Medication Therapy Management | CMS
22 hours ago · Medication Therapy Management. This section contains information related to Part D Medication Therapy Management (MTM) Program requirements and information. Requirements for Medication Therapy Management (MTM) Programs: Under 423.153 (d), a Part D sponsor must have established a MTM program that: Ensures optimum therapeutic outcomes … >> Go To The Portal
What is included in the MTM document?
To ensure that the MTM definition was inclusive of the types of services and programs that are or can be provided in diverse pharmacy practice segments To include in the MTM document a description of examples of services that can be implemented by a majority of pharmacy practitioners
What is an example of an MTM recommendation?
The recommendations that occur in the course of the MTM must be communicated to other members of the patient’s healthcare team to ensure continuity of care and the realization of positive outcomes. Examples of this type of action may include: Referral to another pharmacist who is a Certified Diabetes Educator for targeted education. 9
What is an MTM encounter in pharmacy?
During an MTM encounter 6, the pharmacist uncovers and itemizes medication-related problems that may be amenable to an outside referral. A pharmacist may intervene on behalf of the patient to facilitate hand-off to the professional most suited to manage the identified problem.
What is MTM in cardiovascular disease prevention?
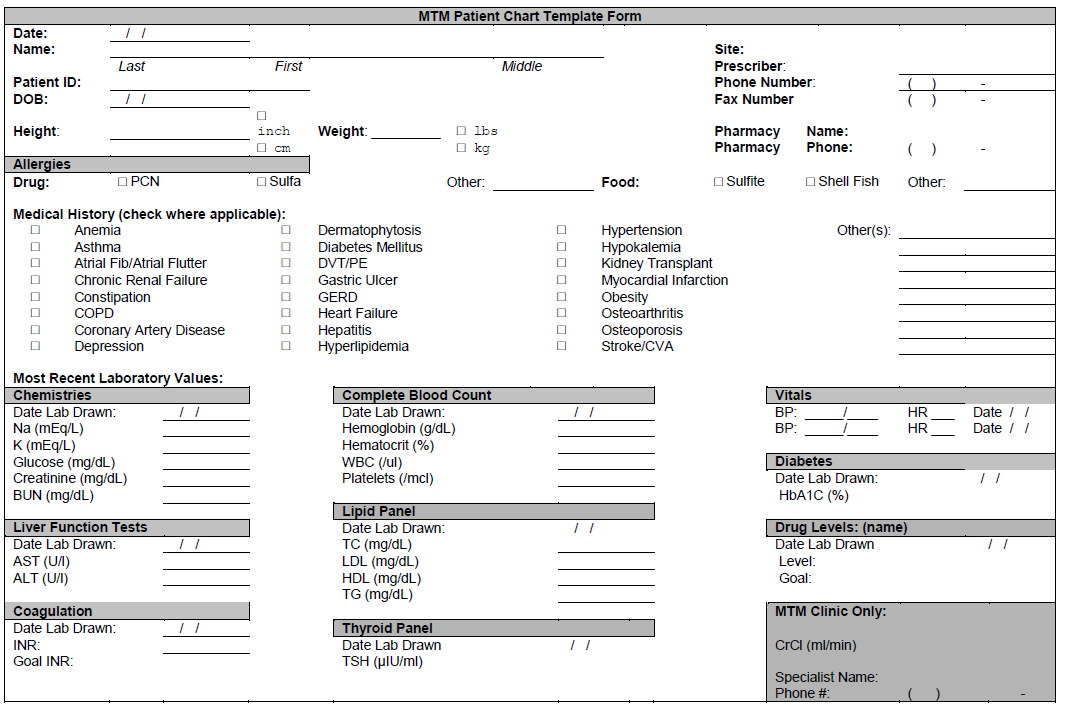
MTM includes five core elements: medication therapy review, a personal medication record, a medication-related action plan, intervention or referral, and documentation and follow-up. Within the context of cardiovascular disease (CVD) prevention, MTM can include a broad range of services, often centering on the following:
What are the 5 components of MTM?
MTM includes five core elements: medication therapy review, a personal medication record, a medication-related action plan, intervention or referral, and documentation and follow-up.
What is the main purpose of MTM?
The goal of MTM is to optimize the therapeutic outcomes of an individual patient as well as detect and prevent costly medication related adverse events.
What are the roles of the pharmacists in medication therapy management MTM )?
Pharmacists provide medication therapy management to help patients get the best benefits from their medications by actively managing drug therapy and by identifying, preventing and resolving medication-related problems.
What is the name of the legislation that required MTM services to be a part of Medicare Part D?
