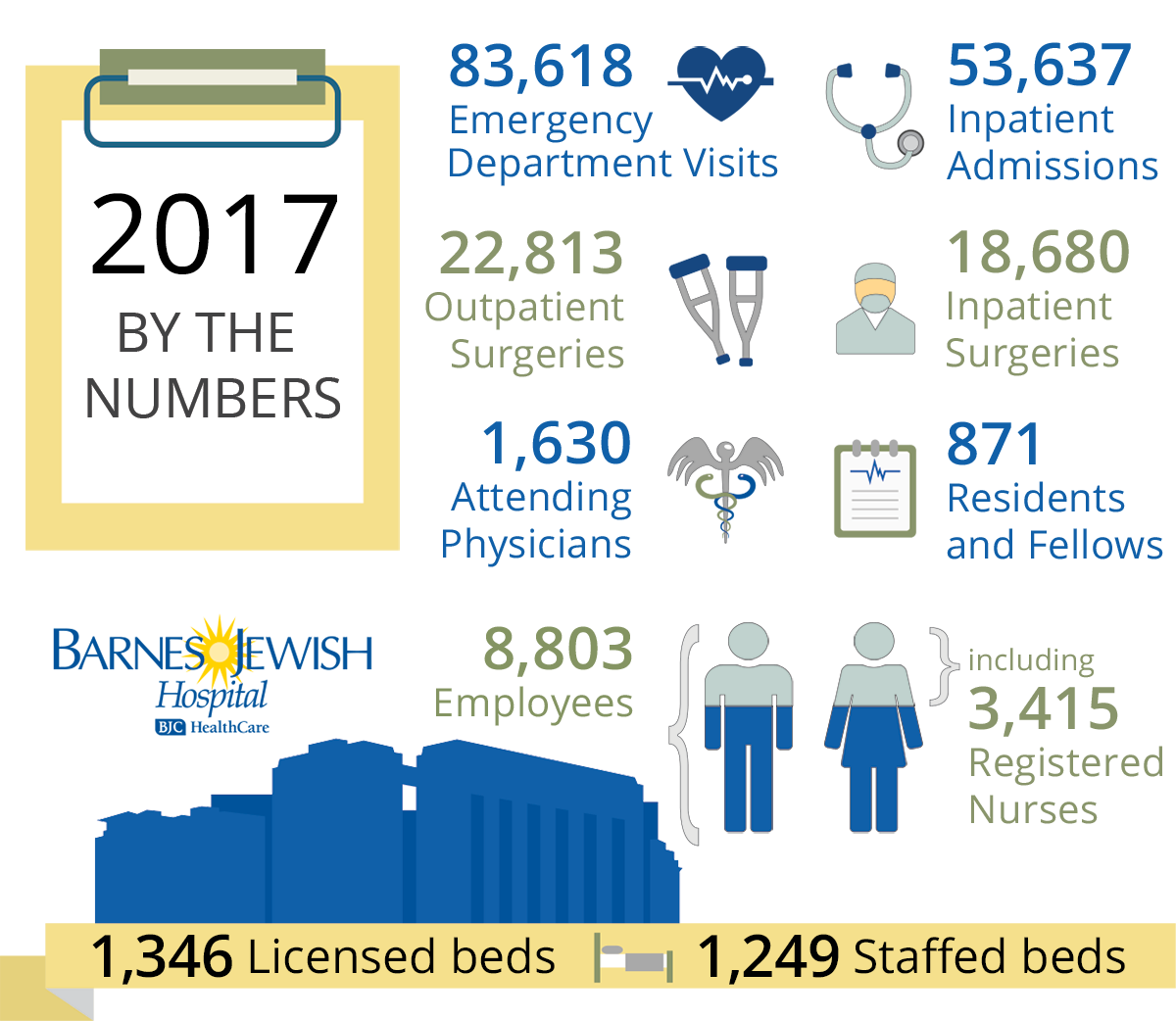
PATIENT SAFETY - National Healthcare Quality and …
13 hours ago This Patient Safety Chartbook is part of a family of documents and tools that support the National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report (NHQDR). The NHQDR is an annual report to Congress mandated in the Healthcare Research and Quality Act of 1999 (P.L. 106-129). >> Go To The Portal
The National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Reports review analysis specific to tracking patient safety challenges and improvements across ambulatory, home health, hospital, and nursing home environments. The most recent update documented improvements in approximately half of the patient safety measures tracked.
