Know the Signs and Symptoms of Infection | Preventing …
7 hours ago Fever for patients younger than 3 months: An under-the-arm (axillary) temperature of 99.4 degrees F (37.4 degrees C) or higher. Fever is usually a sign of infection; it may be the only sign. (To learn more, see “Do you know…How to take a temperature.”) Coughing or fast breathing; Blisters, rash, or skin sores; Runny nose; Earache; Loose bowels >> Go To The Portal
What should be included in a patient's report of infection?
The patient should report risk factors associated with infection and precautions needed. Patient remains free of infection, as evidenced by normal vital signs and absence of signs and symptoms of infection. Early recognition of infection to allow for prompt treatment.
What are the signs of an infection?
However, in most cases there will be characteristic signs that are indicative of an infection. As mentioned, inflammation is the body’s response to tissue injury. A host of chemicals and immune cells play a role in mediating inflammation. This leads to pain, swelling, heat, redness and sometimes loss of function of the infected area.
How do you know if a patient is free of infection?
Patient remains free of infection, as evidenced by normal vital signs and absence of signs and symptoms of infection. Early recognition of infection to allow for prompt treatment. Patient will demonstrate a meticulous hand washing technique. Nursing Care Plans for Risk for Infection
How do you know if you have an infection after surgery?
Protect: Know the Signs and Symptoms of Infection. Redness, soreness, or swelling in any area, including surgical wounds and ports. Diarrhea. Vomiting. Pain in the abdomen or rectum. New onset of pain. Find out from your doctor when your white blood cell count is likely to be the lowest, since this is when you’re most at risk for infection.
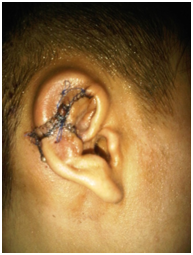
How do you know if you have a bacterial infection?
However, some general symptoms of a bacterial infection include: fever. feeling tired or fatigued. swollen lymph nodes in the neck, armpits, or groin.
What are the symptoms of an infected cut?
Symptoms of an infected cut or wound can include: redness in the area of the wound, particularly if it spreads or forms a red streak.
Why do antibiotics depend on bacteria?
This is because some bacteria may be susceptible to a specific antibiotic, but others may not.
What is the name of the bacteria that causes strep throat?
Strep throat is an infection of the throat caused by a type of bacteria called group A Streptococcus. Symptoms include: sore throat. difficulty swallowing. red or white patches on the back of the throat. headache.
What are the symptoms of food poisoning?
Some types of bacteria that cause food poisoning include Escherichia coli, Listeria, and Salmonella. Symptoms can include: nausea or vomiting.
What are the symptoms of a UTI?
UTI symptoms can include: a burning sensation when urinating. having to urinate frequently. cloudy urine. abdominal cramps.
How do you know if you have a burn?
Symptoms that a burn has become infected include: an increase in pain or discomfort around the affected area. redness in the area of the burn, especially if it begins to spread or form a red streak. swelling or warmth in the affected area. fluid or pus oozing from the burn site. a bad smell around the burn.
What are the causes of infection?
Infections are caused by different biological agents, most of which are living. This includes: 1 Bacteria 2 Protozoa 3 Fungi 4 Viruses
What is the temperature of a fever?
There are instances where the body temperature may be raised even without an infection being present. A fever is defined as a body temperature above 98.6ºF (37°C) but it is usually not considered to be significant until it exceeds 100.4°F (38°C).
What is the effect of inflammation on the immune system?
Inflammation also increases the amount of immune cells at the infected site which can then neutralize the threat, which is useful for infections in particular. Read more about inflammation. The signs of inflammation include: Another feature of an infection that may not always be obvious is loss of function.
What does it mean when you feel unwell?
Malaise is a general feeling of being unwell. It occurs with most types of systemic infections but is less common with localized infections, unless the infectious agent and/or its toxins enter the bloodstream. Malaise is not a realiable sign of an infection as it occurs with many other non-infectious diseases. Therefore malaise should be considered in conjunction with other signs of an infection, like a fever and the signs of inflammation.