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PL 111-148) authorized grants for “medication management services” in all practice settings (Section 3503), noting that such services will help manage chronic disease, reduce medical errors, and improve patient adherence to therapies while reducing acute-care costs and ...
How do you conduct a MTM?
Ten Tips for MTM successTalk to other healthcare providers. ... Provide incentives. ... Get the staff involved. ... Think about the patient. ... Document, document, document. ... Communicate well. ... Market MTM. ... Take advantage of technology.
What is a factor when determining a patient's eligibility for MTM?
The Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (PPACA) laid out a set of MTM eligibility criteria for eligible entities to target patients for MTM services: “(1) take 4 or more prescribed medications …; (2) take any 'high risk' medications; (3) have 2 or more chronic diseases… or (4) have undergone a transition of care ...
What information is required when documenting a typical adherence claim?
When documenting an adherence claim, the pharmacist will be required to provide the patient-specific barriers that led to the non-adherence. During an Education and Monitoring intervention, a pharmacist provides counseling and follow-up for a new or changed prescription or OTC medication.
What are the correct steps to take during the production process CVS?
Acquire the Prescription label.Obtain the Medication.Perform Accuracy scan.Choose container.Count, pour, and dispense medication.Prepare for final verification.
What is patient medication management?
It ensures ongoing safe and effective use of medicines at all stages of the medication management pathway, including at the point of prescribing, dispensing and administering a medicine.
What is the map portion of a medication therapy review MTM?
Medication-related Action Plan (MAP) The MAP does not include problems to be referred out to other members of the patient's healthcare team. The patient and pharmacist complete this portion together and include action steps for the patient.
What are the 4 phases of Medicare Part D coverage?
Throughout the year, your prescription drug plan costs may change depending on the coverage stage you are in. If you have a Part D plan, you move through the CMS coverage stages in this order: deductible (if applicable), initial coverage, coverage gap, and catastrophic coverage.
Which of the following is an important distinction between MTM services?
Which of the following is an important distinction between MTM services and disease management programs? Disease management programs focus on a specific disease rather than the patient's overall health concerns.
What is MTM in pharmacy?
MTM is especially effective for patients with multiple chronic conditions, complex medication therapies, high prescription costs, and multiple prescribers. MTM can be performed by pharmacists with or without a collaborative practice agreement (CPA), and it is a strategy that can be considered to straddle Domain 3 (health care system interventions) ...
What is medication management?
Medication therapy management (MTM) is a distinct service or group of services provided by health care providers, including pharmacists, to ensure the best therapeutic outcomes for patients. MTM includes five core elements: medication therapy review, a personal medication record, a medication-related action plan, intervention or referral, ...
Is MTM effective for pharmacists?
Strong evidence exists that the use of MTM by pharmacists is effective. Although the exact combination of MTM activities tends to vary between settings, studies examining MTM have generally found it to be effective and to have strong internal and external validity.
What is MTM in medical terminology?
To describe events leading to development of a profession-wide consensus definition of medication therapy management (MTM) and attendant programs and services and present the document (definition, services, and program requirements) resulting from the process.
What is MTM in pharmacy?
Medication Therapy Management (MTM) Following the late 2003 passage of the Medicare Prescription Drug Improvement and Modernization Act, the pharmacy profession had a need to act quickly to define MTM so that a consensus definition would be available as regulations implementing the Medicare Part D benefit were being written.
What is MTM services?
Through the extraordinary efforts of the numerous organizations and participants, the MTM Services Definition is one that is applicable within diverse pharmacy practice segments, whose services are feasible for a majority of practitioners to implement, and whose elements are supported by a profession-wide consortium of 11 national professional pharmacy organizations.
What is medication management?
Definition. Medication Therapy Management is a distinct service or group of services that optimize therapeutic outcomes for individual patients. Medication Therapy Management services are independent of, but can occur in conjunction with, the provision of a medication product.
What is the role of a pharmacist in MTM encounter 6?
During an MTM encounter 6, the pharmacist uncovers and itemizes medication-related problems that may be amenable to an outside referral. A pharmacist may intervene on behalf of the patient to facilitate hand-off to the professional most suited to manage the identified problem. The recommendations that occur in the course of the MTM must be communicated to other members of the patient’s healthcare team to ensure continuity of care and the realization of positive outcomes.
What is a PMR in a MTM appointment?
6 The PMR contains an up-to-date list of medications that helps a patient manage their pharmacotherapy. Throughout the MTM process, the pharmacist should generate the document using the information provided by the patient. The patient may also generate it with the help of the pharmacist. It may be electronic or manually generated.
What is MTM 4?
The APhA consensus definition of MTM 4 is: Medication Therapy Management is a distinct service or group of services that optimize therapeutic outcomes for individual patients. Medication Therapy Management services are independent of, but can occur in conjunction with, the provision of a medication product.