Full Answer
What is the national healthcare quality and Disparities Report?
The National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report presents trends for measures related to access to care, affordable care, care coordination, effective treatment, healthy living, patient safety, and person-centered care.
What is the AHRQ patient safety work?
AHRQ’s Patient Safety Work > AHRQ is the lead Federal agency for patient safety research. AHRQ funds work to help frontline providers prevent HAIs by improving how care is delivered to patients. Research-based tools to get your team on board and help them understand and use core concepts of patient safety.
What is the national healthcare safety network?
CDC’s National Healthcare Safety Network is the nation’s most widely used healthcare-associated infection tracking system. NHSN provides facilities, states, regions, and the nation with data needed to identify problem areas, measure progress of prevention efforts, and ultimately eliminate healthcare-associated infections.
Why is patient safety important in healthcare?
Patient safety is fundamental to delivering quality essential health services. Indeed, there is a clear consensus that quality health services across the world should be effective, safe and people-centred. In addition, to realize the benefits of quality health care, health services must be timely, equitable, integrated and efficient.
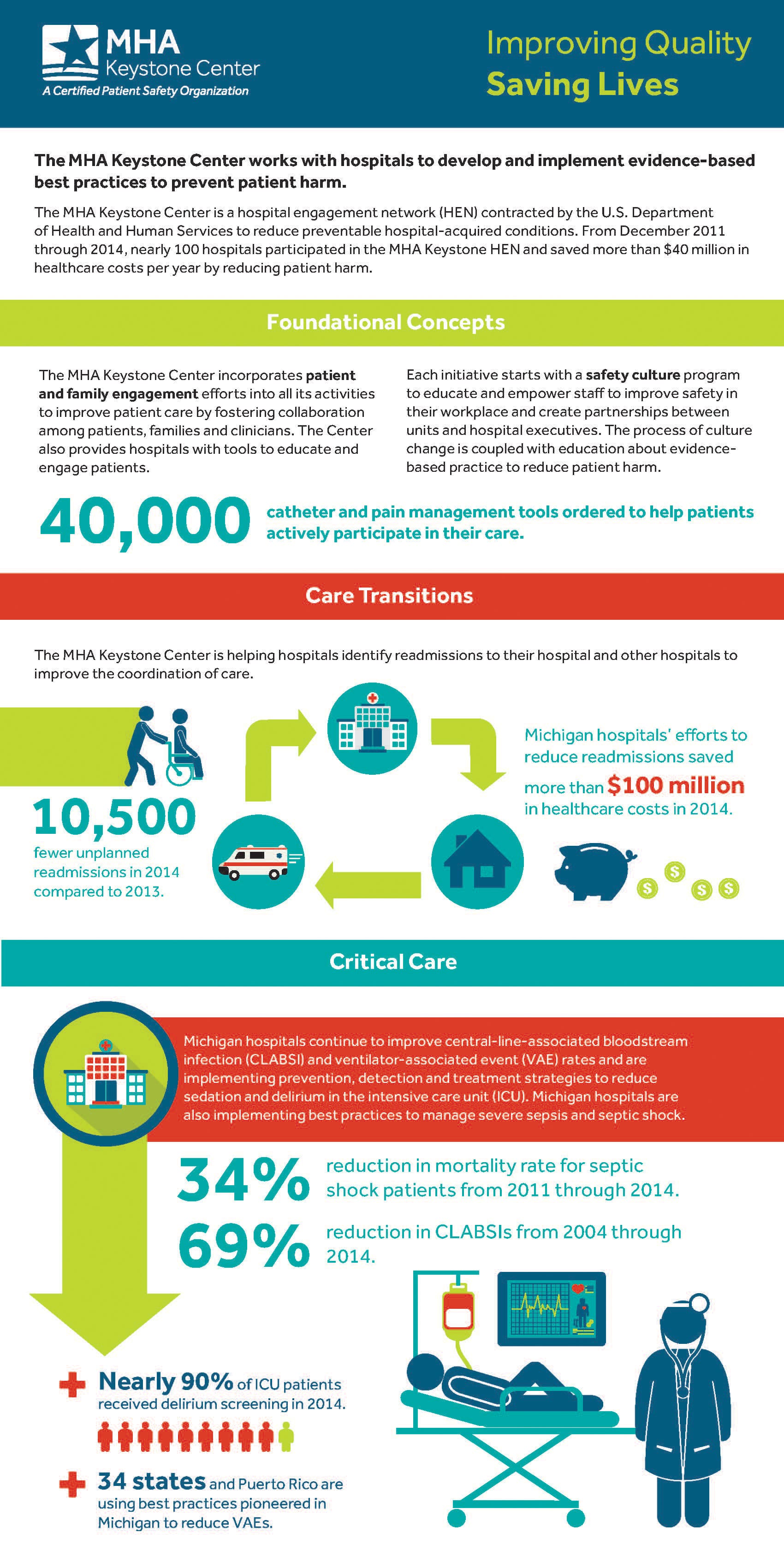
What is the National Health Care Quality Report?
AHRQ has produced the National Healthcare Quality Report (NHQR) and the National Healthcare Disparities Report (NHDR) annually since 2003. These reports measure trends in effectiveness of care, patient safety, timeliness of care, patient centeredness and efficiency of care.
What is the purpose of the National health quality Report NHQR )?
The NHQR collects data on health care quality for States and uses maps to present some of the data. The State-level data provide an indication of the variation of the national measures. The measure with the greatest amount of variation is the percentage of chronic nursing home patients who were physically restrained.
What is the difference between patient safety and quality?
