A case report on recurrent appendicitis: An often …
1 hours ago · Herein, we described a case report of a male patient with recurring right lower quadrant abdominal pain that he got complete relief of the symptoms of pain after he underwent appendectomy. The case was atypical form of appendicitis in that the patient had very mild tenderness during physical examination with no signs of peritonitis and Rovsing's sign. >> Go To The Portal
Medication
Appendicitis Recovery After Surgery. While getting up from sitting or sleeping position, get up gently and walk slowly in small paces. Going for short walks is the best exercise during the appendectomy recovery period. Similar to other surgeries, infection is a probable complication of appendectomy.
Procedures
The case report could help to improve the awareness of medical practitioners who come across similar cases so that they can consider recurrent appendicitis in their differential diagnosis; and hence outline appropriate diagnosis as well as early medical interventions. Discussion
Self-care
In patients with complicated appendicitis, the timing of the operation depends on the clinical status of the patient, the nature of the perforation, and, in some cases, the therapeutic strategy preferred [15, 16]. In severely sick patients with signs of free perforation or generalized peritonitis, emergency appendectomy should be performed.
Nutrition
If you have appendicitis, you'll likely be hospitalized and referred to a surgeon to remove your appendix. When you make the appointment, ask if there's anything you need to do in advance, such as fasting before having a specific test. Make a list of:
How to recover from appendicitis after surgery?
Can a case report help in the diagnosis of recurrent appendicitis?
When is emergency appendectomy indicated in complicated appendicitis?
What should I expect when I make an appointment for appendicitis?
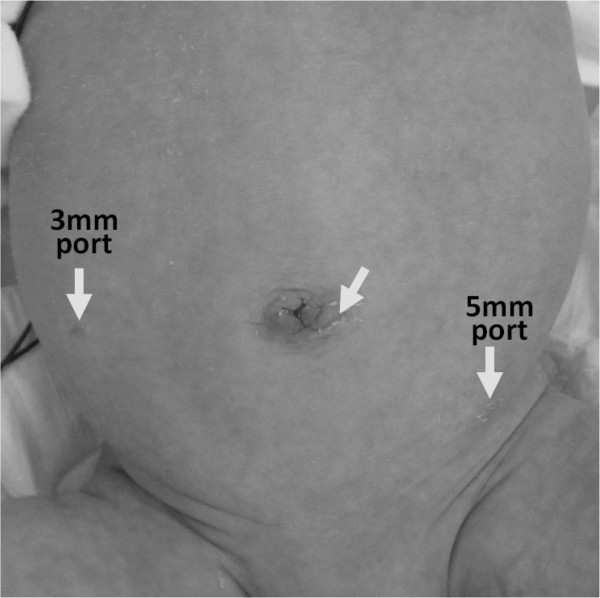
What should I look for after appendix surgery?
Call your healthcare provider if you have any of the following:Fever or chills.Redness, swelling, bleeding, or other drainage from the incision site.More pain around the incision site.Vomiting.Loss of appetite or unable to eat or drink anything.Constant coughing, trouble breathing, or shortness of breath.More items...
What changes after appendix removal?
Your belly may be swollen and may be painful. If you had laparoscopic surgery, you may have pain in your shoulder for about 24 hours. You may also feel sick to your stomach and have diarrhea, constipation, gas, or a headache. This usually goes away in a few days.
What are the common clinical findings in a patient with appendicitis?
The most specific physical findings in appendicitis are rebound tenderness, pain on percussion, rigidity, and guarding. Although RLQ tenderness is present in 96% of patients, this is a nonspecific finding.
What is the most common complication after appendectomy?
One of the most common complications following appendectomy is infection. Around 20 per cent of people who have a ruptured appendix develop an abscess (ball of pus) within the abdominal cavity about two weeks or so after the appendectomy. These abscesses must be surgically drained.
How long is appendicitis recovery?
With a laparoscopic surgery, a patient is often able to resume normal activities in one to three weeks. An open surgery may require about two to four weeks for recovery. With a ruptured appendix, it may take up to six weeks or more.