What is MTR in pharmacy?
The goal of MTR is to identify and prioritize medication-related problems. MTR is a person-to-person consultation between the pharmacist and the patient. The pharmacist spends dedicated time reviewing the information provided by the patient and provides medication education while addressing other concerns as needed.
What is a medication therapy review?
A Medication Therapy Review (MTR) is the systematic process of reviewing a patient’s medication list and collecting other medical history, including the current problem list, treatment history, social history, over-the-counter (OTC) medications or supplements, adverse medication reactions, adherence history, and any subjective concerns.
What is a medication-related action plan?
Medication-related Action Plan (MAP) The pharmacist includes medication-related problems that they can address in their scope of practice in the MAP. 6 The MAP does not include problems to be referred out to other members of the patient’s healthcare team.
What is Medication Therapy Management: Defining MTM
So, what is MTM? Let's look at how some organizations and publications define medication therapy management.
The Core Components of Medication Therapy Management
Generally speaking, medication therapy management includes five core elements:
The Problems With Medication Therapy Management
On the surface, medication therapy management may seem like a good service to offer and provide to patients. But once you dig a little deeper, flaws begin to emerge.
Comprehensive Medication Management: A More Effective Way to Help Patients
What is comprehensive medication management? We like this explanation from an American Association of Colleges of Pharmacy article: "CMM is a patient-centered approach to optimizing medication use and improving patient health outcomes that is delivered by a clinical pharmacist working in collaboration with the patient and other healthcare providers.".
Tech-Enabled Comprehensive Medication Management: An Even Better Way
Organizations looking to deliver stronger care and further maximize the benefits of comprehensive medication management can now pair the CMM process with supporting technology, i.e., technology-enabled comprehensive medication management. Cureatr's CMM service powered by Meds 360° works as an extension of an organization's care team.
How to take advantage of MTM opportunities?
To take advantage of the available MTM opportunities, pharmacies and other entities seeking to become authorized MTM Centers must first complete a network participation agreement. Retail Pharmacy: Most retail pharmacies are contracted via their parent chain organization or their PSAO.
How many patients does OutcomesM cover?
Contracted with more than 50 U.S. health plans, OutcomesMTM ® provides MTM coverage to more than 8.5 million patients. We link more than 100,000 local chain, independent, clinic and health system pharmacists with contracted plans across the country.
What is MTM in healthcare?
MTM encourages patients to be active participants in their health care, empowering them to be more knowledgeable about and responsible for their health and medication use. MTM services facilitate a more effective partnership among patients, their pharmacists, physicians, and other health care providers to achieve optimum medication therapy results.
Is Medicare Part D a MTM?
As currently structured, Medicare Part D prescription drug plan incentives are misaligned for providing robust MTM services. While MA-PD plans may immediately benefit from MTM services through a reduction in overall health care costs (e.g., medical visits & hospitalizations) for which they are at risk in addition to medications, stand-alone PDPs have minimal incentive to offer comprehensive MTM programs that offer the most beneficial outcomes for patients.x Pharmacist-provided MTM often improves adherence and compliance with established medication regiments and treatment guidelines, thus potentially increasing medication consumption, and costs, while decreasing overall health expenditures. PDPs that are at risk only for the costs of beneficiaries’ drug expenditures may be hesitant to provide a robust MTM program that could adversely impact their bottom line, despite the overall benefit for the patient and for the health care system.
What Is a Medical Summary Report?
A medical summary report is a document that holds all the information that doctors, nurses or anyone working in hospitals would need. A summary of the important information that doctors use to avoid wasting time on reading the whole paper.
How to Write a Medical Summary Report?
How do you begin with your medical summary report? That has always been the question. If you think writing a medical summary report is difficult, there are some easy ways for you to do one. However, in general, a medical summary report only gets difficult if you have to fill in the blanks of your summary report.
What is a medical summary report?
A medical summary report is a document used by doctors, nurses or anyone working in the medical field that holds the summarized information of a patient.
What is the purpose of doing a medical summary report?
As it is not common for people in the medical field to waste time reading the whole information, a medical summary report gives out the shortened and important details.
What should be avoided when writing a medical summary report?
There are a lot of things that should be avoided, one important thing is to watch your tone and words when writing the report.
Do all doctors and nurses use a medical summary report?
This depends on the doctors and nurses, but the majority often use medical summary reports to shorten the report by taking away the information that may not be as important.
Why is it necessary to place the medical history of a patient in the summary report?
The purpose of writing a medical summary report is to take out the unnecessary information and leave the important ones. For a patient’s medical history, that is important for doctors so they could give out a proper diagnosis.