Quality has been defined by the federal Agency for Healthcare Research and Quality (AHRQ) as “doing the right thing at the right time for the right person and having the best possible result.” Patient safety is simply defined by the World Health Organization as “the prevention of errors and adverse effects to patients ...
How is patient safety related to quality improvement?
It aims to prevent and reduce risks, errors and harm that occur to patients during provision of health care. A cornerstone of the discipline is continuous improvement based on learning from errors and adverse events. Patient safety is fundamental to delivering quality essential health services.
What is the National quality Strategy?
The National Quality Strategy (NQS) is a nationwide effort to provide direction for improving the quality of health and healthcare in the United States. It is guided by three aims: better care, healthy people and communities, and affordable care.
What are quality patient indicators?
Quality Indicators (QIs) are standardized, evidence-based measures of health care quality that can be used with readily available hospital inpatient administrative data to measure and track clinical performance and outcomes.
What are the 3 components of quality health care?
Effective – providing evidence-based healthcare services to those who need them; Safe – avoiding harm to people for whom the care is intended; and. People-centred – providing care that responds to individual preferences, needs and values.
What is patient safety NHS?
Patient safety is the avoidance of unintended or unexpected harm to people during the provision of health care. We support providers to minimise patient safety incidents and drive improvements in safety and quality. Patients should be treated in a safe environment and protected from avoidable harm.
What is the relationship between health care quality and patient safety?
Safety is often defined as the avoidance of injury and harm, while quality is typically defined as achieving the best possible health care outcomes. Safety can be considered one of multiple domains of quality, and safety can also be considered synonymous with quality.
What are the 2020 National Patient Safety Goals?