Which fruit is good after appendix surgery?
Including immune-boosting foods in the diet always helps in fighting possible infections. Of course, the patient will be put on antibiotics until recovery but including vitamin A, C foods such as eggs, carrot, fresh vegetables, lemon, oranges, amla (Indian Gooseberry) help in the production of antibodies, digestion.
What is the nursing diagnosis for appendicitis?
Diagnosis. Based on the assessment data, the most appropriate diagnoses for a patient with appendicitis are: Acute pain related to obstructed appendix. Risk for deficient fluid volume related to preoperative vomiting, postoperative restrictions.
How do you assess an appendicitis patient?
Tests and procedures used to diagnose appendicitis include:Physical exam to assess your pain. Your doctor may apply gentle pressure on the painful area. ... Blood test. This allows your doctor to check for a high white blood cell count, which may indicate an infection.Urine test. ... Imaging tests.
What is the major complication of appendicitis?
Complications of Appendicitis The main problem with appendicitis is the risk of a burst appendix. This may happen if the appendix is not removed quickly. A burst appendix can lead to infection in the belly, called peritonitis. Peritonitis can be very serious and even cause death if not treated right away.
What is life like without an appendix?
Some studies have shown, however, that people without an appendix may have slightly higher rates of infection than those with a functioning organ. “It may also take them slightly longer to recover from illness, especially those in which the beneficial gut bacteria has been flushed out of the body,” Smith added.
Can the appendix cause long-term problems?
Chronic appendicitis is a long-term condition characterized by appendicitis symptoms that come and go over time. It is different from acute appendicitis, but it can also have serious complications. While a person may live with chronic appendicitis for years, it is important that they do not ignore the symptoms.
Does removal of appendix affect immune system?
Behind the study lay evidence that removal was associated with moderate long-term effects on the immune system and alterations in risk for some autoimmune disorders. Studies suggest that between 10 and 20% of all young people have tonsils or appendix removed.
Does removal of appendix affect immune system?
Behind the study lay evidence that removal was associated with moderate long-term effects on the immune system and alterations in risk for some autoimmune disorders. Studies suggest that between 10 and 20% of all young people have tonsils or appendix removed.
Can your appendix grow back after being removed?
An appendectomy is done if you are diagnosed with appendicitis. Because you only have one appendix and it cannot grow back after being removed, you can only have an appendectomy once.
How serious is appendix removal?
Appendix surgery could hurt nearby areas such as the bladder, large intestine (colon), or small intestine. You might need another surgery if this happens. There is a small risk of an abscess (collection of pus/bacteria) following surgery if the inflammation of the appendix is severe at the time of surgery.
How do you poop after an appendectomy?
MOST PATIENTS DO NOT HAVE THEIR FIRST BOWEL MOVEMENT UNTIL AT LEAST 3 DAYS AFTER SURGERY. WHILE UTILIZING NARCOTICS, YOU SHOULD REMAIN ON AN OVER THE COUNTER STOOL SOFTENER SUCH AS COLACE OR DOCUSATE. FIBER SUPPLEMENTATION WITH METAUMUCIL OR CITRUCEL (1 TABLESPOON WITH 8OZ WATER) IS ALSO RECOMMENDED.
How to diagnose appendicitis?
To help diagnose appendicitis, your doctor will likely take a history of your signs and symptoms and examine your abdomen. Tests and procedures used to diagnose appendicitis include: Physical exam to assess your pain. Your doctor may apply gentle pressure on the painful area. When the pressure is suddenly released, ...
What does a doctor look for in an appendix?
Your doctor may also look for abdominal rigidity and a tendency for you to stiffen your abdominal muscles in response to pressure over the inflamed appendix (guarding). Your doctor may use a lubricated, gloved finger to examine your lower rectum (digital rectal exam).
How long does it take for an appendix to heal?
