Improving the patient discharge process: implementing …
10 hours ago · 1. Introduction. The process of discharging patients from acute hospitals is characterised by a range of patient circumstances and needs. Discharge planning for older patients is particularly challenging (Bauer et al., 2009; Mitchell, Gilmour, & Mclaren, 2010; Victor, Healy, Thomas, & Seargeant, 2000), as these patients often have a broad range of needs … >> Go To The Portal
Before the day of discharge, inform the patient’s family of the time and date of discharge Obtain a written discharge order from the physician. If the patient discharges himself against medical advice, obtain the appropriate form
Full Answer
What is a hospital discharge summary?
A discharge summary plays a crucial role in keeping patients safe after leaving a hospital. As an Advances in Patient Safety report notes, "Hospital discharge summaries serve as the primary documents communicating a patient's care plan to the post-hospital care team.
What is discharge planning for acute care?
Planning for discharge actually begins on admission, when information about the patient is collected and documented. The key to successful discharge planning is an exchange of information among the patient, the caregivers, and those responsible for care while the patient is in the acute care setting and after the patient returns home.
What does the Massachusetts acute care hospital inpatient discharge data include?
Massachusetts Acute Care Hospital Inpatient Discharge Data (FFY 2016-2019) presents key measures of inpatient utilization overall and by hospital, patient, and discharge characteristics.
How do you report discharge status on Medicare?
Medicare requires that when discharging a patient from an inpatient stay, the discharging facility reports the discharge disposition in the “Patient Discharge Status” field (FL 17). The claim must include the discharge status code that most accurately reflects the discharge of the patient.
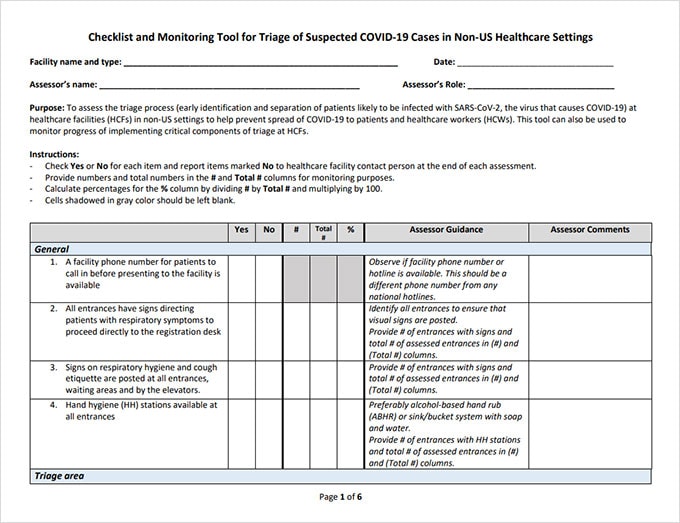
Which orders are required for a patient discharge?
Additional Hospital Discharge Summary Recommendationsemergency plan and contact number and person;treatment and diagnostic plan;prognosis and goals of care;advance directives, power of attorney, consent;planned interventions, durable medical equipment, wound care, etc.;assessment of caregiver status; and.More items...•
What is included in a discharge report?
The discharge report must give a summary of everything the patient went through during the hospital admission period – physical findings, laboratory results, radiographic studies and so on. An AHRQ study points out that the Joint Commission mandates six components to be present in all U.S. hospital discharge summaries.
What should a discharge plan include?
Your discharge plan should include information about where you will be discharged to, the types of care you need, and who will provide that care. It should be written in simple language and include a complete list of your medications with dosages and usage information.
What steps should they follow after discharge from hospital?
The Post Discharge Checklist: 5 Important StepsMake a Post-Discharge Care Plan. ... Reconcile Medications. ... Schedule Follow-Up Visits. ... Ask Questions. ... Seek Support.
What should a nurse include in a discharge summary?
Information for the patient Most discharge letters include a section that summarises the key information of the patient's hospital stay in patient-friendly language, including investigation results, diagnoses, management and follow up. This is often given to the patient at discharge or posted out to the patient's home.
Who is responsible for the discharge summary?
Interpretive Guidelines §484.48 - The HHA must inform the attending physician of the availability of a discharge summary. The discharge summary must be sent to the attending physician upon request and must include the patient's medical and health status at discharge.
What is discharge procedure?
Introduction: NABH defines discharge as a process by which a patient is shifted out from the hospital with all concerned medical summaries ensuring stability. The discharge process is deemed to have started when the consultant formally approves discharge and ends with the patient leaving the clinical unit.
What is the nurses role in discharge planning?
Nurses play an integral role in the discharge process by coordinating care and providing timely communication with key stakeholders including families and community providers to ensure smooth transitions of care.
What are the key factors you need to consider when planning patient's discharge from hospital?
Discharge planning involves taking into account things like:follow-up tests and appointments.whether you live alone.whether someone can help you when you go home.your mobility.equipment needed for your recovery.wound care, if needed.medicines, especially if you need multiple medications.dietary needs.More items...
How would you maintain contact with patients after they are discharged?
4 steps to maintaining communication after dischargeStep One: Help the Patient and Family Understand the Diagnosis. ... Step Two: Ensure the Patient and Family Are Committed to the Care Plan. ... Step Three: Keep the Patient and Family Actively Involved in Care Transitions.More items...•
What is post-discharge follow-up?
Relevant post-discharge follow-up was defined as outpatient, non-emergency department telephone calls or clinic visits with internal medicine, family medicine, or cardiology providers.
What happens when an elderly person is discharged from hospital?
If the person will need continued support or care after leaving the hospital, they should be assigned a case manager. The case manager will work with ward staff to make sure that the person and their family are fully informed of the next steps. The case manager will: set out the person's discharge and follow-up care.