This is done to make sure that each patient gets the correct medicine and treatment.Identify patients correctly.Prevent infection.Improve staff communication.Identify patient safety risks.Prevent mistakes in surgery.
What are the key elements of patient safety?
The key elements of a culture of safety include (1) a shared belief that although health care is a high-risk undertaking, delivery processes can be designed to prevent failures and harm to participants; (2) an organizational commitment to detecting and analyzing patient injuries and near misses; and (3) an environment ...
What are examples of patient safety?
The Nurse's Role in Patient SafetyIdentify “wrong site, wrong procedure, wrong patient” errors. High quality hospitals view nurses as the physician's partner in avoiding errors such as these. ... Catch medication mistakes. ... Educate patients about their medications. ... Reduce patient falls. ... Monitor patients for deterioration.
Previous Reports
The newest Data Spotlight (PDF, 825 KB) shows that emergency department visits for opioid-related diagnoses are increasing while access to treatment for illicit drug use remains flat.
Data Spotlights
The newest Data Spotlight (PDF, 825 KB) shows that emergency department visits for opioid-related diagnoses are increasing while access to treatment for illicit drug use remains flat.
What is AHRQ in healthcare?
AHRQ has developed tools that can help organizations build the capacity for change to make health care safer. By understanding patient safety concepts and how team and individual behaviors and attitudes influence safety culture, teams build the foundations for a future of safer care.
What is AHRQ free?
AHRQ offers free tools to help prioritize concerns and maximize interactions between providers, patients, and families. Guide to Patient and Family Engagement in Hospital Quality and Safety. Guide to Improving Patient Safety in Primary Care Settings. About AHRQ's Quality & Patient Safety Work. AHRQ is the lead Federal agency for patient safety ...
What is patient safety?
Patient Safety is a health care discipline that emerged with the evolving complexity in health care systems and the resulting rise of patient harm in health care facilities. It aims to prevent and reduce risks, errors and harm that occur to patients during provision of health care.
Why is patient safety important?
Patient safety is fundamental to delivering quality essential health services. Indeed, there is a clear consensus that quality health services across the world should be effective, safe and people-centred. In addition, to realize the benefits of quality health care, health services must be timely, equitable, integrated and efficient.
What is the WHO patient safety and risk management unit?
The Patient Safety and Risk Management unit at WHO has been instrumental in advancing and shaping the patient safety agenda globally by focusing on driving improvements in some key strategic areas through:
When did WHO start working on patient safety?
WHO's work on patient safety began with the launch of the World Alliance for Patient Safety in 2004 and this work has continued to evolve over time. WHO has facilitated improvements in the safety of health care within Member States through establishment of Global Patient Safety Challenges.
When is World Patient Safety Day?
Recognizing that Patient Safety is a global health priority, the World Health Assembly (WHA) adopted a resolution on Patient Safety which endorsed the establishment of World Patient Safety Day to be observed annually by Member States on 17 September.
How many measures were approved for the 2016 Patient Safety Standing Committee?
On July 27-28, 2016, the Patient Safety Standing Committee evaluated 13 newly submitted measures and 2 maintenance measures. During the meeting, a total of 11 measures were recommended for endorsement, two measures were not recommended, one measure consensus was not reached, and one measure was recommended for trial use approval.
What is the NQF?
The National Quality Forum’s (NQF) portfolio of safety measures spans a variety of topic areas. Many measures in the portfolio are used in public accountability and quality improvement programs. However, significant gaps in measurement remain.
What is a patient safety chartbook?
This Patient Safety Chartbook is part of a family of documents and tools that support the National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Reports (QDR). The QDR are annual reports to Congress mandated in the Healthcare Research and Quality Act of 1999 (P.L. 106-129).
What is the QDR?
The National Healthcare Quality and Disparities Report (QDR) is the product of collaboration among agencies across the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Many individuals guided and contributed to this effort. Without their magnanimous support, the report would not have been possible.