What is pus in the body?
Pus. Pus is the fluid composed of cellular debris, dead and living microbes, the body’s immune cells, sometimes blood and fluid from the site of the infection. It is not always present or detectable but is commonly seen with infections on the skin surface that have not been properly treated in the early stages.
Can inflammation be localized?
This causes the sensation of pain that it typically felt with inflammation anywhere in the body. All of these symptoms may be localized when the infection is isolated to one area of the body or it may be generalized if the infection is throughout the body (systemic).
Is inflammation a response to infection?
This is the body’s response to tissue damage and it is intended to minimize any further damage or tissue death. Inflammation is not specific to infections. It can occur with any tissue injury, such as a physical, electromagnetic or chemical injury.
What are the symptoms of a low white blood cell count?
Loose bowels. Sore throat. Stomach pain. Sores or pain around the rectum. Headache and stiff neck. If your child develops an infection while his white blood cell count is low, the usual warning signs such as pus (or drainage), redness, and swelling may not always be present.
What temperature is fever?
An under-the-arm (axillary) temperature of 99.4 degrees F (37.4 degrees C) or higher. Fever is usually a sign of infection; it may be the only sign. (To learn more, see “ Do you know…How to take a temperature .”) Coughing or fast breathing. Blisters, rash, or skin sores.
Common Signs and Features by Organ System
Dennis Sifris, MD, is an HIV specialist and Medical Director of LifeSense Disease Management. James Myhre is an American journalist and HIV educator.
General Symptoms
Whenever an infection is established, the body's first-line response is inflammatory. Inflammation is the body's way of defending itself against disease while promoting the healing of affected tissues. Inflammation is characterized by five cardinal signs: redness, swelling, heat, pain, and the temporary loss of tissue function. 1
Respiratory Tract
The respiratory tract is the passage through which air passes from the mouth and nose to the lungs. An infection can develop in the upper respiratory tract (involving the sinuses, nasal passages, pharynx, and larynx) or the lower respiratory tract (involving the trachea and the bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli of the lungs).
Urinary Tract
The urinary tract is the system through which urine is excreted from the body and includes two kidneys, two ureters, a bladder, and a urethra. A urinary tract infection (UTI) affects any part of this system, including urethritis (infection of the urethra), cystitis (bladder infection), or acute pyelonephritis (kidney infection). 4
Brain and Spinal Cord
The central nervous system (CNS) is comprised of the brain and spinal cord. Infections of the CNS typically involve the brain ( encephalitis) or the protective membrane around the brain and spinal cord ( meningitis ). 5
Blood
Bloodstream infections are most commonly associated with bacteria ( bacteremia ). They often develop as a secondary infection to pneumonia, meningitis, or cellulitis, or when bacteria enter the bloodstream during surgery or intravenous drug use. 6
Liver
Liver infections are primarily viral in nature, caused by the viruses hepatitis A, B, C, D, or E. Some acute hepatitis infections resolve on their own without treatment. Others may become chronic and lead to progressive liver injury (particularly with hepatitis B and hepatitis C ). 8
What is the most common sign of a wound infection?
Here are some of the most common signs and symptoms associated with a wound infection: 1. Fever . After surgery, it is common for patients to run a low-grade fever of under 100 degrees Fahrenheit. However, if the fever goes to 101 or above and persists, that can indicate a possible wound infection.
Why is my wound red?
Initially, wounds appear slightly red because of the natural inflammatory process of healing, but that redness should gradually decrease in approximately 5-7 days. A deeper redness around the wound that continues to expand and worsen is a sign of wound infection.
What does it mean when a wound drains clear?
If the drainage becomes purulent with a pungent or foul odor it can indicate an infection.
Why does my wound feel warm?
Although it can be normal for skin surrounding a wound to feel somewhat warmer, when the skin around the incision feels very warm to the touch and doesn't start cooling down, that can indicate that the body is mounting a campaign against an infection.
