Meaningful Use and the Patient Portal: Patient enrollment ...
17 hours ago Oct 31, 2016 · Outside of the benefits to the patient, implementation of patient portals had come to the attention of healthcare providers due to the inclusion of Meaningful Use of objectives centered on the use of patient portals and electronic engagement with patients. Stage 3 requirements are still being explored and the impact it will have on Health Centers is unknown. >> Go To The Portal
Stage 2 Meaningful Use requirements call for providing patients with clinical summaries, patient-specific education support, secure messaging tools, follow-up care or preventive health reminders, and access to their medical records. When developing a patient portal, it is useful to have interactive features that are relevant to patient needs.
How do you benefit from your patient portal?
Oct 31, 2016 · Outside of the benefits to the patient, implementation of patient portals had come to the attention of healthcare providers due to the inclusion of Meaningful Use of objectives centered on the use of patient portals and electronic engagement with patients. Stage 3 requirements are still being explored and the impact it will have on Health Centers is unknown.
How to get your patients to use your patient portal?
Many physicians are adopting patient portals in response to governmental incentives for meaningful use (MU), but the stage 2 requirements for portal use may be particularly challenging for newer electronic health record (EHR) users. This study examined ...
What are the benefits of a patient portal?
Nov 10, 2014 · Meaningful Use and Patient Portals. In order to qualify for CMS Meaningful Use Stage 2 incentives, eligible providers need to ensure that at least 5% of their patients use the provider’s “patient portal.”. This means that patients must send an online message to their clinician, or patients need to view, download or transmit health ...
What is the value of a patient portal?
Mar 26, 2015 · Stage 2 Meaningful Use requirements call for providing patients with clinical summaries, patient-specific education support, secure messaging tools, follow-up care or preventive health reminders,...

What is the purpose of patient portal?
A patient portal is a secure online website that gives patients convenient, 24-hour access to personal health information from anywhere with an Internet connection. Using a secure username and password, patients can view health information such as: Recent doctor visits.Sep 29, 2017
What safeguards are in place for patient portals?
Patient portals have privacy and security safeguards in place to protect your health information. To make sure that your private health information is safe from unauthorized access, patient portals are hosted on a secure connection and accessed via an encrypted, password-protected logon.
How would you encourage patients to use patient portal?
How to get patients to sign up for a patient portalEnroll at the first appointment. ... Auto-enroll to schedule online appointments. ... Include a link to the portal when patients sign in. ... Link your portal sign up on all correspondence. ... Optimize for desktop and mobile. ... Empower all staff to sign patients up. ... Offer incentives.More items...•Aug 12, 2019
What does patient portal contain?
A patient portal is a website for your personal health care. The online tool helps you to keep track of your health care provider visits, test results, billing, prescriptions, and so on. You can also e-mail your provider questions through the portal. Many providers now offer patient portals.Aug 13, 2020
What are the pros and cons of patient portals?
What are the Top Pros and Cons of Adopting Patient Portals?Pro: Better communication with chronically ill patients.Con: Healthcare data security concerns.Pro: More complete and accurate patient information.Con: Difficult patient buy-in.Pro: Increased patient ownership of their own care.Feb 17, 2016
What is the goal of HIE?
The purpose of HIE is to promote the appropriate and secure access and retrieval of a patient's health information to improve the cost, quality, safety and speed of patient care.
What should be done when setting up a patient portal to ensure it meets the needs of all patients?
3.1 Ensure portal access for all patientsOffer your patient portal in multiple languages.Make sure your portal is mobile-friendly, and that the pages load quickly, so that users with limited data or slow connections can still access it.More items...•Apr 17, 2019
How can patient compliance with portal registration be increased?
Hang posters in the office that promote the portal and include a QR code at the bottom, so patients can quickly navigate to the portal on their smartphones. Place printed portal instructions in your waiting room for patients to browse, which can prompt them to register while waiting.
What is meaningful use?
'Meaningful Use' is the general term for the Center of Medicare and Medicaid's (CMS's) electronic health record (EHR) incentive programs that provide financial benefits to healthcare providers who use appropriate EHR technologies in meaningful ways; ways that benefit patients and providers alike.
What makes the patient portal different from a PHR?