Expect a few weeks of recovery from an appendectomy, or longer if your appendix burst. To help your body heal: Avoid strenuous activity at first. If your appendectomy was done laparoscopically, limit your activity for three to five days. If you had an open appendectomy, limit your activity for 10 to 14 days.
How to drain an abscess before surgery?
If your appendix has burst and an abscess has formed around it, the abscess may be drained by placing a tube through your skin into the abscess. Appendectomy can be performed several weeks later after controlling the infection.
How to control pain from medication?
Some complementary and alternative treatments, when used with your medications, can help control pain. Ask your doctor about safe options, such as: Distracting activities, such as listening to music and talking with friends, that take your mind off your pain. Distraction can be especially effective with children.
Is appendectomy better for obesity?
During a laparoscopic appendectomy, the surgeon inserts special surgical tools and a video camera into your abdomen to remove your appendix. In general, laparoscopic surgery allows you to recover faster and heal with less pain and scarring. It may be better for older adults and people with obesity.
Is laparoscopic surgery better for obesity?
It may be better for older adults and people with obesity. But laparoscopic surgery isn't appropriate for everyone. If your appendix has ruptured and infection has spread beyond the appendix or you have an abscess, you may need an open appendectomy, which allows your surgeon to clean the abdominal cavity.
How is appendicitis treated?
Appendicitis, an inflammation of appendix, is treated either by nonsurgical method or surgery. If surgical procedure is adopted, then the time required for recovery may differ from one patient to another.
How long does it take to recover from appendix surgery?
For those with ruptured appendix before surgery, recovery time may extend to about 2 months. On the brighter side, majority of the candidates who have participated in the surgical treatment for appendicitis recover fully without requiring major lifestyle changes.
What is the best treatment for acute appendicitis?
Appendicitis Surgery and Recovery Time. Appendectomy or appendicitis surgery is considered as a reliable treatment approach for acute appendicitis. Basically, there are two common surgical methods for addressing appendicitis, namely laparotomy and laparoscopic surgery. In the former type, a single incision is made in the lower right abdomen ...
What is the most common cause of appendicitis?
The most probable cause of appendicitis is blockage at the appendix opening due to mucus or stool accumulation.
Why is my appendix blocked?
The most probable cause of appendicitis is blockage at the appendix opening due to mucus or stool accumulation. Over a period of time, these unwanted materials harden and bacterial infection occurs, leading to inflammation of the appendix.
How long do you stay in the hospital after appendectomy?
Following the surgery, the patient will be suggested to stay in the hospital for a few days to a week. If there are suspected complications, the length of hospital stay will be longer. The concerned physician may suggest certain lifestyle changes to be followed during the appendectomy recovery period. Appendicitis recovery after surgery is usually ...
How long does it take for an appendectomy to heal?
Do not indulge in strenuous physical activities or household works for at least 1 – 2 weeks after appendectomy, or as directed by the surgeon. Proper rest and sleep are necessary until the body heals completely.
What is the best test to rule out appendicitis?
Pregnancy test. A pregnancy test may be performed for women of childbearing age to rule out ectopic pregnancy and before x-rays are obtained. Laparoscopy. A diagnostic laparoscopy may be used to rule out acute appendicitis in equivocal cases.
What happens if you leave appendix untreated?
If appendicitis is left untreated, a complication could occur. Perforation of the appendix. This is a major complication of appendicitis, which can lead to peritonitis, abscess formation, or portal pylephlebitis. Perforation generally occurs 24 hours after the onset of pain.
What is the procedure to remove appendix?
Immediate surgery is typically indicated if appendicitis is diagnosed. Appendectomy. Appendectomy or the surgical removal of the appendix is performed as soon as it is possible to decrease the risk of perforation. Laparotomy and laparoscopy.
What is the pathophysiology of appendicitis?
Pathophysiology. The simple pathophysiology of appendicitis follows the typical pathophysiology of infection. Obstruction. The appendix becomes inflamed and edematous as a result of becoming kinked or occluded by a fecalith, tumor, or foreign body. Inflammation.
