Understanding Blood Counts in Leukemia
1 hours ago · Takeaway. A complete blood count (CBC) test plays an important role in detecting chronic myeloid leukemia (CML). CML is a slow-growing cancer in which the bone marrow produces too many immature ... >> Go To The Portal
A complete blood cell (CBC) count with differential demonstrates anemia and thrombocytopenia to varying degrees in individuals with acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). Patients with ALL can have a high, normal, or low white blood cell (WBC
White blood cell
White blood cells are the cells of the immune system that are involved in protecting the body against both infectious disease and foreign invaders. All white blood cells are produced and derived from multipotent cells in the bone marrow known as hematopoietic stem cells. Leukocytes are found throughout the body, including the blood and lymphatic system.
Full Answer
Does a CBC always show leukemia?
Follow-up tests and detailed evaluation is necessary, but CBC is one of the earliest indicators to pave way for further investigation. Will a CBC detect leukemia for sure? The answer is no. But a detailed analysis of its various components can definitely contribute towards the diagnosis in a significant way.
Can you have a normal CBC and still have leukemia?
The Red blood cells and platelets are also not presented in their normal range and their value in CBC can deviate from the normal. So, the chances of Leukaemia with normal CBC is very rare and it can be attributed to the false positive or false negative tests.
What does CBC look like with leukemia?
What would a CBC look like with leukemia? Complete blood count (CBC): This blood test gives details about red blood cells, white blood cells and platelets. If you have leukemia you will have lower than normal counts of red blood cells and platelets, and higher than normal counts of white blood cells.
Can a CBC blood test show if I have leukemia?
Complete blood count (CBC) is a common blood test often performed for people living with leukemia. If a CBC shows high or low numbers of any type of blood cell, this can help doctors better understand how your leukemia and any treatments for leukemia are affecting your body.
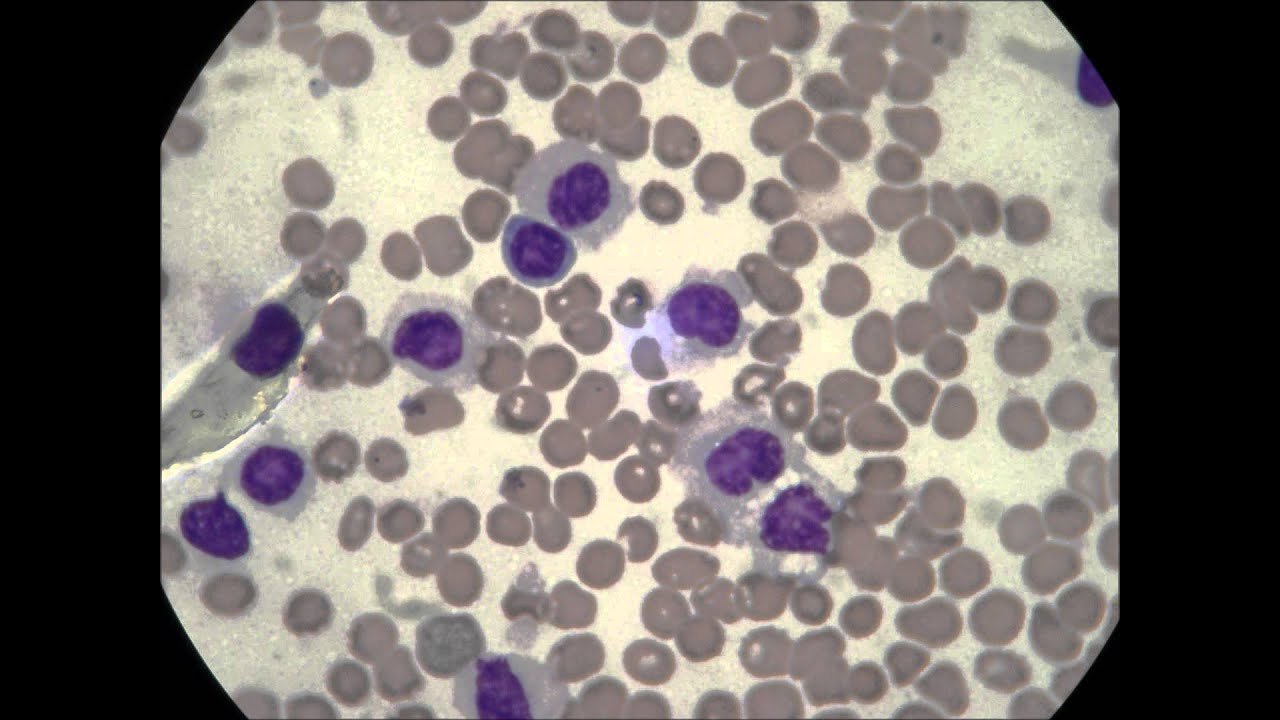
What will CBC show with leukemia?
