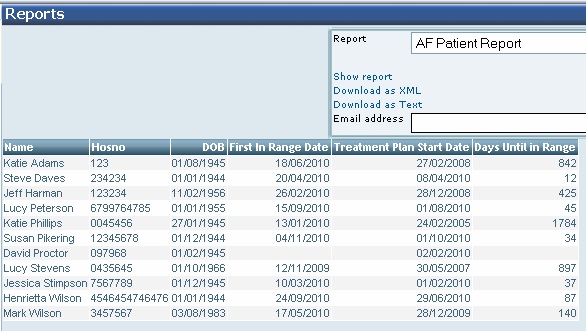
Falls Dashboard | Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality
21 hours ago This dashboard details the extent of harm due to falls, the presence of fall assistance, presence of fall assistance by patient harm, type of fall injury, and fall location. Selecting one of the options in the top table below will display a related figure and table. This information can also be downloaded as an Excel file from the links in the ... >> Go To The Portal
The mechanism for recording and reporting a patient fall will vary depending on the state and the in-house mechanism the healthcare facility uses. Generally, mishaps such as falls are recorded in an incident report. After the fall, a nurse and a medical provider will likely perform an examination of the patient and document their findings.
Full Answer
How is a patient Fall recorded and reported?
The mechanism for recording and reporting a patient fall will vary depending on the state and the in-house mechanism the healthcare facility uses. Generally, mishaps such as falls are recorded in an incident report. After the fall, a nurse and a medical provider will likely perform an examination of the patient and document their findings.
What happens when a patient falls in the hospital?
They may faint, they may have a seizure, or they may have a heart attack or a stroke. Behavioral Falls: These are falls that happen because a patient becomes unruly or acts out for one reason or another.
What happens if a medical provider fails to prevent a fall?
It could also include failing to diagnose conditions, like a stroke or a seizure, that could lead to falling. In these cases, a medical provider may have broken or violated the appropriate standard of care, because they failed to address conditions that led to a fall or failed to take the necessary precautions to prevent a fall from occurring.
Where can I find forms for data collection from patient falls?
Forms for data collection are available on the NDNQI website: Select Facility → Select Unit → Patient Falls → Documents → Patient Falls Data Collection Form. Forms for data collection may be modified to collect additional facility specific data.
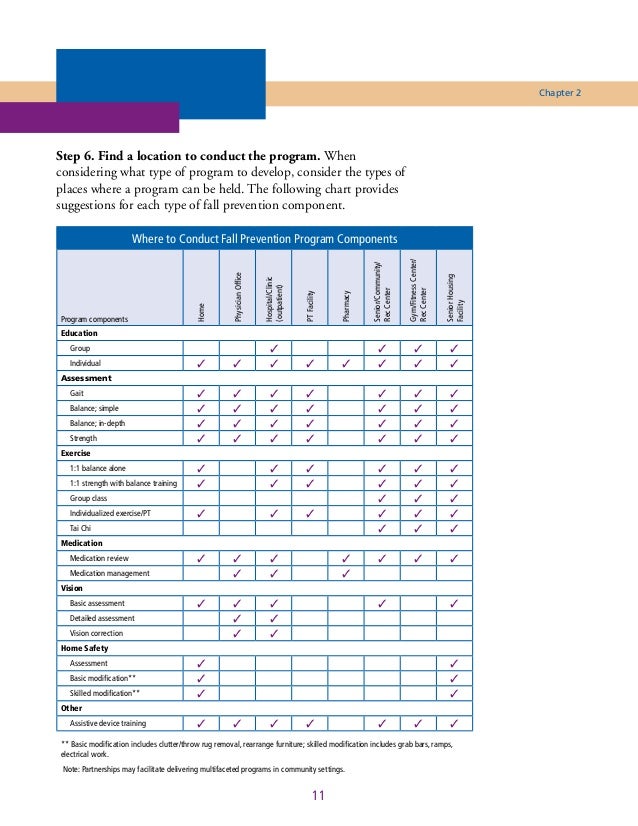
How do you document a patient fall?
Start by asking the patient why they think the fall occurred and assess associated symptoms, and then check the patient's vital signs, cranial nerve, signs of skin trauma, consciousness and cognitive changes, and any other pain or points of tenderness that could have resulted from the fall.
How do you evaluate patient falls?
During an assessment, your provider will test your strength, balance, and gait, using the following fall assessment tools:Timed Up-and-Go (Tug). This test checks your gait. ... 30-Second Chair Stand Test. This test checks strength and balance. ... 4-Stage Balance Test. This test checks how well you can keep your balance.
How do hospitals collect data on patient falls?
Some hospitals have electronic incident reporting systems that will make it easier to count the number of falls that have occurred on your unit or in your hospital. ). This will take you to the document Guidelines for Data Collection on the American Nurses Association's National Quality Forum Endorsed Measures.
When should a fall be reported?
Residents should have increased monitoring for the first 72 hours after a fall. Each shift, the nurse should record in the medical record a review of systems, noting any worsening or improvement of symptoms as well as the treatment provided.
Why is it important to report falls?
