Understanding My Report - Brain Tumor | Johns Hopkins …
26 hours ago Pathology reports contain information about the patient, the tissue specimen being evaluated, and the final diagnosis. The pathology report is a succinct description of all the features encountered by examination of the tumor under the microscope, and the specialized testing performed. Components of the pathology report include location of the operative procedure … >> Go To The Portal
What are the actual warning signs of a brain tumor?
What were your first symptoms of a brain tumor?
- Irritability, drowsiness, apathy or forgetfulness.
- Numbness or tingling in the arms or legs.
- Dizziness.
- Partial loss of vision or hearing.
- Hallucinations, depression or mood swings.
- Personality changes, including abnormal and uncharacteristic behavior.
Is a brain tumor the same thing as brain cancer?
Some brain tumors are noncancerous (benign), and some brain tumors are cancerous (malignant). Brain tumors can begin in your brain (primary brain tumors), or cancer can begin in other parts of your body and spread to your brain as secondary (metastatic) brain tumors. How quickly a brain tumor grows can vary greatly.
What are the symptoms of a tumor in the brain?
Examples include:
- Gliomas. These tumors begin in the brain or spinal cord and include astrocytomas, ependymomas, glioblastomas, oligoastrocytomas and oligodendrogliomas.
- Meningiomas. ...
- Acoustic neuromas (schwannomas). ...
- Pituitary adenomas. ...
- Medulloblastomas. ...
- Germ cell tumors. ...
- Craniopharyngiomas. ...
How is a brain tumor diagnosed without biopsy?
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). ...
- Intravenous (IV) gadolinium-enhanced MRI is typically used to help create a clearer picture of a brain tumor. ...
- An MRI technique called "diffusion weighted imaging" helps show the cellular structure of the brain. ...
- A spinal MRI may be used to diagnose a tumor on or near the spine.
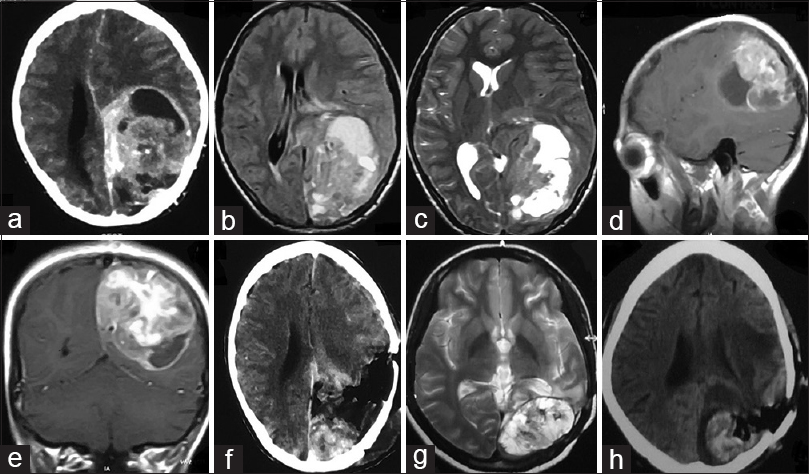
How long can a brain tumor patient live?
Survival for all types of cancerous (malignant) brain tumour 40 out of 100 people (40%) survive their cancer for 1 year or more. more than 10 out of 100 people (more than 10%) survive their cancer for 5 years or more.
Can you live a normal life after a brain tumor?
Some brain tumours grow very slowly (low grade) and cannot be cured. Depending on your age at diagnosis, the tumour may eventually cause your death. Or you may live a full life and die from something else. It will depend on your tumour type, where it is in the brain, and how it responds to treatment.
What happens to brain tumor patients?
A brain tumor can form in the brain cells (as shown), or it can begin elsewhere and spread to the brain. As the tumor grows, it creates pressure on and changes the function of surrounding brain tissue, which causes signs and symptoms such as headaches, nausea and balance problems.