What is the inflammation of the appendix?
Appendicitis (also known as epityphlitis) is the inflammation of the appendix which is a small finger-like appendage attached to the cecum. The appendix is a small, finger-like appendage attached to the cecum just below the ileocecal valve. Because the appendix empties into the colon inefficiently and its lumen is small, ...
How to prevent sepsis?
To prevent sepsis, antibiotics are administered until the surgery is performed. Drainage. When perforation of the appendix occurs, an abscess may form and the patient is initially treated with antibiotics and the surgeon may place a drain in the abscess.
What is the most common cause of abdominal surgery?
Appendicitis is actually a common disorder in the United States. Appendicitis is the most common cause of acute surgical abdomen in the United States. It is the most common reason for emergency abdominal surgery in the United States. Appendicitis commonly occurs between the ages 10 and 30 years.
How do you know if you have appendicitis?
The pain may not go away. You may also have a rigid (hard) abdomen, nausea (upset stomach), or vomiting (throwing up). A fever may be one of the later signs that you have appendicitis.
Where is the appendix located?
The appendix is a small pouch that is attached to the large intestine in the lower right side of the abdomen (stomach). Experts are unsure of the purpose of the appendix, but it can become infected. A piece of food or hardened stool may get trapped in it. The appendix may get blocked, swollen, and filled with pus.
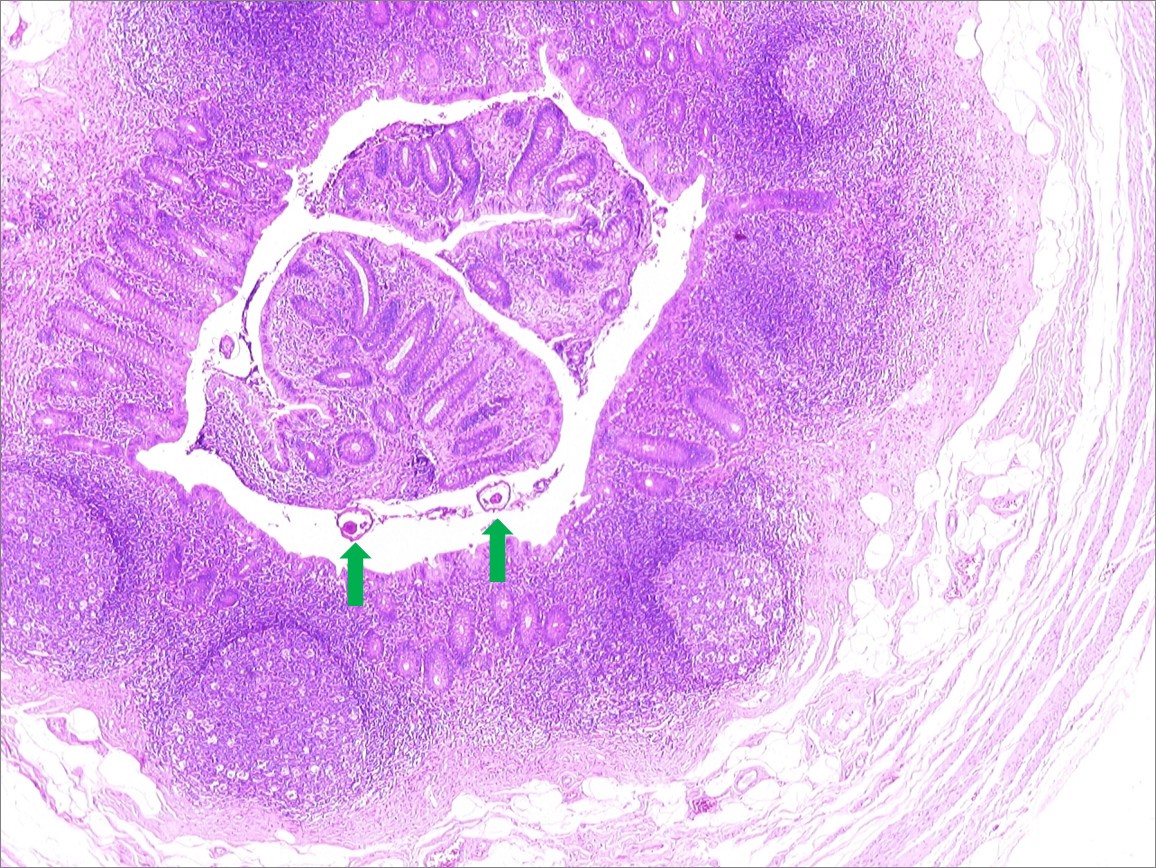
Diagnosis
Treatment
Lifestyle and Home Remedies
Alternative Medicine
Specialist to consult
Preparing For Your Appointment
- To help diagnose appendicitis, your doctor will likely take a history of your signs and symptoms and examine your abdomen. Tests and procedures used to diagnose appendicitis include: 1. Physical exam to assess your pain. Your doctor may apply gentle pressure on the painful area. When the pressure is suddenly released, appendicitis pain will often feel worse, signaling that th…
What Is Appendicitis?