Leukemia is most often diagnosed through a diagnostic test called a complete blood count (CBC). If a patient's CBC shows abnormal levels of white blood cells or abnormally low red blood cells or platelets, he or she has leukemia.
What WBC count indicates leukemia?
Effects of Too Many White Blood Cells Typically a healthy person has a white blood cell count of about 4,000-11,000. Patients with acute or even chronic leukemia may come in with a white blood cell count up into the 100,000-400,000 range.
Is CBC normal with leukemia?
CBC is the most useful initial laboratory test in patients suspected of having leukemia. Most patients will show some abnormality in the CBC and some blasts will be seen in the peripheral smear in patients with acute leukemias. To diagnose CLL, a lymphocytosis of greater than 5000/mm3 must be present.
Why is WBC low in leukemia?
Leukemia can also present with very low white blood cell counts, because the immature cells get trapped in the bone marrow and are not detected in blood tests. A decreasing number of blasts in the blood indicates that you're responding to treatment.
Why are WBC high in leukemia?
Leukemia usually involves the white blood cells. Your white blood cells are potent infection fighters — they normally grow and divide in an orderly way, as your body needs them. But in people with leukemia, the bone marrow produces an excessive amount of abnormal white blood cells, which don't function properly.
Does leukemia always have high WBC?
While having an elevated or abnormally high white blood cell count does not necessarily indicate leukemia, the source of the condition will need to be identified if it is found to exceed the levels and duration of a normal immune response to an infection.
Does leukemia cause high platelets?
Elevated platelet counts can also be seen in chronic myelogenous leukemia (CML).
Can blood test detect leukemia?
Blood tests. By looking at a sample of your blood, your doctor can determine if you have abnormal levels of red or white blood cells or platelets — which may suggest leukemia. A blood test may also show the presence of leukemia cells, though not all types of leukemia cause the leukemia cells to circulate in the blood.
What is clinical research?
Clinical trials are research studies that evaluate a new medical approach, device, drug, or other treatment. As a Stanford Health Care patient, you may have access to the latest, advanced clinical trials.
Why are red blood cells important?
Red blood cells are important for carrying oxygen and fighting anemia and fatigue. The hemoglobin portion of the CBC measures the oxygen carrying capacity of the red blood cells while the hematocrit measures the percentage of red blood cells in the blood. White blood cells fight infection.
What does increased white blood cells mean?
White blood cells fight infection. Increased numbers of white blood cells, therefore, may indicate the presence of an infection. Decreased levels may indicate certain rheumatic diseases or reaction to medication. Platelets prevent the body from bleeding and bruising easily. It is usually performed to check for a blood infection.
What is the new Stanford Cancer Center?
The new Stanford Cancer Center South Bay brings together world-class specialists and sophisticated technology in a spacious, serene, state-of-the-art building designed by cancer patients, for cancer patients.
What is CBC test?
A CBC test can help track the potential progression of the cancer. Periodic CBC testing can also assess whether treatment is working.
How long does it take to get a CBC?
It helps to wear short sleeves or sleeves you can roll up. It should take only a few minutes.
What is CML in blood?
CML is a slow-growing cancer of the bone marrow and blood. Symptoms can be mild and often go unnoticed early on.
Why is CBC important?
A CBC is an important tool for detecting CML, but other tests are needed to help a healthcare professional diagnose or monitor the condition.
What percentage of people with CML have a Ph chromosome?
According to the Leukemia & Lymphoma Society, about 95 percent of people with CML have a Ph chromosome.
Why do we need blood tests?
These tests help a healthcare professional make a diagnosis and lets them check how your body is responding to treatment.
How many types of white blood cells are there?
