The Pathology Report | Johns Hopkins Medicine
21 hours ago The pathology report may include the following information ( 1 ): Patient information: Name, birth date, biopsy date Gross description: Color, weight, and size of tissue as seen by the naked eye Microscopic description: How the sample looks under the … >> Go To The Portal
The pathology report may include the following information ( 1 ):
- Patient information: Name, birth date, biopsy date
- Gross description: Color, weight, and size of tissue as seen by the naked eye
- Microscopic description: How the sample looks under the microscope and how it compares with normal cells
- Diagnosis: Type of tumor/cancer and grade (how abnormal the cells look...
What does a pathology report tell you?
A pathology report is a medical document written by a pathologist. A pathologist is a doctor who diagnoses disease by:Explaining laboratory testsEvaluating cells, tissues, and organsThe report gives a diagnosis based on the pathologist’s examination of a sample of tissue taken from the patient’s tumor. This sample of tissue, called a specimen, is removed during a biopsy. Learn about the ...
What to expect from pathology report?
- How large is the tumor?
- Is the cancer invasive or noninvasive?
- How fast are the cancer cells growing?
- What is the grade of the cancer? ...
- Has the whole cancer been removed, or is there evidence of cancerous cells at the edges of the sample?
- Are there cancerous cells in the lymph or blood vessels?
- What is the stage of the cancer?
- What does this mean?
What is the purpose of a pathology report?
The specimen is analyzed by a pathologist, who then writes up a report for the medical provider who has either ordered the report or performed the procedure. Pathology reports are used by your medical provider to determine a diagnosis or treatment plan for a specific health condition or disease.
What is an example of a pathology report?
Your pathology report. The breast tissue removed during a biopsy is sent to a pathologist. A pathologist is the doctor who looks at the tissue under a microscope and determines whether or not the tissue contains cancer. The pathologist prepares a report of the findings, including the diagnosis, and sends it to your surgeon (or your oncologist).
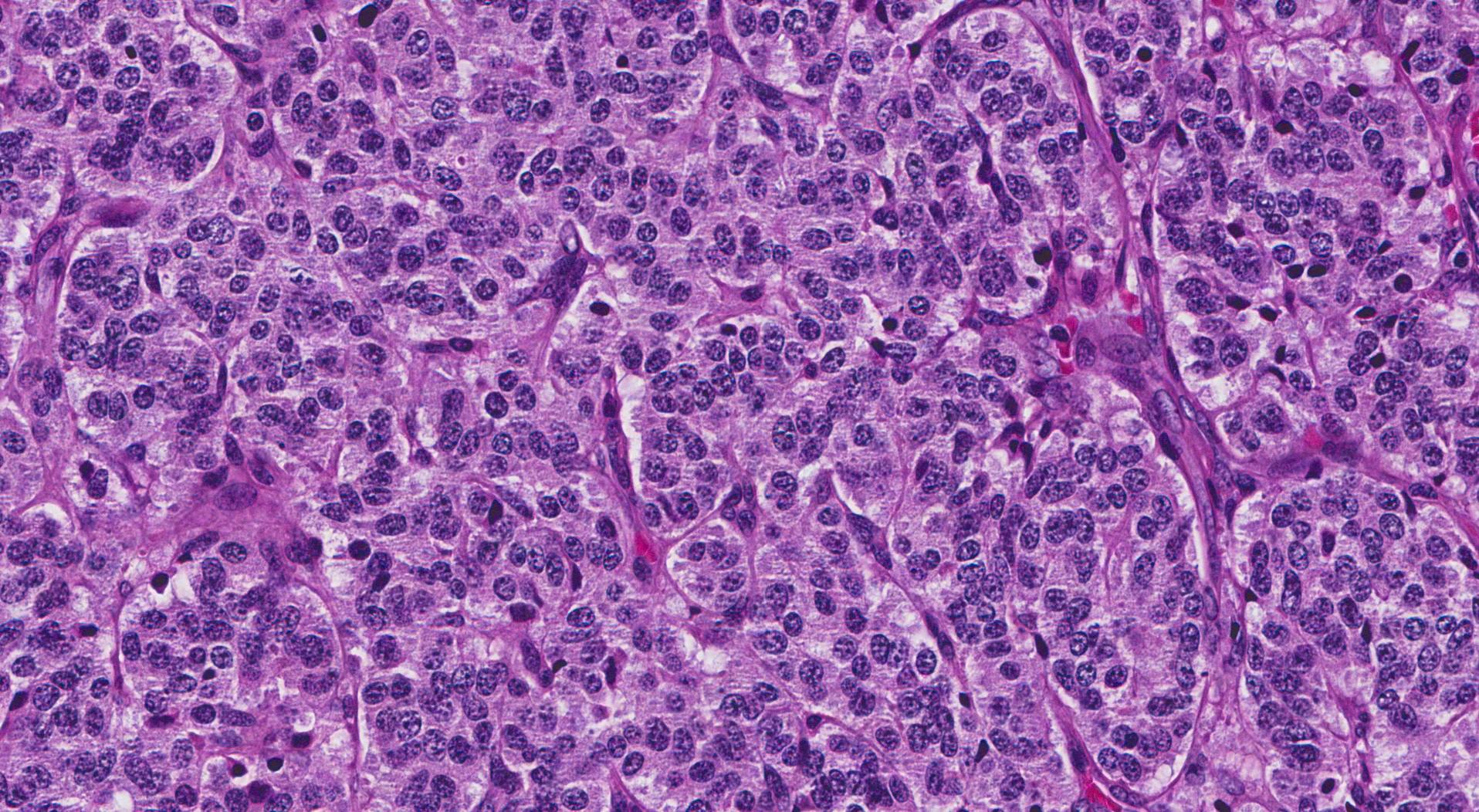
Who reads pathology reports?
A doctor called a pathologist studies it under a microscope. They may also do tests to get more information. These findings go into your pathology report. It includes your diagnosis, if and how much your cancer has spread, and other details.
How do I write a pathology report?
Components of a pathology reportYour name and your individual identifiers. ... A case number. ... The date and type of procedure by which the specimen was obtained (for instance, a blood sample, surgery, or biopsy)Your medical history and current clinical diagnosis.A general description of the specimen received in the lab.More items...
How long does it usually take to get a pathology report back?