The key principles of effective discharge planning | Nursing Times
IDEAL Discharge Planning Overview, Process, and Checklist
What is discharge planning?
The Centers for Medicare & Medicaid Services (CMS) today issued a final rule that empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care as they are discharged from acute care into post-acute care (PAC), a process called “discharge planning.”.
What are the changes to the CAH and HHA requirements?
Final changes to hospital, CAH, and HHA requirements. Under the final rule, hospitals, CAHs, and HHAs would be required to: New discharge planning requirements, as mandated by the IMPACT act for hospitals, HHAs, and CAHs, that requires facilities to assist patients, their families, or the patient’s representative in selecting a post-acute care ...
Do hospitals have to provide access to medical records?
Hospitals must ensure and support patients’ rights to access their medical records in the form and format requested by the patient , if it is readily producible in such form and format (including in an electronic form or format when such medical records are maintained electronically).
How to discharge a patient before discharge?
Procedure. Before the day of discharge, inform the patient’s family of the time and date of discharge. Obtain a written discharge order from the physician . If the patient discharges himself against medical advice, obtain the appropriate form.
What is discharge planning?
Discharge planning is an integral part of the continuity of nursing care for patients throughout their hospital stay.
What to do if a patient refuses to sign an AMA form?
If the patient refuses to sign the AMA form, do not detain him. This violates his legal rights. After the patient leaves, document the incident thoroughly in your notes and notify the physician.
What is discharge in medical terms?
Discharge is preparation of patient to leave hospital and to return to own environment. Patient is prepared for discharge when he is admitted in the hospital. He should be prepared physically and mentally to leave the hospital or ward
Did the patient's relatives sign anything?
Doctor had said that taking the patient out may endanger life. Patient/patient’s relatives did not sign anything.
Do police have to be informed before a patient leaves the hospital?
Police have to be immediately informed, the moment such an instance comes to the notice of the doctor/hospital staff.
What is an acute care record?
Acute care is given, often in an emergency department, when a patient has a severe but usually brief illness or condition. The medical record of the patient, both as an in-patient and later as an out-patient, should be kept up to date and include a plan of care.
When is acute care given?
Acute care is given, often in an emergency department, when a patient has a severe but usually brief illness or condition. The medical record of the patient, both as an in-patient and later as an out-patient, should be kept up to date and include a plan of care.
What is a nurse's note?
Nurses' Notes and Medication Records. The nurses care for the patient day to day and monitor progress or decline. They document this and their observations in the “Nurses’ Notes” or nursing progress notes. These records are maintained by licensed nursing staff.
What is admission and consent?
The admission records contain all the pertinent information about the patient and include physician’s name, patient address, date of birth, consents for treatment and procedures, insurance data, Social Security number, family information and phone numbers.
What is a radiology record?
The record contains all radiologic findings, laboratory reports, surgical consultations and operative reports, pathology findings, special consultations and specialty care such as nuclear medicine or psychiatric interventions or observations. It contains records of all care and results of diagnostic procedures.
What is progress note?
The progress notes are an ongoing record of the treatments planned and initiated, and the patient’s response to each therapy. It includes an ongoing plan of care. When a specialist is consulted, he may send a complete report of his findings later, but the consultation visit is documented in the progress notes.
Do nurse orders have to be written?
All physicians’ orders must be in writing and signed. If a nurse takes a verbal order from the doctor, it must be written on the physician’s orders record, reviewed and signed as with telephone orders .
How many components are in a discharge summary?
As a For the Record report points out, The Joint Commission mandates all discharge summaries must contain six high-level components , which are also noted as requirements in the National Quality Forum's Safe Practices for Better Healthcare.
What is discharge summary?
August 20, 2018. A discharge summary plays a crucial role in keeping patients safe after leaving a hospital. As an Advances in Patient Safety report notes, "Hospital discharge summaries serve as the primary documents communicating a patient's care plan to the post-hospital care team. Often, the discharge summary is the only form ...
How to facilitate a patient's safe discharge from an inpatient unit?
To facilitate a patient’s safe discharge from an inpatient unit, physicians should: Determine that the patient is medically stable and ready for discharge from the treating facility. Collaborate with those health care professionals and others who can facilitate a patient discharge to establish that a plan is in place for medically needed care ...
What is discharge plan?
The discharge plan should be developed without regard to socioeconomic status, immigration status, or other clinically irrelevant considerations. Physicians also have a long-standing obligation to be prudent stewards of the shared societal resources with which they are entrusted.
What is discharge summary?
A discharge summary is a clinical report prepared by a health professional at the conclusion of a hospital stay or series of treatments. It is often the primary mode of communication between the hospital care team and aftercare providers.
What are some examples of diagnoses for which you should include specific details?
Some examples of diagnoses for which you should include specific details include: Diabetes: type 1, type 2, steroid-induced, gestational. Myocardial infarction: NSTEMI, STEMI.
What is advance decision?
Advance decisions about treatment: Whether there are written documents, completed and signed when a person is legally competent, that explains a person’s medical wishes in advance, allowing someone else to make treatment decisions on his/her behalf late in the disease process. Location of these documents.
Is discharge summary legal?
It is considered a legal document and it has the potential to jeopardize the patient’s care if errors are made. Delays in the completion of the discharge summary are associated with higher rates of readmission, highlighting the importance of successful transmission of this document in a timely fashion.

Popular Posts:
- 1. mcleod loris patient portal
- 2. patient with multiple sclerosis--case report
- 3. central pediatrics patient portal login
- 4. ahmc patient portal
- 5. patient portal ca laws and federal laws
- 6. st joseph candler hospital patient portal
- 7. genesis patient portal tucson az
- 8. children's hospital of philadelphia patient portal
- 9. tenet health patient portal
- 10. cu anschutz patient portal