The Portal is controlled by the source system (EMR/EHR/Hospital). On the other hand, the Personal Health Record (PHR) is more patient centric, is controlled by a patient or family member, and may or may not be connected to a doctor or hospital (i.e. it may be tethered or untethered).Sep 6, 2012
What are the different types of patient portals?
There are two main types of patient portals: a standalone system and an integrated service. Integrated patient portal software functionality usually comes as a part of an EMR system, an EHR system or practice management software. But at their most basic, they're simply web-based tools.Feb 12, 2021
What is a well designed patient portal?
Well-designed patient portals, when combined with policies that promote use, offer significant opportunity for patients to engage in their healthcare. Without proper management, portals can suffer from decreased use and poor support from providers. In this work, we discuss the patient portal policies that govern account registration and management, shared access, and test result reporting at VUMC. We anticipate that other organizations can implement concepts from our policies to support the meaningful use of patient portals.
What is a patient portal?
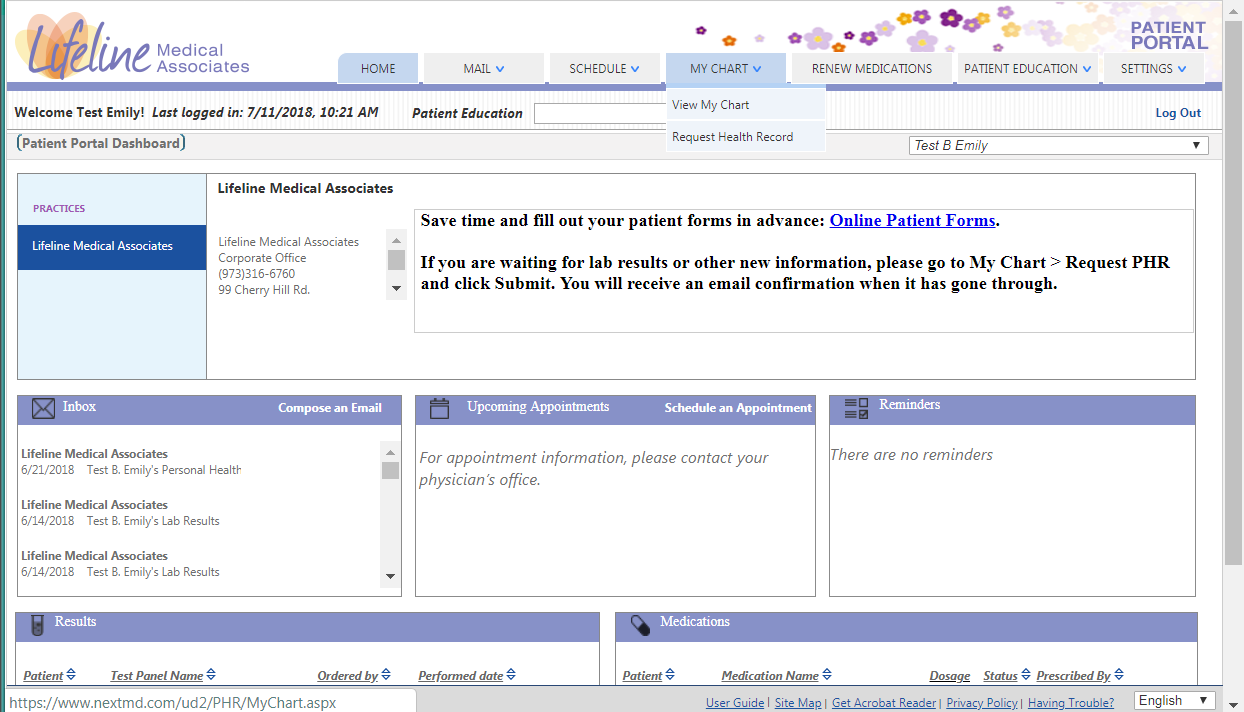
Patient portals are web- and mobile-based programs that allow patients and their proxies remotely to interact with healthcare systems and their care providers. 1–3 These portals commonly allow users to view selected information from the electronic health record (EHR), review test results, message providers, schedule appointments, and pay medical bills. 4 A report by the Institute of Medicine specifies online access to personal health records, such as patient portals, as a promising technology to support patient engagement. 5 Functionality delivered through patient portals has been shown to improve chronic disease management, increase adherence to preventive care such as immunizations and screening, improve patient satisfaction, and better outcomes for some patients with chronic disease. 6–14
What is MHAV in Vanderbilt?