- Appendicitis treatment usually involves surgery to remove the inflamed appendix. Before surgery you may be given a dose of antibiotics to treat infection.
Pathophysiology
- Expect a few weeks of recovery from an appendectomy, or longer if your appendix burst. To help your body heal: 1. Avoid strenuous activity at first.If your appendectomy was done laparoscopically, limit your activity for three to five days. If you had an open appendectomy, limit your activity for 10 to 14 days. Always ask your doctor about limitatio...
Statistics and Epidemiology
- Your doctor will prescribe medications to help you control your pain after your appendectomy. Some complementary and alternative treatments, when used with your medications, can help control pain. Ask your doctor about safe options, such as: 1. Distracting activities, such as listening to music and talking with friends, that take your mind off your pain. Distraction can be e…
Clinical Manifestations
- Make an appointment with your family doctor if you have abdominal pain. If you have appendicitis, you'll likely be hospitalized and referred to a surgeon to remove your appendix.
Complications
Assessment and Diagnostic Findings
- The simple pathophysiology of appendicitis follows the typical pathophysiology of infection. 1. Obstruction. The appendix becomes inflamed and edematous as a result of becoming kinked or occluded by a fecalith, tumor, or foreign body. 2. Inflammation.The inflammatory process increases intraluminal pressure, initiating progressively severe, generalized, or periumbilical pain…
Medical Management
- Appendicitis is actually a common disorder in the United States. 1. Appendicitis is the most common cause of acute surgical abdomen in the United States. 2. It is the most common reason for emergency abdominal surgeryin the United States. 3. Appendicitis commonly occurs between the ages 10 and 30 years.
Surgical Management
- Signs and symptoms of appendicitis are listed below. 1. Pain. Vague epigastric or periumbilical pain progresses to right lower quadrant pain usually accompanied by low-grade fever, nausea,and sometimes vomiting. 2. Tenderness. In 50% of presenting cases, local tenderness is elicited at McBurney’s pointwhen pressure is applied. 3. Rebound tenderness...
Practice Quiz: Appendicitis
- If appendicitis is left untreated, a complication could occur. 1. Perforation of the appendix. This is a major complication of appendicitis, which can lead to peritonitis, abscess formation, or portal pylephlebitis. 2. Perforation generally occurs 24 hoursafter the onset of pain. 3. Symptoms include a fever of 37.7⁰C or greater, a toxic appearance, and continued abdominal pain or tender…
See Also
- Diagnosis is based on the results of a complete physical examination and on laboratory findings and imaging studies. 1. CBC count. A complete blood cell count shows an elevated WBC count, with an elevation of the neutrophils. 2. Imaging studies.Abdominal x-ray films, ultrasound studies, and CT scans may reveal a right lower quadrant density or localized distention of the bowel. 3. P…