There are five main types of white blood cells:
Complete blood count
red blood cells (erythrocytes), which help move oxygen from the lungs to cells all around the body
White blood cell differential
A white blood cell differential is usually included with the CBC. For this test, the pathologist (a medical professional who studies diseases) smears a drop of blood on a slide. Then they examine it under a microscope.
Flow cytometry
In this test, the blood sample is treated with special antibodies and passed through a laser beam. These antibodies attach to cells with corresponding antigens. When that happens, they give off light that can be analyzed by a computer.
What is the most useful initial laboratory test for leukemia?
Answer. CBC is the most useful initial laboratory test in patients suspected of having leukemia. Most patients will show some abnormality in the CBC and some blasts will be seen in the peripheral smear in patients with acute leukemias. To diagnose CLL, a lymphocytosis of greater than 5000/mm 3 must be present.
What is the normal neutrophil count for CLL?
To diagnose CLL, a lymphocytosis of greater than 5000/mm 3 must be present. The absolute neutrophil count is usually normal (see the Absolute Neutrophil Count calculator) and red blood cell counts and platelet counts are mildly decreased. In addition, the peripheral smear or bone marrow should show normal mature small lymphocytes with less than 55% atypical or blast forms.
The Role of White Blood Cells
White blood cells are manufactured by the bone marrow, the spongy tissue found in the center of some of the larger bones in your body. Under normal conditions, a person’s bone marrow produces plenty of stem cells that develop into the various WBCs. There are five primary types of white blood cells:
High vs. Low White Blood Cell Counts in Leukemia
It’s important for doctors to track WBC counts in a person living with leukemia or undergoing treatment for leukemia. A low WBC or a high WBC count can provide important information for a doctor, helping them to interpret symptoms and achieve good treatment outcomes.
Other Conditions That May Cause Low WBC Counts
Having a low or high WBC is not always an indication of leukemia. Five percent of people will experience a high or low WBC in their lifetime. In fact, several noncancerous conditions can lead to an abnormal WBC count.
How To Avoid Infections
A person with leukemia is susceptible to foreign pathogens (viruses, bacteria, and allergens) and less equipped to fight off and heal from infections. This is especially true for a person undergoing chemotherapy as part of their treatment.
Connect With Others Who Understand
If you have leukemia, it can help to have the support of others who understand. MyLeukemiaTeam is the social network for people with leukemia and their loved ones. More than 9,000 members come together to ask questions, give advice, and share their experiences with others who understand life with leukemia.
Recent articles
People with all types of cancer may choose to continue working through cancer treatment because...
What is CBC test?
A complete blood count (CBC) is a common blood test that your doctor may recommend to: Help diagnose some blood cancers, such as leukemia and lymphoma. Find out if cancer has spread to the bone marrow. See how a person’s body is handling cancer treatment. Diagnose other, noncancerous conditions. If you are receiving chemotherapy, your doctor will ...
What does a doctor do when you are receiving chemotherapy?
If you are receiving chemotherapy, your doctor will likely watch your blood cell counts often using a CBC.
What causes low platelet count?
Low platelet count. Some cancer treatments, such as chemotherapy or radiation therapy, may cause a decrease in platelets. Cancers that directly involve the bone marrow can also lower the platelet count. An unusually low number of platelets is called thrombocytopenia. People with low platelet levels have a greater risk of serious bleeding or bruising. If your platelet count falls to very low levels, your doctor may recommend platelet transfusions.
What is the most common way to measure red blood cells?
There are several ways to measure red blood cells. Two of the most common are: Platelet count. A platelet count measures the number of platelets in a sample of blood.
What is it called when your platelet count is low?
An unusually low number of platelets is called thrombocytopenia. People with low platelet levels have a greater risk of serious bleeding or bruising. If your platelet count falls to very low levels, your doctor may recommend platelet transfusions.
What is a white blood cell differential?
A white blood cell differential measures the number of each type of white blood cell. There are 5 major types of white blood cells, and each type plays a different role in protecting the body. Your doctor can learn valuable information about your health by measuring the levels of these cells: Red blood cell count.
How do white blood cells protect the body?
These cells protect the body from infection by attacking invading bacteria, viruses, and other foreign materials in the body. Some white blood cells can also attack cancer cells. White blood cell differential. A white blood cell differential measures the number of each type of white blood cell.