What do you say to someone diagnosed with a brain tumor?
Here are some ideas:"I'm not sure what to say, but I want you to know I care"."I'm sorry to hear that you are going through this"."How are you doing?""If you would like to talk about it, I'm here"."Please let me know how I can help"."I'll keep you in my thoughts".
Can you fully recover from a brain tumor?
Some people may complete recovery in a few weeks or months, others will have to learn to adjust to permanent changes in their life such as not being able to work or accomplish all the same tasks they did before.
Can a brain tumor be cured?
Outlook. The outlook for a malignant brain tumour depends on things like where it is in the brain, its size, and what grade it is. It can sometimes be cured if caught early on, but a brain tumour often comes back and sometimes it isn't possible to remove it.
At what age brain tumor can occur?
They most often develop in children ages 5 to 8. Also called low-grade gliomas, these are the most common brain tumors in children. Medulloblastomas are the most common type of childhood brain cancer. Most medulloblastomas occur before age 10.
Can you live a normal life after brain surgery?
Some people recover well after brain surgery, but this can take some time. Other people have some problems, or long term difficulties. The problems you may have depends on the area of the brain where the tumour was (or still is if you only had part of the tumour removed).
What are the final stages of a brain tumour?
What Are the Symptoms of End-Stage Brain Cancer?Frequent headaches.Agitation and delirium.Agonal breathing (gasping breaths that occur when a person is struggling to breathe)Prolonged confusion.Hallucinations.Loss of appetite.Vision loss.Involuntary movements.More items...
How do you comfort someone with brain tumor?
Ways to help and cope when someone you love is diagnosed with a brain tumourAsk anything. “Don't be afraid to ask anything during appointments. ... Don't think too far ahead. ... Keep things calm. ... Ask for hands-on help. ... Choose one special confidante. ... Plan only what you can. ... Listen to your loved one's fears. ... Let it out.More items...•
How do you take care of someone with a brain tumor?
Brain Tumors: Helping a Family Member or FriendBeing a caregiver. ... Other ways to help. ... Chip in with tasks. ... Spend some quality time. ... Keep things organized. ... Help them get emotional support. ... Be a social buffer. ... Help them through rehab.More items...
How do you encourage someone with a brain tumor?
Use these words and resources listed to help you positively cope with your brain tumor experience.Choose to be Positive and Grateful.Maintain Hope.Find Your New Day-to-Day Life.Surround Yourself with Support.
What is brain tumor support?
The Brain Tumor Support Conversations are an online support group run by the brain tumor community for the brain tumor community. This group is attended and run by patients and care partners who have had firsthand experience with the challenges and effects of a brain tumor diagnosis.
What is a NBTS patient navigator?
NBTS Patient Navigator is a medical professional who responds to outreach from brain tumor patients and care partners with quality, unbiased information, resources, support programs and services, and assists in meeting other brain tumor-related needs of patients and care partners.
What is the purpose of clinical trials?
The purpose of a clinical trial is to determine the most effective and safest treatment for a disease. Clinical trial evaluation is a key step to translating research into new medicines that can provide better outcomes for patients.
Can brain tumors be fatal?
Brain tumors can be deadly, significantly impact quality of life, and change everything for a patient and their loved ones. They do not discriminate, inflicting men, women, and children of all races and ethnicities. Learn More.
Overview
Brain and spinal cord (also known as central nervous system, or CNS) tumors can be benign or malignant. Explore the links on this page to learn more about the many different CNS tumor types and how they are treated. We also have information about brain cancer statistics, research, and clinical trials.
Causes & Prevention
NCI does not have PDQ evidence-based information about prevention of brain tumors.
Screening
NCI does not have PDQ evidence-based information about screening for brain tumors.
Coping with Cancer
The information in this section is meant to help you cope with the many issues and concerns that occur when you have cancer.
Rare Brain & Spine Tumor Network
Connects patients, providers, and advocates to help people with rare brain and spine tumors get better care.