My Health at Vanderbilt (MHAV) is an institutionally developed patient portal which launched in a limited fashion in 2003 before being more widely deployed throughout all clinical specialties starting in 2007 ( Figure 1 ). The VUMC informatics, legal and operational teams internally established policies and procedures to govern MHAV use by patients, proxies, and healthcare providers. The initial policies are described by Osborn et al. 29 MHAV and its associated EHR were certified for Meaningful Use stages 1 and 2. MHAV supports core functionality similar to those of other patient portals, including secure messaging, appointment scheduling, bill management, access to select laboratory results, and access to select EHR data. 29,32 There were incremental changes to usage logging and functionality throughout the duration of continuous use.
What is proxy access?
Proxy access is defined as an access class in which one individual receives access to another individual’s protected health information, communication tools, and functions in MHAV. In all cases, the proxy had to meet the eligibility criteria outlined in the table, even if the patient did not. Individuals could serve as proxies for competent adult patients, patients who were children or adolescents, and adult patients who met legal criteria for lacking the capacity to make medical decisions. VUMC policy distinguished two general categories of proxies: delegates and surrogates. The policy defined delegates as “an adult individual invited by a MHAV account holder to have access to that account holder’s MHAV account,” and stipulated that the account holder be a competent adult. For example, a competent adult may invite her spouse, adult friend, and adult child aged 18 or older to have delegate access to her account.
Background and Significance
- Patient portals are web- and mobile-based programs that allow patients and their proxies remotely to interact with healthcare systems and their care providers.1–3 These portals commonly allow users to view selected information from the electronic health record (EHR), review test results, message providers, schedule appointments, and pay medical bills.4 A report …
Methods
- Study site
Vanderbilt University Medical Center (VUMC) is a private, nonprofit, and academic healthcare center located in Middle Tennessee. VUMC includes the 758-bed Vanderbilt University Hospital (VUH) and the 267-bed Monroe Carrell Jr. Children’s Hospital at Vanderbilt (MCJCHV). VUH rece… - My Health at Vanderbilt
My Health at Vanderbilt (MHAV) is an institutionally developed patient portal which launched in a limited fashion in 2003 before being more widely deployed throughout all clinical specialties starting in 2007 (Figure 1). The VUMC informatics, legal and operational teams internally establi…
Results
- Policy on patient access and registration
During the period covered by this review, My Health at Vanderbilt was made available to all competent adults age 18 and older, regardless of whether they had an established relationship with a Vanderbilt site (ie, whether they had a medical record number). With permission from a pa… - Proxy and nonpatient access
The access policy also allowed a number of proxy access classes to account for diverse ways that family members or other caregivers support individuals receiving health care. Proxy access is defined as an access class in which one individual receives access to another individual’s protec…
Discussion
- Patients are increasingly interested in accessing their personal health data through the patient portal.4,24,34 There remains a need to understand how portal policies can enable use and promote engagement.13 Previous studies have found evidence supporting patient portal use and improved chronic disease management, improved patient satisfaction, and improved outcomes…
Conclusion
- Well-designed patient portals, when combined with policies that promote use, offer significant opportunity for patients to engage in their healthcare. Without proper management, portals can suffer from decreased use and poor support from providers. In this work, we discuss the patient portal policies that govern account registration and management, shared access, and test resul…
Contributorship Statement
- BS, JW, and TR conceived the study idea and design. BS, JC, BC, GS, and TR retrieved and described relevant policy information. BS and JW conducted quantitative data analysis. All authors participated in writing and reviewed the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Popular Posts:
- 1. bedside shift report implications for patient safety and quality of care
- 2. dr jerry tracy patient "portal"
- 3. aetna dental patient portal
- 4. insignia patient portal
- 5. clinical benefits of patient portal
- 6. community of hope family health and birth center patient portal
- 7. columbus regional healthcare system patient portal
- 8. port orange imaging patient portal
- 9. lowell general patient portal
- 10. arizona ob-gyn patient portal