The pathology report may be ready in as soon as two or three days after the biopsy is taken. If additional testing of the tissue is necessary, the report may take longer to complete (between seven and 14 days). Pathology reports are written in technical language using many medical terms.
Is pathology report same as biopsy?
A histopathology report describes the tissue that the pathologist examined. It can identify features of what cancer looks like under the microscope. A histopathology report is also sometimes called a biopsy report or a pathology report.
What is a pathology report?
A pathology report is a document that contains the diagnosis determined by examining cells and tissues under a microscope. The report may also contain information about the size, shape, and appearance of a specimen as it looks to the naked eye. This information is known as the gross description.
What is pathology test?
Pathology tests cover blood tests, and tests on urine, stools (faeces) and bodily tissues. A pathologist interprets the results of blood and pathology tests and looks for abnormalities that may point to disease, such as cancer and other chronic illnesses, or health risks, such as pre-diabetes.
Why would pathology results take long?
Often, there are technical reasons for delays in reporting results. For instance, certain types of body tissues take longer to process than others. Bone and other hard tissues that contain a lot of calcium need special handling.
Is a negative biopsy good?
Although tests aren't 100% accurate all the time, receiving a wrong answer from a cancer biopsy – called a false positive or a false negative – can be especially distressing. While data are limited, an incorrect biopsy result generally is thought to occur in 1 to 2% of surgical pathology cases.
What happens if biopsy report is positive?
Another important factor is whether there are cancer cells at the margins, or edges, of the biopsy sample. A “positive” or “involved” margin means there are cancer cells in the margin. This means that it is likely that cancerous cells are still in the body. Lymph nodes.
What are the 4 types of pathology?
The American Osteopathic Board of Pathology also recognizes four primary specialties: anatomic pathology, dermatopathology, forensic pathology, and laboratory medicine. Pathologists may pursue specialised fellowship training within one or more subspecialties of either anatomical or clinical pathology.
Can a pathology report be wrong?
The reported frequency of anatomic pathologic errors ranges from 1% to 43% of all specimens, regardless of origin and disease, he said. The error rate for oncology is 1% to 5%.
How do doctors give biopsy results?
After your health care provider obtains a tissue sample, it's sent to a laboratory for analysis. The sample may be chemically treated or frozen and sliced into very thin sections. The sections are placed on glass slides, stained to enhance contrast and studied under a microscope.
What is a pathology report?