Reporting fall incidents provides evidence for accrediting surveyors that the organisation is compliant with requirements of national standards. Health services should aim for minimisation of both falls (particularly repeat falls) and harm from falls.
What is the best fall risk assessment?
The Johns Hopkins Fall Risk Assessment Tool (JHFRAT) was developed as part of an evidence-based fall safety initiative. This risk stratification tool is valid and reliable and highly effective when combined with a comprehensive protocol, and fall-prevention products and technologies.
What is the national benchmark for patient falls?
National benchmarks indicate a rate of 3.44 falls/1000 patient days on general medical, surgical, and medical-surgical units [2]. Approximately one-fourth of inpatient falls are injurious [3], with estimated costs exceeding $7000 per injury [4].
What are the three types of inpatient falls?
Falls can be classified into three types:Physiological (anticipated). Most in-hospital falls belong to this category. ... Physiological (unanticipated). ... Accidental.
Why are monitor falls important?
Falls are associated with increased lengths-of-stay, increased utilization of health care resources, and poorer health outcomes. Soft tissue injuries or minor fractures can cause significant functional impairment, pain, and distress.
How should you respond if your client has a fall?
These may vary between hospitals and settings but will generally include actions such as:reassuring the patient.calling for assistance.checking for injury.providing treatment as indicated.assessing vital signs and neurological observations.notifying medical officer and nurse in charge.notifying next of kin.More items...•
What should a falls assessment include?
identification of falls history. assessment of gait, balance and mobility, and muscle weakness. assessment of osteoporosis risk. assessment of the older person's perceived functional ability and fear relating to falling.
What are the 5 elements of falls safety?
The 5 steps of fall preventionIdentify the risks. There are many potential hazards present when working at heights, particularly pertaining to the risk of falling from an elevated surface. ... Avoid the risk. ... Control the risk. ... Respond to incidents. ... Maintain risk prevention.
What are physiological falls?
Anticipated physiological falls are associated with patients that are confused, elderly with dementia or Alzheimer’s. For this population to minimize falls, bed alarms can be utilized but if the bed alarm is constantly going off then a bedside sitter needs to be available to sit with the patient because a nurse with high nurse patient ratio cannot always get to the room whenever a bed alarm rings. Accidental falls are associated with patient being tethered to Tubing’s, walking with IV pole, or tripping over cluttered room. For these patients, hourly rounding is best because every hour if a nursing team member goes in to check on the patient many falls can be reduced. Unanticipated physiological and behavioral falls are not preventable because in these situations any outcome is…
What should a nurse check before discharge?
According to Ruggiero, Smith, Copeland, and Boxer, before discharge, the nurse should check medications to “identify discrepancies, such as medication omission, duplication, change in frequency, change in dose, adjustments, new medications not accompanied by a prescription, or omission of core measures.” This is referred to as a discharge time out. If the nurse is not confident about medications, the nurse can ask a pharmacist to help. This discharge time out ensures that patients are discharged to home with the correct medications list (Ruggiero, Smith, Copeland, & Boxer, 2015). Success will be determined if the patient uses handrails and grab bars as needed, use an assistive device such as a walker correctly, clutter and spills from the floors, and correctly transfer while using safe transfer procedures. These procedures will keep the patient safe and prevent the patient from falling (Ackley & Ladwig,…
What is the mechanism for recording and reporting a patient fall?
The mechanism for recording and reporting a patient fall will vary depending on the state and the in-house mechanism the healthcare facility uses. Generally, mishaps such as falls are recorded in an incident report. After the fall, a nurse and a medical provider will likely perform an examination of the patient and document their findings.
Where is a fall report sent?
Once the patient has been evaluated and once the report has been compiled, it is generally sent to the hospital’s or the nursing home’s risk management department. The circumstances surrounding the fall are reviewed with the goal of determining what could prevent something like that from happening again. In most cases, medical professionals are ...
What are the different types of falls?
In most medical settings, falls are categorized as: 1 Accidental Falls: These are falls that happen among patients who have very low risk of falling, but they fall because of the environment they are in. They may fall out of bed or slip on a wet floor. 2 Anticipated Physiological Falls: These are the most frequent types of falls. They’re usually caused by an underlying condition affecting the patient. A patient may have a problem walking, their gait may be abnormal, they may be battling with dementia, or they may be on medication that is affecting their balance or their perception. 3 Unanticipated Physiological Falls: These are falls with patients who appear to be low risk for falls, however, they suffer a unexpected negative event. They may faint, they may have a seizure, or they may have a heart attack or a stroke. 4 Behavioral Falls: These are falls that happen because a patient becomes unruly or acts out for one reason or another. These includes instances where patients fall on purpose.
What is an accident fall?
Accidental Falls: These are falls that happen among patients who have very low risk of falling, but they fall because of the environment they are in. They may fall out of bed or slip on a wet floor.
What percentage of hospitalized patients fall?
Research shows that up to 50 percent of hospitalized individuals run the risk of falling. Of those who do fall, 50 percent suffer injury. The injuries sustained from hospital falls range ...
Why do patients fall in hospitals?