Can a fever cause headaches?
Patients who are running a fever may also have headaches and decreased appetite. Contaminated or infected wounds may benefit from antimicrobial dressings. 2. Feeling of Overall Malaise. Asking a patient how they feel can be an important part of assessing for wound infection.
Is wound infection a pathogen?
Whether a pathogen creates a wound infection is highly dependent on the strength of the individual’s immune system. Risks are increased when the wound is in a high-bacteria area of the body, the patient has a chronic condition such diabetes or vascular disease, or poor or inconsistent wound care is provided. Because surgical wound infection is one of the most common hospital-acquired conditions and has become a significant cause of morbidity and mortality, recognizing and treating wound infection need to be primary management objectives for health care professionals.
What to do if you have an infection?
Your surgeon can provide antibiotics and any other therapies that are necessary to prevent the infection from spreading.
What is the fever after a syringe?
A fever can also decrease your appetite, lead to dehydration and a headache. A low-grade fever (100 F or less) is common in the days following surgery. 5 A fever of 101 or more should be reported to the surgeon.
What does it mean when an infected incision is hardening?
Swelling/hardening of the incision: An infected incision may begin to harden 8 as the tissue underneath are inflamed. The incision itself may begin to appear swollen or puffy as well.
Why does my incision feel hot?
Hot incision: An infected incision may feel hot to the touch. 7 This happens as the body sends infection-fighting blood cells to the site of infection. Proper care of your surgical incision plays a significant role in preventing infection.
What happens to a patient after surgery?
Infection delays healing, can increase scarring and can lead to a much longer recovery for the patient. Infection means more pain, and in the worst cases, hospitalization.
Can you get an infection in a catheter?
It is possible to develop an infection in a location other than your incision after surgery. Urinary tract infections are common after surgery, especially in patients who had a urinary catheter during or after their procedure. 1 .
Can a urinary tract infection be life threatening?
Life-threatening infections can start with a very small area of infection, such as an infected tooth or even a small wound on the skin. A urinary tract infection can also become sepsis, an infection that begins to spread through the bloodstream.
Why are surgical infections monitored?
Surgical infections are monitored by Public Health England, so that policies can be changed and improved if needed. There are a number of things you can do yourself to reduce your chances of infection.
Why are open wounds more likely to get infected?
This is because the break in the skin provides a route for the germs to travel from the outside to the inside. Some circumstances make it more likely that wounds will become infected. These include: If you have diabetes type 1 or type 2.
How to keep germs away from a wound?
Use an antiseptic around the wound area to help keep the germs away. Put a clean dressing over your wound to protect it from germs. Do not use gauze or a type of dressing which will stick to the wound. Your pharmacist should be able to advise you if the wound is too big for an ordinary plaster.
How to tell if you have a swollen skin?
Look red around the skin edges. This red area may feel warm or hot. Look swollen. Ooze a yellow material (pus) which may be smelly. If the infection spreads further, the redness will keep spreading to more areas of skin. You may feel unwell in yourself, with a temperature and aches and pains.
What antibiotics are used for wounds?
If the wound and/or area of infection are small then an antibiotic cream such as fusidic acid may be prescribed. If the wound is larger, or the infection seems to be getting worse, then an antibiotic to be taken by mouth (oral antibiotic) is needed.
Can a wound be infected?
Infected Wounds. Infection can develop in any type of wound. Wounds can be surgical (a cut made during an operation) or due to trauma. Traumatic wounds could be a result of falls, accidents, fights, bites or weapons. They may be cuts, lacerations or grazes.

Popular Posts:
- 1. metro family fitness patient portal san diego
- 2. forrest city medical center patient portal
- 3. greenway medical associates patient portal boone, nc
- 4. unm health patient portal
- 5. fort sanders perinatal center patient portal
- 6. my sanita patient portal
- 7. patient portal for dr todd sheppard, petoskey
- 8. tol patient portal.
- 9. hippa patient privacy breach incident report georgia
- 10. oregon state university patient portal