A pathology report is a document that contains the diagnosis determined by examining cells and tissues under a microscope. The report may also cont...
How is tissue obtained for examination by the pathologist?
In most cases, a doctor needs to do a biopsy or surgery to remove cells or tissues for examination under a microscope. Some common ways a biopsy ca...
How is tissue processed after a biopsy or surgery? What is a frozen section?
The tissue removed during a biopsy or surgery must be cut into thin sections, placed on slides, and stained with dyes before it can be examined und...
How long after the tissue sample is taken will the pathology report be ready?
The pathologist sends a pathology report to the doctor within 10 days after the biopsy or surgery is performed. Pathology reports are written in te...
What information does a pathology report usually include?
The pathology report may include the following information ( 1 ): Patient information: Name, birth date, biopsy date Gross description: Color, weig...
What might the pathology report say about the physical and chemical characteristics of the tissue?
After identifying the tissue as cancerous, the pathologist may perform additional tests to get more information about the tumor that cannot be dete...
What information about the genetics of the cells might be included in the pathology report?
Cytogenetics uses tissue culture and specialized techniques to provide genetic information about cells, particularly genetic alterations. Some gene...
Can individuals get a second opinion about their pathology results?
Although most cancers can be easily diagnosed, sometimes patients or their doctors may want to get a second opinion about the pathology results ( 1...
What research is being done to improve the diagnosis of cancer?
NCI, a component of the National Institutes of Health, is sponsoring clinical trials that are designed to improve the accuracy and specificity of c...
What is a pathology report?
A pathology report is a document that contains the diagnosis determined by examining cells and tissues under a microscope. The report may also contain information about the size, shape, and appearance of a specimen as it looks to the naked eye. This information is known as the gross description.
How long does it take for a pathologist to send a report?
The pathologist sends a pathology report to the doctor within 10 days after the biopsy or surgery is performed. Pathology reports are written in technical medical language. Patients may want to ask their doctors to give them a copy of the pathology report and to explain the report to them. Patients also may wish to keep a copy ...
How to tell if a biopsy is cancerous?
This is known as histologic (tissue) examination and is usually the best way to tell if cancer is present. The pathologist may also examine cytologic (cell) material.
What is an IHC report?
For example, the pathology report may include information obtained from immunochemical stains (IHC). IHC uses antibodies to identify specific antigens on the surface of cancer cells. IHC can often be used to: Determine where the cancer started.
How are tissue samples prepared?
All tissue samples are prepared as permanent sections, but sometimes frozen sections are also prepared. Permanent sections are prepared by placing the tissue in fixative (usually formalin) to preserve the tissue, processing it through additional solutions, and then placing it in paraffin wax.
What is the role of a pathologist in cancer diagnosis?
A pathologist is a doctor who does this examination and writes the pathology report. Pathology reports play an important role in cancer diagnosis and staging (describing the extent of cancer within the body, especially whether it has spread), which helps determine treatment options.
What is cytologic material?
Cytologic material is present in urine, cerebrospinal fluid (the fluid around the brain and spinal cord), sputum (mucus from the lungs), peritoneal (abdominal cavity) fluid, pleural (chest cavity) fluid, cervical/vaginal smears, and in fluid removed during a biopsy.
What is a pathology report?
Reading a Pathology Report. A pathology report is a medical document written by a pathologist. A pathologist is a doctor who diagnoses disease by: The report gives a diagnosis based on the pathologist’s examination of a sample of tissue taken from the patient’s tumor. This sample of tissue, called a specimen, is removed during a biopsy.
How long does it take to get a pathology report?
It may take a few days to a few weeks to receive the full report. The timing depends on the testing needed. You are allowed by law to receive a copy of your pathology report. But you should expect the report to contain highly technical medical terms.
What does it mean when a pathologist tests a tumor?
A cancerous tumor is malignant, meaning it can grow and spread to other parts of the body. A noncancerous, or benign tumor, means the tumor can grow but will not spread.
Why is the pathology report for a biopsy different from a later report for the entire tumor?
This happens because the features of a tumor can sometimes vary in different areas. Your doctor will consider all of the reports to develop a treatment plan specific to you.
What is a synoptic report?
Synoptic report, or summary. When the tumor was removed, the pathologist will include a summary. This lists the most important results in a table. These are the items considered most important in determining a person’s treatment options and chance of recovery.
What is grade in cancer?