In many cases, factors such as having beds in a high position, nurses failing to respond to patient calls, and environmental factors within the hospital ( e.g., a wet floor), increase the likelihood of a patient falling.
Why do elderly people fall?
Patient falls are seen with greater frequency among the elderly as a result of age-related health conditions, including delirium, musculoskeletal conditions, neurological conditions, and side effects from medication.
How to write a fall report?
Step 1: Gather Facts. The first step in writing an incident fall report is to gather the real account of the whole incident. You need to gather all the facts of the events leading up to the incident. This will help you understand the reason behind the incident so that you can avoid the same in the future as well.
How to make a proper incident fall report?
The best way to make sure that you create a proper incident fall report is to use a template with ready-made content and professional structure that makes it easier for you to edit and add all the necessary information and customize the report according to your liking.
How to avoid accidents in the workplace?
Accidents are very common in the workplace and the best way to avoid such incidents is to stay alert and informed. Create an informative incident reportwith the help of our Fall Incident Report Template. We assure you that its highly maintained structure and usable features will not disappoint you. Since it is available in Google Docs, MS Word and Pages for your Apple devices as well, you can well edit and customize your report so that it’s true to the fact!
How to take pictures of a fall?
In a fall incident, taking pictures is the best evidence. Since it’s obvious that everyone has a smartphone with them, it’s wise to click immediate pictures of the incident instantly when you fall. Get pictures of your injury and immediately call for the doctor’s appointment. If the hazard is too much, you can ask someone else to click your picture.
Why do we need to write incident fall reports?
In such cases, we need to write incident fall reports so that we can take precautions for future such incidents. Some inconveniences can be damaging and cost a lot of lives.
Do you need to fill out a post fall incident report?
If you visit the hospital with an injury due to a massive fall, you are likely to fill out an incident report for safety. However, you can save time and get yourself checked instantly if you have this Post Fall Incident Report Form already with you. Get this on your device and use it when you encounter an accident so that you can immediately report and get a doctor’s appointment.
Can an incident occur anywhere?
An incident can occur anytime anywhere if you are not being careful. So it’s better to get this Fall Incident Report Form in PDF format so that you can create sample post-fall reportsimmediately after the accident. Also, you can get easily customizable report templates in MS Wordas well so that you can modify the information as the incident happened to you.
What Is Patient Incident Report?
Medical events can occur for a variety of reasons. Simply put, the medical system views each incident to be something that poses a threat to the health of patients or medical staff members in some way. “Incident Reporting in Healthcare,” as described in the realm of healthcare, is defined as the process of obtaining incident data and accurately presenting it for action. A newly discovered problem is recognized in order to aid in the identification and correction of the mistakes that occur. An incident report can be filed by a designated staff member (someone who has been granted permission to file reports) or by an employee who has witnessed the incident firsthand. The majority of the time, a nurse or other staff member will file a report within 24 to 48 hours of the incident occurring. It is preferable to capture and document an occurrence as soon as it occurs in order to achieve the best possible outcome.
What is the best way to write a patient incident report?
For example, employing precise and simple language will make the inquiry process more efficient and less time-consuming overall. Additionally, appropriate grammar, spelling, and punctuation should be used. Grammar errors can distort the interpretation of details contained within the report, making it more difficult to conduct an investigation into the incident.
What is a negative incident?
A Negative Occurrence: The effect of a detrimental incident is the injury or illness of a patient or another individual. It is possible for a patient to tumble out of bed and break their arm, or for a nurse to scratch them when she is taking their temperature. Missed the Mark by a Hair: A near miss occurs when there was a possibility for injury to a patient or when another person was on the verge of being harmed, but the situation was rectified before the harm could occur. For example, a patient may be apprehended while attempting to leave the facility early or may trip, but a nurse will grab them before they are injured. An incident with No Harm: A no-harm occurrence occurs when something happens to a patient or to another person, but no observable injury or illness results as a result of the event. For example, a patient may be given a blood transfusion intended for another patient, but no harm is done because the blood is compatible with the other patient.
What is incident reporting?
Incident reporting is usually used as a catch-all word for all-volunteer patient safety event reporting systems, which rely on persons who are directly involved in the events to provide specific information about what happened.
Why is incident reporting important?
The ultimate purpose of incident reporting is to improve the safety of the patient. By promoting higher safety standards and decreasing medical errors, incident reporting helps you create a more stable environment for your patients to flourish in. When your hospital provides high-quality patient care over time, it will eventually develop a positive reputation.
Why do medical incidents go unreported?
When an occurrence results in a person’s harm or property damage, it is necessary to file an incident report. Unfortunately, for every medical error that is recorded, there are about 100 other errors that go undetected. There are a variety of reasons why medical accidents go unreported, but one of the most common is a lack of knowledge on when to file a report.
How can hospitals improve their efficiency?
It is also possible to improve the efficiency of healthcare operations by using reporting tools. Hospitals can keep themselves out of legal issues by acquiring and evaluating incident data on a daily basis. A comprehensive medical error study analyzed the medical systems of 17 countries in Southeast Asia and investigated how inadequate reporting raises the cost burden on healthcare institutions and providers.