What are researchers looking for in brain tumors?
As discussed in Diagnosis, researchers are currently looking for biomarkers in the tumor tissue that could make a brain tumor easier to diagnose and allow for the staging of an adult brain tumor in the future. Researchers are also looking at other genetic tests that may predict a patient’s prognosis.
How to decide on the best treatment for a brain tumor?
To decide on the best treatment for a brain tumor, both the type and grade of the tumor must be determined. There are several factors that help doctors determine the appropriate brain tumor treatment plan and a patient's prognosis: Tumor histology. As outlined in the Diagnosis section, a sample of the tumor is removed for analysis.
What is tumor histology?
Tumor histology includes finding out the type of tumor, the grade, and additional molecular features that predict how quickly the tumor can grow. Together, these factors will help your doctor understand how the tumor will likely behave. These factors may also help determine your treatment options.
Why are some tumors harder to treat than others?
Some tumor locations cause more damage than others, and some tumors are harder to treat because of their location. Molecular features. Certain genetic mutations found in the tumor may help determine prognosis. These include: IDH1 , IDH2 , MGMT, and a 1p/19q co-deletion.
What is residual tumor?
Extent of tumor residual. Resection is surgery to remove a tumor. Residual refers to how much of the tumor remains in the body after surgery. A patient’s prognosis is better when all of the tumor can be surgically removed. There are 4 classifications: Gross total: The entire tumor was removed.
What does grade mean in cancer?
Grade describes certain features in the tumor that are linked with specific outcomes. For example, doctors may consider whether the tumor cells are growing out of control or if there are a lot of dead cells. Tumors with features generally linked with growing more quickly are given a higher grade.
What is a recurrent tumor?
A recurrent tumor is one that has come back after treatment. If the tumor does return, there will be another round of tests to learn about the extent of the recurrence. These tests and scans are often similar to those done at the time of the original diagnosis.
How to tell if a brain tumor is a tumor?
In general, diagnosing a brain tumor usually begins with magnetic resonance imaging ( MRI). Once MRI shows that there is a tumor in the brain, the most common way to determine the type of brain tumor is to look at the results from a sample of tissue after a biopsy or surgery.
Who diagnoses brain tumors?
Often a brain tumor is initially diagnosed by an internist or a neurologist. An internist is a doctor who specializes in treating adults. A neurologist is a doctor who specializes in problems with the brain and central nervous system.
How to find out if a tumor has spread to the spinal fluid?
The doctor may recommend a myelogram to find out if the tumor has spread to the spinal fluid, other parts of the brain, or the spinal cord. A myelogram uses a dye injected into the CSF that surrounds the spinal cord. The dye shows up on an x - ray and can outline the spinal cord to help the doctor look for a tumor.
Why are biomarkers important?
Researchers are examining biomarkers to find ways to diagnose a brain tumor before symptoms begin. Results of these tests may help determine your treatment options.
What is tissue biopsy?
A biopsy is the removal of a small amount of tissue for examination under a microscope and is the only definitive way a brain tumor can be diagnosed. A pathologist then analyzes the sample (s).
What is the procedure to remove a tumor?
This may be done in a procedure called a biopsy or by removing part or all of the tumor with surgery. In a biopsy, the doctor takes a small sample of tissue for testing in a laboratory. If this is not possible, the doctor may suggest other tests that will help make a diagnosis.
Why is a fMRI used for surgery?
This test is used to help plan surgery, so the surgeon can avoid damaging the functional parts of the brain while removing the tumor .

Popular Posts:
- 1. modern ob gyn patient portal
- 2. bay city mi patient portal
- 3. whole health dentistry patient portal
- 4. "patient portal" advancedmd
- 5. empry patient portal
- 6. dr. free patient portal
- 7. premier medical monroeville patient portal
- 8. lmh patient portal login
- 9. wilcox patient portal
- 10. patient portal lone