Grade. Grade describes how the cancer cells look compared with healthy cells. In general, the pathologist is looking for differences in the size, shape, and staining features of the cells. A tumor with cells that look more like healthy cells is called "low grade" or "well differentiated.".
Can you have more than one doctor for a diagnosis?
It may be helpful to talk with more than one doctor about your diagnosis and treatment plan. This is called a second opinion. It is important to get a copy of the pathology report and any other medical records.
How to access pathology results?
Patients also benefit from being able to access their pathology reports in their My Health Record. This helps them to: 1 keep track of their tests 2 monitor results over time 3 access their results at any time.
What to do if you don't want a pathology report?
If you or your patient does not want a pathology report uploaded to a My Health Record the pathology laboratory should be notified. A patient may withdraw consent or ask that a report not be uploaded at any time before the report is uploaded to their My Health Record. If a patient changes their mind about a report upload, ...
What to do if a patient changes their mind about a report upload?
If a patient changes their mind about a report upload, after it has been sent to their My Health Record, they can do one of the following: they can remove the report online or with the support of the My Health Record helpline (1800 723 471)
Is a pathology test sensitive?
Sensitive results. If the results of a pathology test could be considered sensitive, you may wish to discuss with your patient whether to upload the report. A pathology service will not upload a report to a My Health Record where existing state or territory legislation prohibits the disclosure of sensitive information without the express consent ...
Can a medical practice check conformant software?
Medical practices can check the list of conformant software systems. Practices can also confirm with their software vendors that their requesting process options are supported with their version of software. See the list of pathology providers that are connected to and sharing information to the My Health Record system.
Can pathology be uploaded to my health record?
Pathology reports can be uploaded to the My Health Record once the pathology service is registered to participate in the My Health Record system. The service will also need to use software that allows their reports to be uploaded. Medical practices can check the list of conformant software systems. Practices can also confirm with their software ...
What should a physician note in a medical test?
Instead, the physician must note the type of test, the methodology used, the normal range for the test, and then comment on whether the finding is abnormal or normal in relation to that range.
What is a print post?
Print Post. A provider must document in the patient’s medical record medical necessity for pathology and laboratory services, as well as indicate that he or she ordered the tests. The ordering physician must also note in the patient’s record how he or she used the findings to select a diagnosis and a treatment plan.
Do outpatient labs have to be reimbursed by Medicare?
Outpatient hospital laboratories are reimbursed based on a fee schedule for Medicare.
Can you copy a number value from a computer to a patient's chart?
Because most tests are computerized, the results usually are reported by a number value on a computer printout. It is not sufficient to copy that number value into the patient’s chart or attach the computer printout to the patient record.
What is a pathology report?
Stages of Cancer . A pathology report is a medical document that gives information about a diagnosis, such as cancer. To test for the disease, a sample of your suspicious tissue is sent to a lab. A doctor called a pathologist studies it under a microscope. They may also do tests to get more information.
What is the identifying information on a blood test?
Identifying information: This has your name, birth date, and medical record number. It also lists contact information for your doctor, the pathologist and lab where the sample was tested.
How to grade a tumor?
Grade: The pathologist compares the cancer cells to healthy cells. There are different scales for specific cancers. A tumor grade reflects how likely it is to grow and spread. In general, this is what those grades mean: 1 Grade 1: Low grade, or well-differentiated: The cells look a little different than regular cells. They aren’t growing quickly. 2 Grade 2: Moderate grade, or moderately differentiated: They don’t look like normal cells. They’re growing faster than normal. 3 Grade 3: High grade, or poorly differentiated: The cells look very different than normal cells. They’re growing or spreading fast.
What does grade mean in cancer?
Grade: The pathologist compares the cancer cells to healthy cells. There are different scales for specific cancers. A tumor grade reflects how likely it is to grow and spread. In general, this is what those grades mean: Grade 1: Low grade, or well-differentiated: The cells look a little different than regular cells.
Popular Posts:
- 1. faulkner patient portal
- 2. western connecticiu patient portal
- 3. which entity is mandated to provide a report on the status of patient safety to congress each year
- 4. steward primary care patient portal
- 5. middlesex endocrinology patient portal login
- 6. patient portal, family associates,holtonks
- 7. what to report to doctor concerning a patient with urinary tract infection
- 8. non surgical orthopedics patient portal
- 9. uof, patient portal
- 10. grace health corbin ky patient portal