). On the other hand, the Personal Health Record (PHR) is more patient centric, is controlled by a patient or family member, and may or may not be connected to a doctor or hospital (i.e. it may be tethered or untethered).Sep 6, 2012
What's the main difference between a PHR and an EHR?
What's the Difference? Whereas an electronic health record (EHR) is a computer record that originates with and is controlled by doctors, a personal health record (PHR) can be generated by physicians, patients, hospitals, pharmacies, and other sources but is controlled by the patient.
What's the difference between EHR and MPI?
An EMR provides the clinical information about a patient, while the MPI is the index for that data. An MPI typically lists data points about a patient, such as a patient's last name, first name, date of birth, gender, address, phone number, and dates and types of visits to the healthcare organization.”Jun 25, 2007
What is a patient portal?
The Patient Portal UI (patient-portal-ui) is a patient user interface component of Consent2share (C2S) used by the patient to manage his or her health information and consent. Patients can use this application to register, log in, visit their home page, review their health records, conduct consent management activities, and view prior consent decisions.
What is a server module?
The server module runs with some default configuration that is primarily targeted for development environment. It utilizes Configuration Server which is based on Spring Cloud Config to manage externalized configuration, which is stored in a Configuration Data Git Repository. We provide a Default Configuration Data Git Repository.
What prompted you to conduct this research on patient-centered clinical decision support?
Traber Giardina: The patient portal has been heralded as an amazing tool to engage and empower patients. While patient access to their health information is an essential part of patient engagement, data on the usage of these portals from many healthcare organizations shows that this tool is used far less than developers had hoped.
What are the key takeaways from your research and how do they differ from or build upon previous research?
Giardina: Our study highlights the need for user-centered design in patient portal design. Identifying patients’ information needs through needs assessments and requirement studies is a first step. However, interfaces must be designed so that the information patients need is presented in a way that is easy to use and easy to interpret.
What implications do your findings have for the development and dissemination for future patient-centered clinical decision support?
Giardina: Patient portals, specifically the laboratory test result interface, would benefit from rigorous user-centered design to create an easy-to-use and meaningful interface for patients to view test results.
What additional research is needed in patient-centered clinical decision support and how can others build on your research?
Giardina: Patient portal use continues to be low despite increased access to health information. Future research should expand on our findings to thoroughly explore the relationship between patients’ use of patient portals, the perceived usability of the portal interface, and patient’s understanding of the information presented in the portal.
What is a patient portal?
Patient portals are intended to engage patients by giving them access to medical information ; however, if patients are unable to understand the information or the system is not usable, patients will not take advantage of them. Despite several aforementioned drawbacks, apps have used evolving innovative designs to engage consumers and offer unique features and functions that could be translated to patient portal design. For instance, Apple's ResearchKit's Diabetes app pings the user daily to update disease and symptom-related information. Check-in questions or user-friendly alerts in portals could similarly be explored for engaging more patients their health care. Alerts could ask if the patient understands an abnormal result, direct them to helpful resources, and encourage test result follow-up. Finally, test results in the portal need to be easily understood by laypeople or displayed using simplified medical terms. For example, a portal might display elevated cholesterol as "↑LDL cholesterol," or even just display the number without a flag, whereas a health app may label it as “bad cholesterol.”
Who wrote Patient Portals and Health Apps: Pitfalls, Promises, and What One Might Learn from the
This statement accompanies the article Patient portals and health apps: Pitfalls, promises, and what one might learn from the other authored by Jessica L. Baldwin and co-authored by Hardeep Singh, Dean F. Sittig, Traber Davis Giardina and submitted to Healthcare as an Article Type. Authors collectively affirm that this manuscript represents original work that has not been published and is not being considered for publication elsewhere.We also affirm that all authors listed contributed significantly to the project and manuscript. Furthermore we confirm that none of our authors have disclosures and we declare noconflict of interest.
How can information technology improve patient care?
There is growing interest in electronic access to health information and the use of digital data for both disease and health-related tracking. Widespread use of health information technology (IT) could potential ly increase patients’ access to their health information and facilitate future goals of advancing patient-centered care.1 For example, health IT can be used to facilitate information exchange with clinicians and instruct patients when to act upon clinical issues, such as out of range physiologic parameters, follow-up of test results, and complications of medication use. 2 Tools such as personal health records, patient portals, and various mobile health (mHealth) applications (apps) have been developed to help patients engage in their own care. Already, a significant number of patients use health IT; therefore, it is essential that patient-facing health IT be tailored to their needs. In this paper, we discuss two forms of patient-facing health IT tools—patient portals and apps—to highlight how, despite several limitations of each, combining high-yield features of mHealth apps with portals could increase patient engagement and self-management and be more effective than either of them alone. This could potentially improve both patient experience and outcomes related to patient-facing health IT.
What is the use of health information technology?
Widespread use of health information technology (IT) could potentially increase patients’ access to their health information and facilitate future goals of advancing patient-centered care. Despite having increased access to their health data, patients do not always understand this information or its implications, ...
What is the HealthKit app?
In June 2014, Apple announced the HealthKit cloud application programming interface (API) and its partnership with Epic (Verona, WI), an electronic health record vendor who also makes MyChart (a popular patient portal), and the Mayo Clinic (Rochester, MN).
What is Carepaths EHR?
CarePaths EHR is an online (ASP), integrated electronic medical record (EMR) and practice management (PM) system. It is designed for psychiatry, psychology, mental and behavioral health, and social services. Some of the CarePaths'... Read more
What is Jahia DXP?
Jahia DXP is a cloud-based platform that helps businesses monitor customers’ experiences and provide personalized content accordingly. Professionals can use the built-in CMS solution, jContent, to create, store, manage and share e... Read more
What is referral MD?
ReferralMD is a cloud-based fax management software designed to help the healthcare industry manage inbound and outbound faxes from a unified platform . Key features include task assignment, categorization, fax routing and notifica... Read more

Popular Posts:
- 1. smg patient portal nj
- 2. family clinic of oak ridge patient portal
- 3. patient portal weakness
- 4. dr sayal patient portal
- 5. register for navicent patient portal healthelife
- 6. farmington family practice patient portal maine
- 7. rajiv parikh patient portal
- 8. patient portal ohio gastro
- 9. vanguard specialists patient portal
- 10. hospital radio patient report